CoreFreq is a CPU monitoring software designed for 64-bits Processors w/ architectures Intel Atom, Core2, Nehalem, SandyBridge and superior, AMD Family 0F
CoreFreq provides a framework to retrieve CPU data with a high degree of precision:
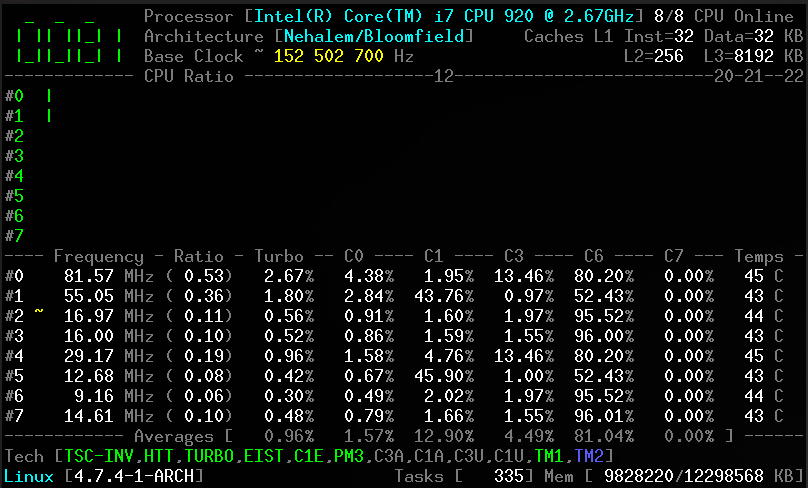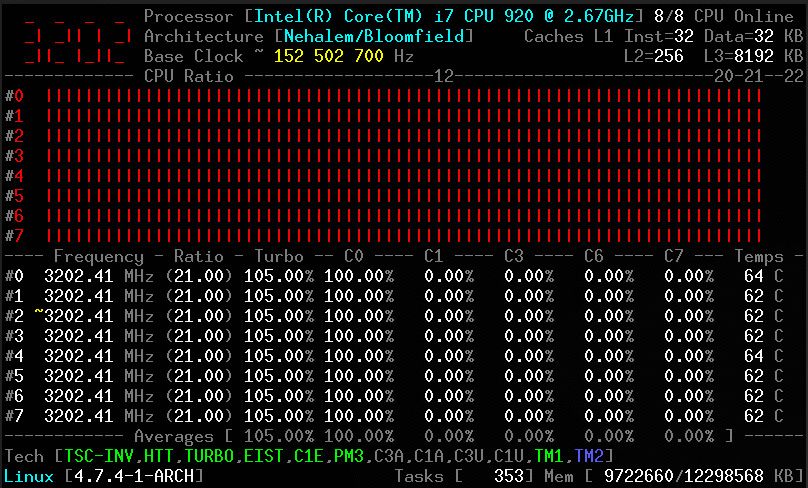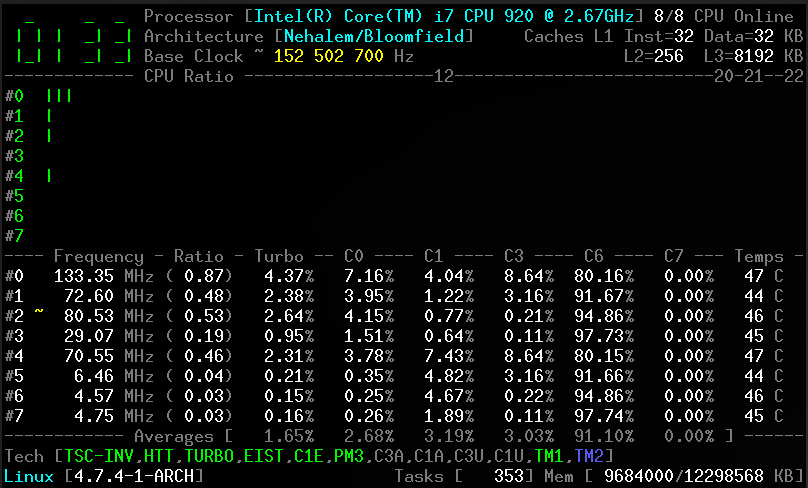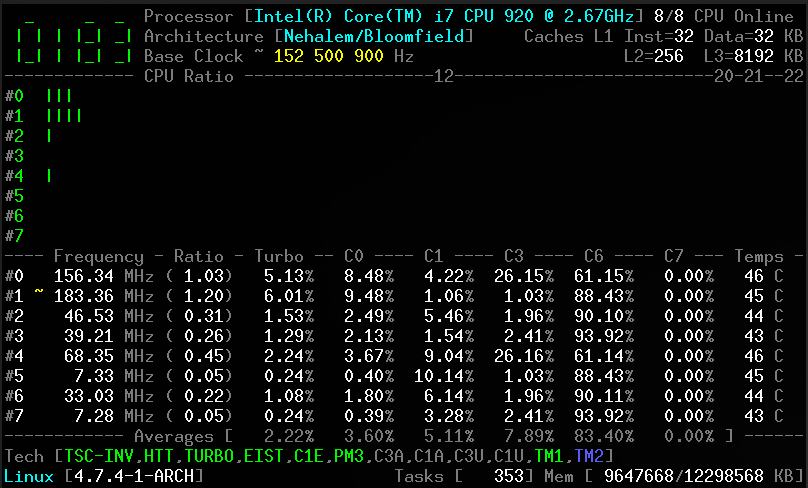
