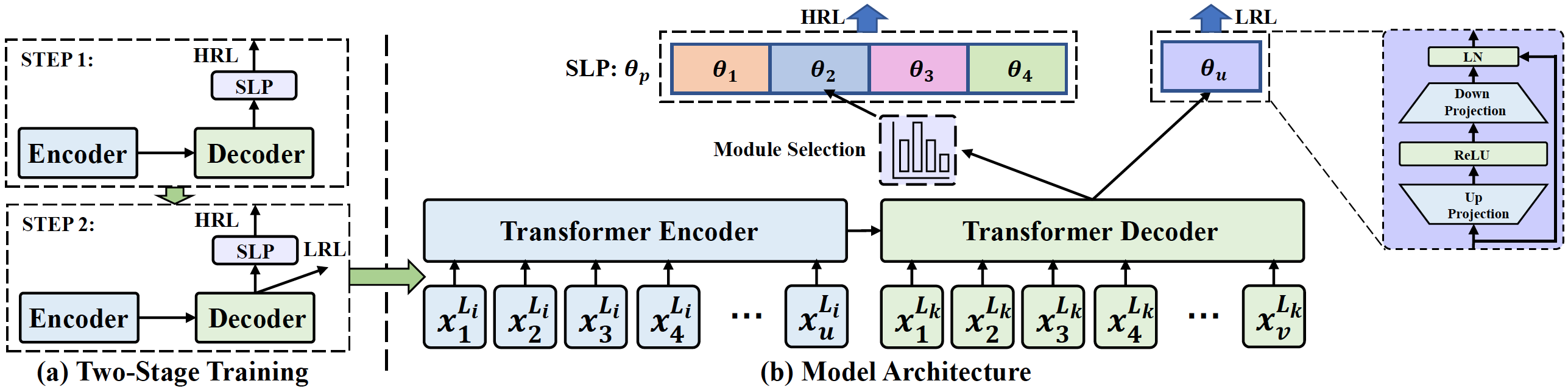
Multilingual neural machine translation (MNMT) trained in multiple language pairs has attracted considerable attention due to fewer model parameters and lower training costs by sharing knowledge among multiple languages. Nonetheless, multilingual training is plagued by language interference degeneration in shared parameters because of the negative interference among different translation directions, especially on high-resource languages. In this paper, we propose the multilingual translation model with the high-resource language-specific training (HLT-MT) to alleviate the negative interference, which adopts the two-stage training with the language-specific selection mechanism. Specifically, we first train the multilingual model only with the high-resource pairs and select the language-specific modules at the top of the decoder to enhance the translation quality of high-resource directions. Next, the model is further trained on all available corpora to transfer knowledge from high-resource languages (HRLs) to low-resource languages (LRLs). Experimental results show that HLT-MT outperforms various strong baselines on WMT-10 and OPUS-100 benchmarks. Furthermore, the analytic experiments validate the effectiveness of our method in mitigating the negative interference in multilingual training.
- WMT-10
- Multilingual dataset (from the WMT corpus) with 11 languages: 10 English-centric language pairs.
- English (En), French (Fr), Czech (Cs), German(De), Finnish (Fi), Latvian (Lv), Estonian (Et), Romanian (Ro), Hindi(Hi), Turkish (Tr), and Gujarati (Gu).
- OPUS-100
- Massively multilingual dataset (from the OPUS-100 corpus) with 100 languages.
- 94 English-centric language pairs are used after dropping out 5 languages that lack corresponding test sets.
Statistics and sources of the training, valid, and test sets from WMT between English and other languages:
| Language | #Bitext | Training | Valid | Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fr (French) | 10M | WMT15 | Newstest13 | Newstest15 |
| Cs (Czech) | 10M | WMT19 | Newstest16 | Newstest18 |
| De (German) | 4.6M | WMT19 | Newstest16 | Newstest18 |
| Fi (Finnish) | 4.8M | WMT19 | Newstest16 | Newstest18 |
| Lv (Latvian) | 1.4M | WMT17 | Newsdev17 | Newstest17 |
| Et (Estonian) | 0.7M | WMT18 | Newsdev18 | Newstest18 |
| Ro (Romanian) | 0.5M | WMT16 | Newsdev16 | Newstest16 |
| Hi (Hindi) | 0.26M | WMT14 | Newsdev14 | Newstest14 |
| Tr (Turkish) | 0.18M | WMT18 | Newstest16 | Newstest18 |
| Gu (Gujarati) | 0.08M | WMT19 | Newsdev19 | Newstest19 |
OPUS-100: Improving Massively Multilingual Neural Machine Translation and Zero-Shot Translation
cd HLT-MT
pip install --editable ./- For faster training install NVIDIA's apex library:
git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA/apex
cd apex
pip install -v --no-cache-dir --global-option="--cpp_ext" --global-option="--cuda_ext" \
--global-option="--deprecated_fused_adam" --global-option="--xentropy" \
--global-option="--fast_multihead_attn" ./# parameters
NODES=${1}
MAX_TOKENS=${2}
UPDATE_FREQ=${3}
MAX_EPOCH=${4}
LR=${5}
WARMUP_STEPS=${6}
WEIGHT_DECAY=${7}
HIGH_LANGS=${8}
LOW_LANGS=${9}
LANG_PAIRS=${10}
ADAPTER_NUM=${11}
