An end-to-end framework for training and deploying LLMs with billions and trillions of parameters.
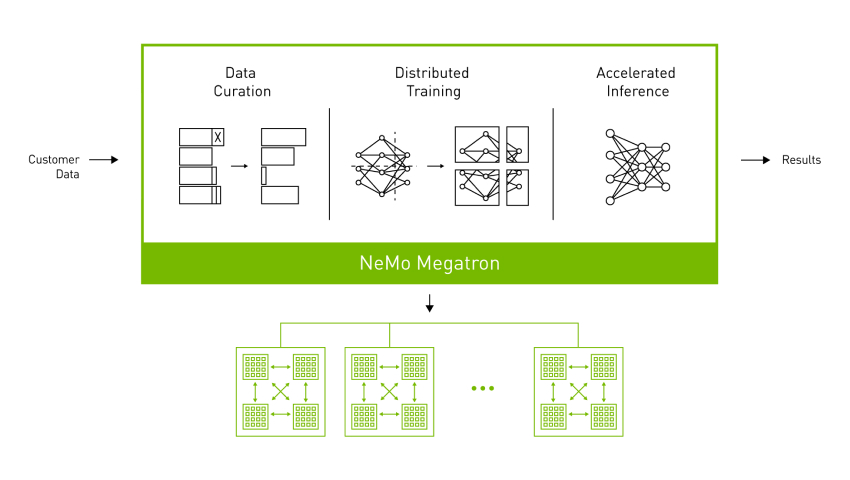
NVIDIA NeMo Megatron, part of the NVIDIA AI platform, offers an easy, efficient, and cost-effective containerized framework to build and deploy LLMs. Designed for enterprise application development, it builds upon the most advanced technologies from NVIDIA research and provides an end-to-end workflow for automated distributed data processing, training large-scale customized GPT-3, T5, and multilingual T5 (mT5) models, and deploying models for inference at scale.
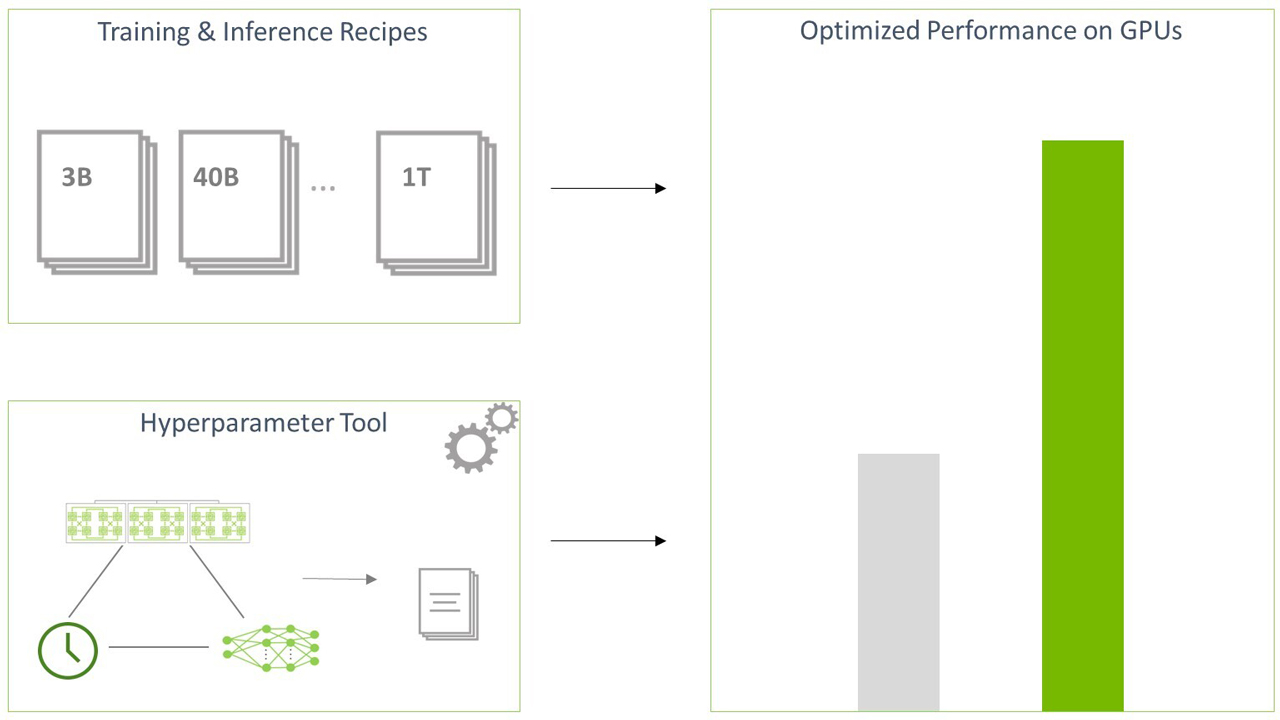
Harnessing the power of LLMs is made easy through validated and converged recipes with predefined configurations for training and inference. Customizing models is simplified by the hyperparameter tool, which automatically searches for the best hyperparameter configurations and performance for training and inference on any given distributed GPU cluster configuration.