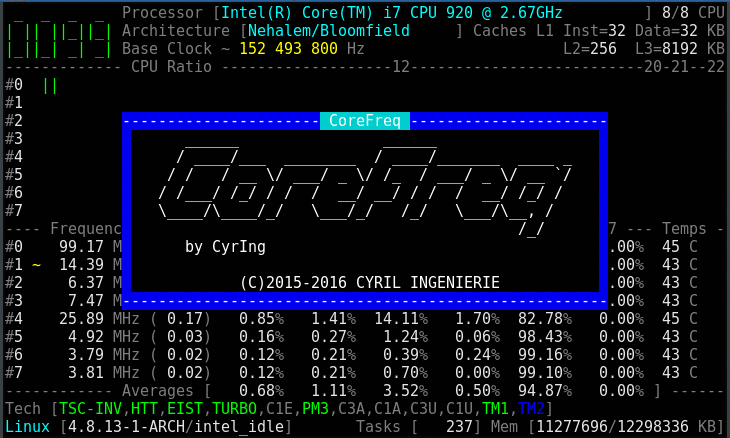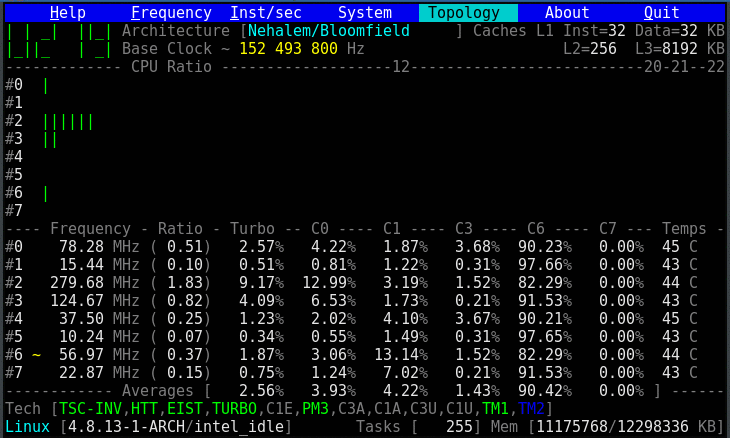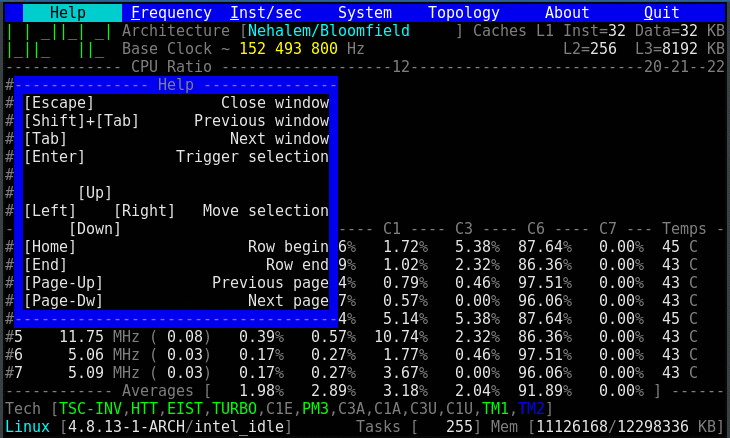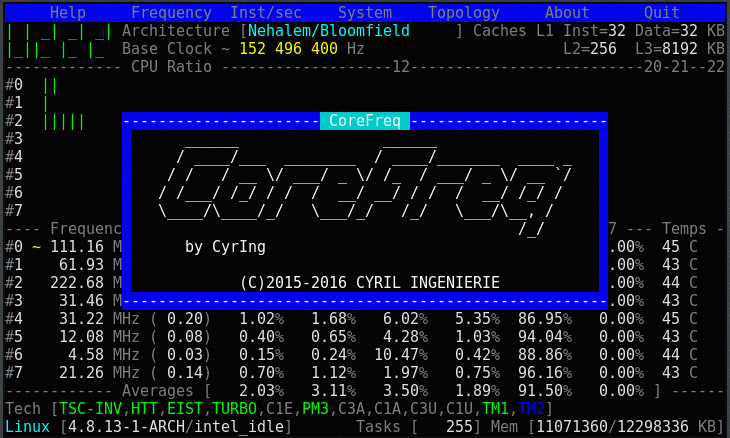
- Core frequencies & ratios; SpeedStep (EIST), Turbo Boost, Hyper-Threading (HTT) and Base Clock
- Performance counters including Time Stamp Counter (TSC), Unhalted Core Cycles (UCC), Unhalted Reference Cycles (URC)
- Number of instructions per cycle or second, IPS, IPC, or CPI