ADAPTER_DIM=${12}
APPEND_CMDS=${13}
# default values
if [ ! ${NODES} ]; then
NODES=4
fi
if [ ! ${MAX_TOKENS} ]; then
MAX_TOKENS=4096
fi
if [ ! ${UPDATE_FREQ} ]; then
UPDATE_FREQ=4
fi
if [ ! ${LR} ]; then
LR=3e-4
fi
if [ ! ${WARMUP_STEPS} ]; then
WARMUP_STEPS=4000
fi
if [ ! ${WEIGHT_DECAY} ]; then
WEIGHT_DECAY=0
fi
if [ ! ${ADAPTER_NUM} ]; then
ADAPTER_NUM=3
fi
if [ ! ${ADAPTER_DIM} ]; then
ADAPTER_DIM=3072
fi
LANGS="en,fr,cs,de,fi,lv,et,ro,hi,tr,gu"
GPUS=8
bsz=$((${MAX_TOKENS}*${UPDATE_FREQ}*${NODES}*${GPUS}))
TEXT=/path/to/data-bin/
MODEL=/path/to/model/
PRETRAINED_ENCODER_MODEL=/path/to/xlmr_model
python -m torch.distributed.launch \
--nproc_per_node=${GPUS} --nnodes=${NODES} --node_rank=${OMPI_COMM_WORLD_RANK} \
--master_addr=${MASTER_ADDR} --master_port=${MASTER_PORT} train.py ${TEXT} \
--save-dir ${MODEL} --arch "two_stage_sparse_transformer" \
--variant addffn --pretrained-infoxlm-checkpoint ${PRETRAINED_ENCODER_MODEL} \
--init-encoder-only --init-decoder-only --task "translation_multi_simple_epoch" \
--sampling-method "linear" --sampling-temperature 5.0 --min-sampling-temperature 1.0 \
--encoder-langtok "tgt" --langtoks '{"main":("tgt",None)}' --langs ${LANGS} \
--high-langs ${HIGH_LANGS} --low-langs ${LOW_LANGS} --lang-pairs ${LANG_PAIRS} \
--ddp-backend=no_c10d --enable-reservsed-directions-shared-datasets \
--share-all-embeddings --max-source-positions 256 --max-target-positions 256 \
--criterion "label_smoothed_cross_entropy_with_sparse" --label-smoothing 0.1 \
--optimizer adam --adam-betas '(0.9, 0.98)' --lr-scheduler inverse_sqrt --lr ${LR} \
--warmup-epoch 5 --warmup-updates 4000 \
--max-update 400000 --max-epoch ${MAX_EPOCH} --max-tokens ${MAX_TOKENS} --update-freq ${UPDATE_FREQ} \
--dropout 0.1 --attention-dropout 0.0 --weight-decay ${WEIGHT_DECAY} \
--seed 1 --log-format simple --skip-invalid-size-inputs-valid-test \
--fp16 --truncate-source --same-lang-per-batch --enable-lang-ids \
--use-adapter --adapter-num ${ADAPTER_NUM} --adapter-dim ${ADAPTER_DIM} \
--swap-adapter 0 --start-hard-epoch 1 --hard-adapter 0.5 --end-soft-epoch 5 --disparity-weight 1.0 \
--log-file ${MODEL}/train.log --tensorboard-logdir ${MODEL}/logs ${APPEND_CMDS}- Metrics: the case-sensitive detokenized BLEU using sacreBLEU:
- BLEU+case.mixed+lang.{src}-{tgt}+numrefs.1+smooth.exp+tok.13a+version.1.3.1
- BiNMT is the bilingual Transformer model. (Attention is All you Need)
- MNMT is jointly trained on all directions, where the target language symbol is prefixed to the input sentence. (Google's Multilingual Neural Machine Translation System: Enabling Zero-Shot Translation)
- mBART is an encoder-decoder pretrained model and then is finetuned on all corpora. (Multilingual Denoising Pre-training for Neural Machine Translation)
- XLM-R is initialized by the pretrained model XLM-R. (Unsupervised Cross-lingual Representation Learning at Scale)
- LS-MNMT integrates the language-specific layers of all languages into the end of the decoder. (Beyond English-Centric Multilingual Machine Translation)
En-X evaluation results for bilingual (1-1), one-to-many (1-N), and many-to-many (N-N) models on WMT-10. The languages are ordered from high-resource languages (left) to low-resource languages (right).