NeMo Megatron also allows for efficiently adapting models for different use cases using prompt-based learning capabilities, such as p-tuning and prompt tuning. These methods are more efficient than traditional fine-tuning and allow LLMs to adapt to new use cases without fine-tuning the full pretrained models.
NeMo Megatron is part of NeMo, an open-source framework for building high-performance and flexible applications for conversational AI, speech AI, and biology.
Fastest training on GPUs.
Use state-of-the-art (SOTA) training techniques to maximize throughput and minimize training time for LLMs with billions or trillions of parameters.
Validated recipes.
Access recipes for training multiple GPT-3, T5, and mT5 models to convergence and deploy for inference
Flexible and customizable.
Train and deploy custom LLMs from scratch with data preprocessing, training, evaluation, and inference. Equipped with fine-tuning and prompt-based learning capabilities to customize for different use cases.
Run on prem and in the cloud.
Train and deploy LLMs of any size on any GPU infrastructure. Supported on NVIDIA DGX SuperPOD™, NVIDIA DGX™ Foundry, Microsoft Azure, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, and Amazon Web Services.
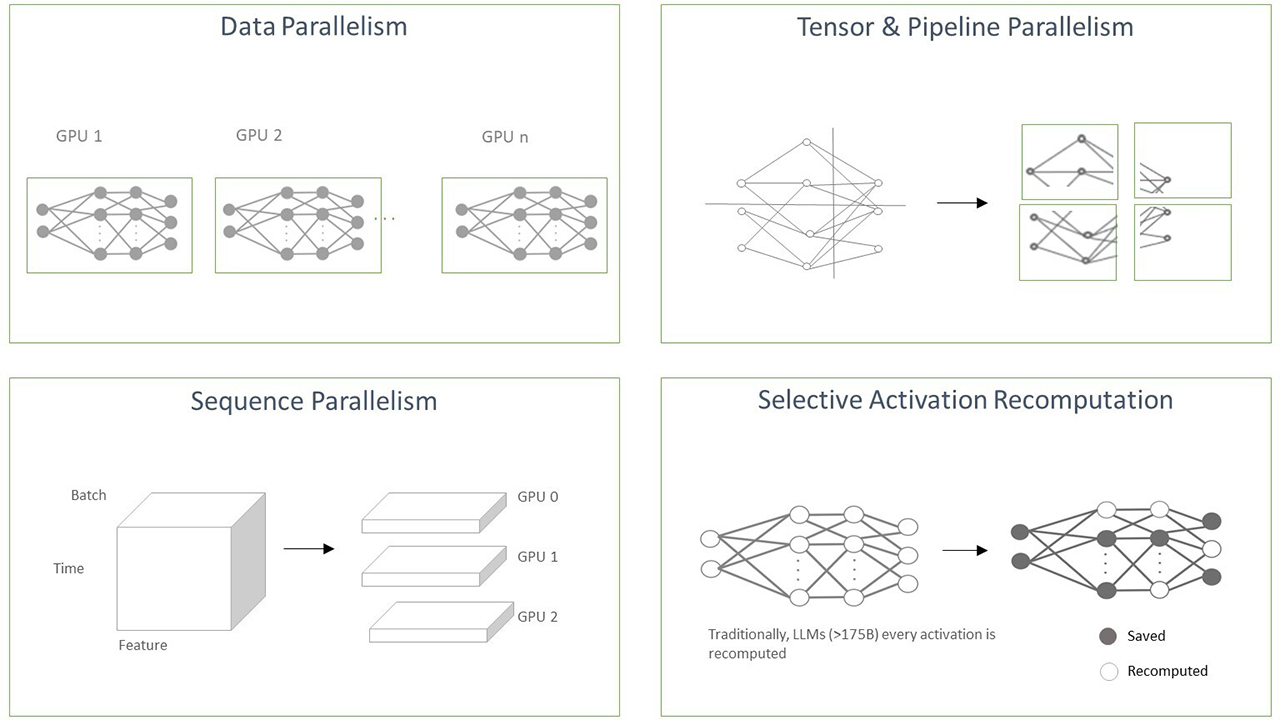
NeMo Megatron delivers high training efficiency, making large-scale natural language processing (NLP) practical, using parallelism techniques such as:
- Tensor parallelism to scale models within nodes
- Data and pipeline parallelism to scale data and models across thousands of GPUs
- Sequence parallelism to distribute activation memory across tensor parallel devices
Alongside tensor parallelism, selective activation recomputing optimizes recomputation and memory usage across tensor parallel devices during backpropagation.