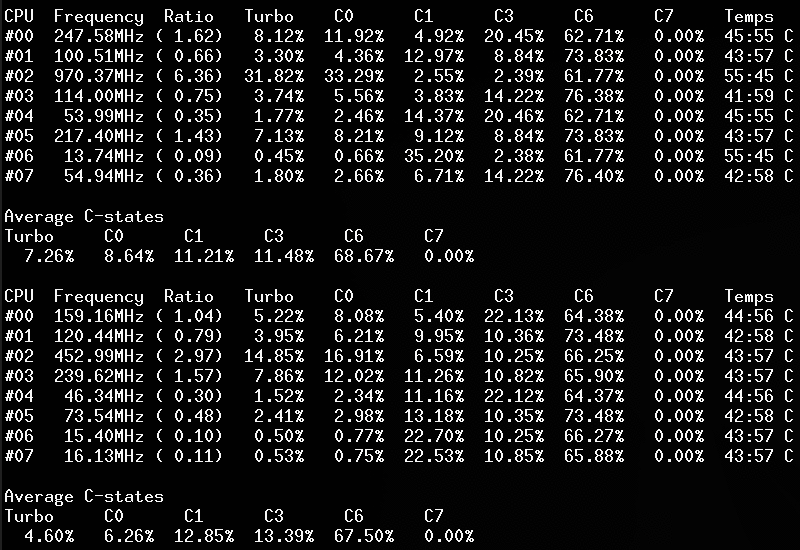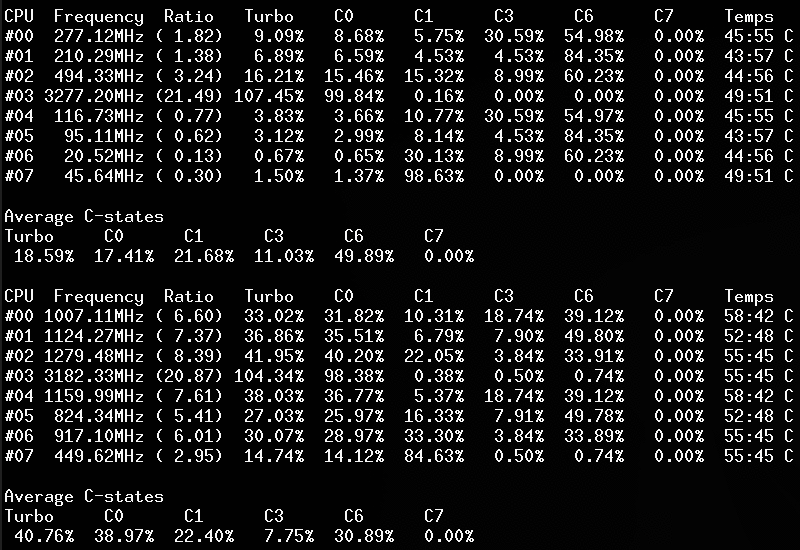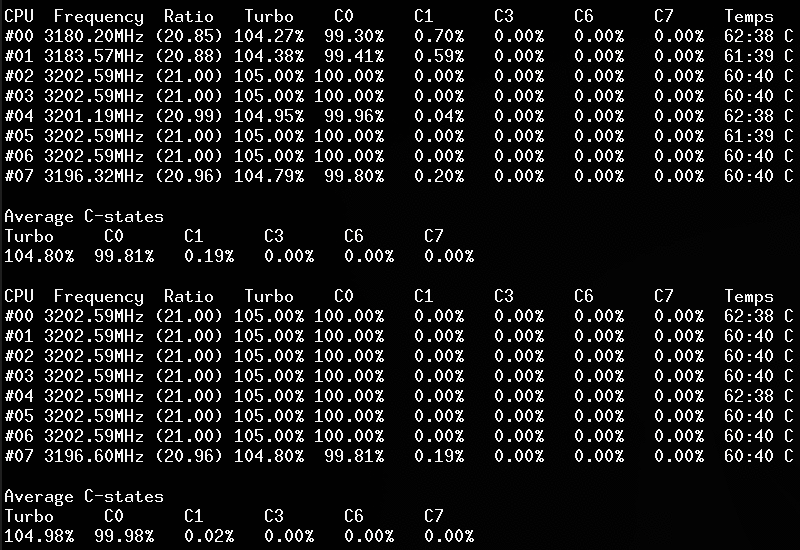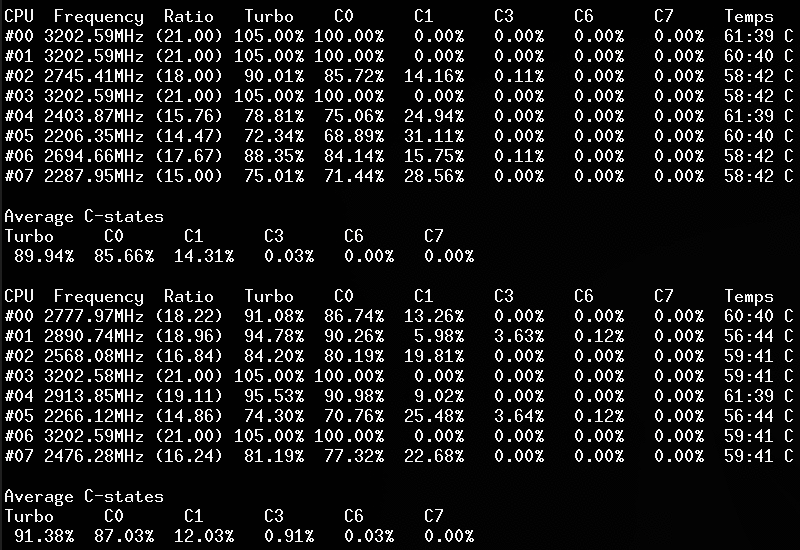
- CPU C-States C0 C1 C3 C6 C7 - C1E - Auto/UnDemotion of C1 C3
- DTS Temperature and Tjunction Max, Thermal Monitoring TM1 TM2 state
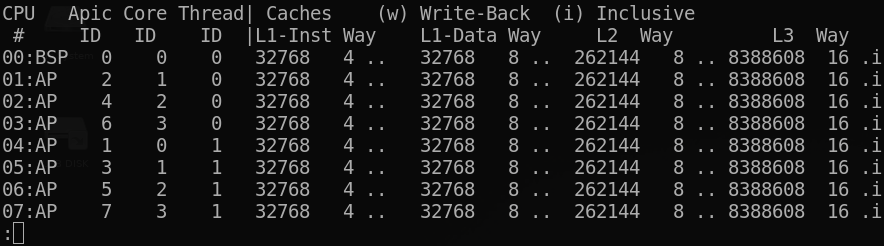
- Topology map including Caches for boostrap & application CPU
- Processor features, brand & architecture strings
To reach this goal, CoreFreq implements a Linux Kernel module which employs the followings:
- asm code to keep as near as possible the readings of the performance counters;
- per-CPU, implements slab data memory and high-resolution timer;
- compliant with suspend / resume and CPU Hot-Plug;
- a shared memory to protect kernel from the user-space part of the software;
- atomic synchronization of threads to avoid mutexes and deadlock.