| En-X test sets | Models | #Params | Fr | Cs | De | Fi | Lv | Et | Ro | Hi | Tr | Gu | Avg (all) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-1 | BiNMT | 242M/10M | 36.3 | 22.3 | 40.2 | 15.2 | 16.5 | 15.0 | 23.0 | 12.2 | 13.3 | 7.9 | 20.2 |
| 1-N | MNMT | 242M | 34.2 | 20.9 | 40.0 | 15.0 | 18.1 | 20.9 | 26.0 | 14.5 | 17.3 | 13.2 | 22.0 |
| 1-N | mBART | 611M | 33.7 | 20.8 | 38.9 | 14.5 | 18.2 | 20.5 | 26.0 | 15.3 | 16.8 | 12.9 | 21.8 |
| 1-N | XLM-R | 362M | 34.7 | 21.5 | 40.1 | 15.2 | 18.6 | 20.8 | 26.4 | 15.6 | 17.4 | 14.9 | 22.5 |
| 1-N | LS-MNMT | 409M | 35.0 | 21.7 | 40.6 | 15.5 | 18.9 | 21.0 | 26.2 | 14.8 | 16.5 | 12.8 | 22.3 |
| 1-N | HLT-MT | 381M | 36.2 | 22.2 | 41.8 | 16.6 | 19.5 | 21.1 | 26.6 | 15.8 | 17.1 | 14.6 | 23.2 |
| N-N | MNMT | 242M | 34.2 | 21.0 | 39.4 | 15.2 | 18.6 | 20.4 | 26.1 | 15.1 | 17.2 | 13.1 | 22.0 |
| N-N | mBART | 611M | 32.4 | 19.0 | 37.0 | 13.2 | 17.0 | 19.5 | 25.1 | 15.7 | 16.7 | 14.2 | 21.0 |
| N-N | XLM-R | 362M | 34.2 | 21.4 | 39.7 | 15.3 | 18.9 | 20.6 | 26.5 | 15.6 | 17.5 | 14.5 | 22.4 |
| N-N | LS-MNMT | 409M | 34.8 | 21.1 | 39.3 | 15.2 | 18.7 | 20.5 | 26.3 | 14.9 | 17.3 | 12.3 | 22.0 |
| N-N | HLT-MT | 381M | 35.8 | 22.4 | 41.5 | 16.3 | 19.6 | 21.0 | 26.6 | 15.7 | 17.6 | 14.7 | 23.1 |
X-En test BLEU for high/medium/low resource language pairs in many-to-many setting on OPUS-100 test sets. The BLEU scores are average across all language pairs in the respective groups. "WR": win ratio (%) compared to "ref" (MNMT).
| Models | #Params | High (45) | Med (21) | Low (28) | Avg (94) | WR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPUS-100 baseline | 254M | 30.3 | 32.6 | 31.9 | 31.4 | - |
| MNMT | 242M | 32.3 | 35.1 | 35.8 | 33.9 | ref |
| XLM-R | 362M | 33.1 | 35.7 | 36.1 | 34.6 | - |
| LS-MNMT | 456M | 33.4 | 35.8 | 35.9 | 34.7 | - |
| HLT-MT | 391M | 34.1 | 36.6 | 36.1 | 35.3 | 72.3 |
En-X test BLEU for high/medium/low resource language pairs in many-to-many setting on OPUS-100 test sets.
| Models | #Params | High (45) | Med (21) | Low (28) | Avg (94) | WR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPUS-100 baseline | 254M | 23.7 | 25.6 | 22.2 | 24.0 | - |
| MNMT | 242M | 26.3 | 31.4 | 31.2 | 28.9 | ref |
| XLM-R | 362M | 26.9 | 31.9 | 31.7 | 29.4 | - |
| LS-MNMT | 456M | 27.5 | 31.6 | 31.5 | 29.6 | - |
| HLT-MT | 391M | 27.6 | 33.3 | 31.8 | 30.1 | 77.7 |
Ablation study of our proposed approach on the WMT-10 benchmark. Our method can be easily initialized by the cross-lingual pretrained model XLM-R to enhance the performance.
| XLM-R | Two-stage Training | SLP | Avg (high) | Avg (low) | Avg (all) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | . | . | 24.9 | 17.8 | 22.0 |
| . | ✓ | . | 25.4 | 18.0 | 22.4 |
| . | ✓ | ✓ | 26.0 | 18.1 | 22.8 |
| ✓ | . | . | 25.2 | 18.5 | 22.5 |
| ✓ | ✓ | . | 26.0 | 17.9 | 22.8 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 26.2 | 18.5 | 23.2 |
- arXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.04906
- IJCAI Anthology: https://www.ijcai.org/proceedings/2022/619
@inproceedings{hltmt,
title = {High-resource Language-specific Training for Multilingual Neural Machine Translation},
author = {Yang, Jian and Yin, Yuwei and Ma, Shuming and Zhang, Dongdong and Li, Zhoujun and Wei, Furu},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Thirty-First International Joint Conference on
Artificial Intelligence, {IJCAI-22}},
publisher = {International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence Organization},
editor = {Lud De Raedt},
pages = {4461--4467},
year = {2022},
month = {7},
note = {Main Track},
doi = {10.24963/ijcai.2022/619},
url = {https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2022/619},
}Please refer to the LICENSE file for more details.
If there is any question, feel free to create a GitHub issue or contact us by Email.