It also comes equipped with fine-tuning capabilities, alongside prompt-based learning techniques, that enable customization for different datasets with minimal data, vastly improving performance and few-shot tasks.
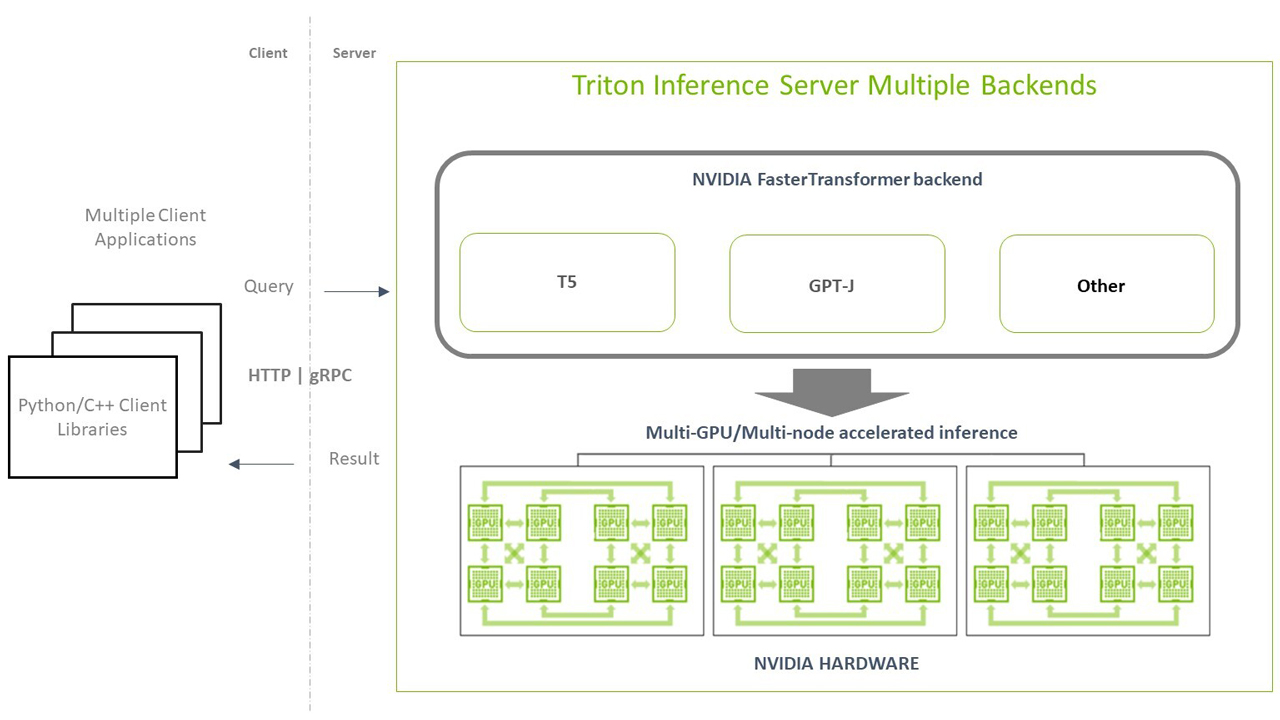
NeMo Megatron supports deploying LLMs for inference using NVIDIA Triton™ Inference Server. With powerful optimization from Faster Transformer, you can achieve state-of-the-art accuracy, latency, and throughput inference performance on single-GPU, multi-GPU, and multi-node configurations.