1- Download or clone the source code into a working directory.
2- Build the programs.
make
cc -c corefreqd.c -o corefreqd.o
cc -lpthread -lrt -o corefreqd corefreqd.c
cc -c corefreq-cli.c -o corefreq-cli.o
cc -lrt -o corefreq-cli corefreq-cli.c
make -C /lib/modules/4.7.2-1-ARCH/build M=/workdir/CoreFreq modules
make[1]: Entering directory '/usr/lib/modules/4.7.2-1-ARCH/build'
CC [M] /workdir/CoreFreq/corefreqk.o
Building modules, stage 2.
MODPOST 1 modules
CC /workdir/CoreFreq/corefreqk.mod.o
LD [M] /workdir/CoreFreq/corefreqk.ko
make[1]: Leaving directory '/usr/lib/modules/4.7.2-1-ARCH/build'
3a- Disable nmi_watchdog (See Q&A below).
3b- Load the kernel module, as root.
modprobe corefreqk
or
insmod corefreqk.ko
4- Start the daemon, as root.
./corefreqd
5- Start the client, as a user.
./corefreq-cli
6- Press [CTRL]+[C] to stop the client.
7- Press [CTRL]+[C] to stop the daemon.
8- Unload the kernel module with the rmmod command
rmmod corefreqk.ko
Use dmesg or journalctl -k to check if the module is started
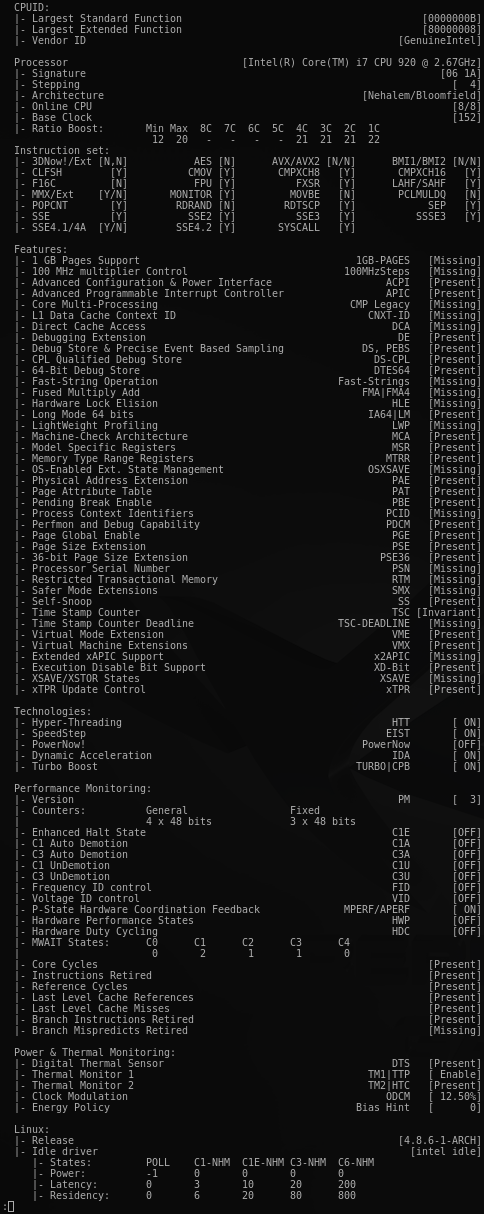
CoreFreq: Processor [06_1A] Architecture [Nehalem/Bloomfield] CPU [8/8]
CoreFreq Daemon. Copyright (C) 2015-2017 CYRIL INGENIERIE
Processor [Intel(R) Core(TM) i7 CPU 920 @ 2.67GHz]
Architecture [Nehalem/Bloomfield] 8/8 CPU Online.
Without arguments, the corefreq-cli program displays Top Monitoring
-
Remark: Drawing will stall if the terminal width is lower than 80 columns, or its height is less than required.
-
With the option '-i' corefreq-cli traces the number of instructions per second / cycle
CPU IPS IPC CPI
#00 0.000579/s 0.059728/c 16.742698/i
#01 0.000334/s 0.150569/c 6.641471/i
#02 0.000598/s 0.161326/c 6.198641/i
#03 0.000294/s 0.233535/c 4.282013/i
#04 0.000240/s 0.042931/c 23.293141/i
#05 0.000284/s 0.158661/c 6.302765/i
#06 0.000128/s 0.128031/c 7.810631/i
#07 0.000088/s 0.150406/c 6.648674/i
- Use option '-s' to show Processor information (BSP)
corefreq-git can be installed from the Arch User Repository.
- Install the prerequisite packages.
apt-get install dkms git libpthread-stubs0-dev
- Install the prerequisite packages.
yum group install "Development Tools"
- As a user, clone and build CoreFreq.
git clone https://github.com/cyring/CoreFreq.git
cd CoreFreq
make
- As root, change to the build directory then start the module followed by the daemon.
insmod corefreqk.ko
./corefreqd
- As a user, start the client.
./corefreq-cli
- Q: Turbo Technology is activated however CPUs don't reach those frequencies ?
- Q: The CPU ratio does not go above its minimum value ?
- Q: UI crash frequently ?
A: In the kernel command argument line, disable nmi_watchdog (if suitable with your setup)
nmi_watchdog=0
A: Check also what the current idle driver is. In the CoreFreq client UI, should be written the driver name beside the Linux version, "intel_idle" is the recommended driver.
* Q: The deep sleep states do not produce any value ?
A: Check if the intel_idle module is running.
Accordingly to the Processor specs, provide a max_cstate value in the kernel argument as below.
intel_idle.max_cstate=value
* Q: The CoreFreq UI refreshes itself slowly, with a delay after the actual CPUs usage ?
A: The sampling time to read the counters can be reduced or increased using a CoreFreq module argument:
insmod corefreqk.ko SleepInterval=value
where value is supplied in milliseconds between a minimum of 500 ms and a maximum of 5000 ms. 1000 ms is the default value.
* Q: The base clock reports a wrong frequency value ?
A: CoreFreq uses various algorithms to estimate the base clock.
1- The delta of two TimeStampCounter reads in the interval of 1000 ms
2- The value provided in the Processor brand string divided by the maximum ratio (without Turbo)
3- A static value advertised by the manufacturer specs.
4- The MSR_FSB_FREQ bits provided with the Core, Core2 and Atom architectures.
The algorithms # 2, 3 and 4 will not return any under/over-clock frequency.
The CoreFreq module can be started as follow to ignore the first algorithm (frequency estimation):
insmod corefreqk.ko AutoClock=0
* Q: The CPU temperature is wrong ?
A: CoreFreq employs two msr to calculate the temperature.
MSR_IA32_TEMPERATURE_TARGET - MSR_IA32_THERM_STATUS [DTS]
If the MSR_IA32_TEMPERATURE_TARGET is not provided by the Processor, a default value of 100 degree Celsius is considered as a target.
* Q: The menu option "Memory Ctrl" does not open any window ?
A: Although Uncore and IMC features are under development, they can be activated with the Experimental driver argument:
insmod corefreqk.ko Experimental=1
## Algorithm

# About
[CyrIng](https://github.com/cyring)
Copyright (C) 2015-2017 CYRIL INGENIERIE
-------