NeMo Megatron makes LLMs accessible by solving many of the existing pain points across the entire stack, allowing users to easily deploy applications at scale quickly and efficiently.
Learn more about NVIDIA Triton
NeMo Megatron allows you to bring your own dataset and tokenize data to a digestible format. It includes comprehensive preprocessing capabilities for data filtration, deduplication, blending, and formatting on datasets, on Piles and multilingual C4 (mC4). These help researchers and engineers save months of development and compute time, letting them focus on building applications.
NeMo Megatron includes prepackaged scripts, reference examples, and documentation across the entire pipeline, making LLMs possible from day one.
Several validated and converged recipes for various model sizes, for GPT-3 and T5/mT5 architectures, allow for easy training and deployment of LLMs.
Custom LLMs are also made easy through a unique offering from NeMo Megatron—the hyperparameter tool, which automatically searches for the best hyperparameter configurations to optimize training and inference for any given multi-GPU configuration, training, or deployment constraints.
The promise of LLMs serving several use cases with a single model can enable enterprises to develop a plethora of applications, ranging from content generation to text summarization to chatbots. Yet, using customized LLMs isn’t for the faint of heart, requiring immense amounts of compute resources and technical expertise.
NVIDIA NeMo LLM Service running on the NVIDIA AI platform provides the fastest path to customizing and using LLMs for AI applications. Developers can run them in private and public clouds, run them through an API, or experiment via a playground. Models can be trained from any framework or run out of the box. State-of-the-art prompt learning capabilities, which are compute-efficient techniques, embed context in user queries to allow for greater accuracy in specific use cases.
- Amphere or Hopper Generation GPU (>1 for Tensor Parallelism)
- Docker & Docker Compose
- Ubuntu 20.04 or newer
docker compose build
fastertransformer-triton-convert: Convert NeMo model to Triton+FasterTransformer format for tensor parallelism. The default is 2 gpus, if you have fewer or more, please read models/triton_models/README.md and change the NUM_GPU variable in the entrypoint.sh file.
fastertransformer-triton-server: Triton server with FasterTransformer backend configured to serve NVIDIA's 20B parameter Megatron GPT type LLM.
fastertransformer-triton-client: A simple JupyterLab container from which you can send requests to the Triton server and begin experimenting, locally. Start with workspace/Evaluation.ipynb for some examples!
fastertransformer-triton-convert: docker compose up fastertransformer-triton-convert
fastertransformer-triton-server: docker compose up fastertransformer-triton-server
fastertransformer-triton-client: docker compose up fastertransformer-triton-client
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Number of Tokens | Specifies how much text to generate. Tokens can be either an entire word, or parts of words. For English, 100 tokens form approximately 75 words. |
| Temperature | Controls the randomness of selecting the next token during text generation. Lower values reduce randomness, suitable for tasks with a correct answer such as question answering or summarization. Higher values increase randomness, suitable for tasks that require creativity. The [0.5, 0.8] range is a good starting point for experimentation. |
| Top K | Controls the randomness of selecting the next token during text generation. The number of highest-probability tokens to keep, from which the next token will be selected at random. Lower values reduce randomness, suitable for tasks with a correct answer such as question answering or summarization. Higher values increase randomness, suitable for tasks that require creativity. 0 means Top K is not used. 1 means greedy decoding, that is, always selecting the most probable token next. |
| Top P | Controls the randomness of selecting the next token during text generation. This determines the minimum number of highest-probability tokens whose probabilities sum to or exceed the Top P value, from which the next token will be selected at random. Lower values reduce randomness, suitable for tasks with a correct answer such as question answering or summarization. Higher values increase randomness, suitable for tasks that require creativity. |
| Repetition Penalty | How much to penalize tokens based on how frequently they occur in the text. A value of 1 means no penalty, while values larger than 1 discourage repeated tokens. |
| Length Penalty | Only applies to beam search, that is, when the beam width is >1. Larger values penalize long candidates more heavily thus preferring shorter candidates. |
| Beam Search Diversity Rate | Only applies to beam search, that is, when the beam width is >1. A higher value encourages beam search to return a more diverse set of candidates. |
| Beam Width | The number of concurrent candidates to keep track of during beam search. Higher values increase the chance of finding a good output but also require more computation. Streaming is supported with a “beam width” hyperparameter set to 1 only. |
| Random Seed | The model generates random results. Changing the random seed alone will produce a different response with similar characteristics. It is possible to reproduce results by fixing the random seed (assuming all other hyperparameters are also fixed). |
| Stop Words | Set of character sequences, upon generating any of which, the API will stop generating any further text prematurely, even if the output length has not yet reached the specified number of tokens. It is useful to design a stopping template in the examples given to the model so that it can learn to stop appropriately upon completing an intended task. |
The client container containes a Jupyter Notebook for interacting with the model to sample actual results. This container also has the ability to submit requests using NVIDIA's performance analyzer so you may monitor the inference performance.
./run_perf_analyzer.shSample Performance Metrics:
Successfully read data for 1 stream/streams with 8 step/steps.
*** Measurement Settings ***
Batch size: 1
Service Kind: Triton
Using "time_windows" mode for stabilization
Measurement window: 30000 msec
Latency limit: 0 msec
Concurrency limit: 16 concurrent requests
Using asynchronous calls for inference
Stabilizing using p95 latency
Request concurrency: 4
Client:
Request count: 90
Throughput: 0.833305 infer/sec
p50 latency: 6074209 usec
p90 latency: 6894327 usec
p95 latency: 6896744 usec
p99 latency: 6912016 usec
Avg gRPC time: 4795231 usec ((un)marshal request/response 24 usec + response wait 4795207 usec)
Server:
Inference count: 90
Execution count: 90
Successful request count: 90
Avg request latency: 4794564 usec (overhead 524 usec + queue 2607722 usec + compute 2186318 usec)
Composing models:
fastertransformer, version:
Inference count: 90
Execution count: 57
Successful request count: 90
Avg request latency: 4482158 usec (overhead 293 usec + queue 2550380 usec + compute input 264 usec + compute infer 1930569 usec + compute output 651 usec)
postprocessing, version:
Inference count: 90
Execution count: 90
Successful request count: 90
Avg request latency: 144865 usec (overhead 35 usec + queue 45928 usec + compute input 19018 usec + compute infer 79337 usec + compute output 546 usec)
preprocessing, version:
Inference count: 89
Execution count: 89
Successful request count: 89
Avg request latency: 167403 usec (overhead 58 usec + queue 11414 usec + compute input 52 usec + compute infer 155393 usec + compute output 485 usec)
Request concurrency: 8
Client:
Request count: 68
Throughput: 0.629612 infer/sec
p50 latency: 12865170 usec
p90 latency: 12870264 usec
p95 latency: 12873772 usec
p99 latency: 12876681 usec
Avg gRPC time: 12024041 usec ((un)marshal request/response 25 usec + response wait 12024016 usec)
Server:
Inference count: 68
Execution count: 68
Successful request count: 68
Avg request latency: 12023203 usec (overhead 1697 usec + queue 9526636 usec + compute 2494870 usec)
Composing models:
fastertransformer, version:
Inference count: 68
Execution count: 50
Successful request count: 68
Avg request latency: 11725337 usec (overhead 232 usec + queue 9474123 usec + compute input 280 usec + compute infer 2250100 usec + compute output 601 usec)
postprocessing, version:
Inference count: 68
Execution count: 68
Successful request count: 68
Avg request latency: 110337 usec (overhead 27 usec + queue 22910 usec + compute input 8135 usec + compute infer 78769 usec + compute output 495 usec)
preprocessing, version:
Inference count: 73
Execution count: 73
Successful request count: 73
Avg request latency: 186149 usec (overhead 58 usec + queue 29603 usec + compute input 52 usec + compute infer 155951 usec + compute output 484 usec)
Request concurrency: 12
Client:
Request count: 85
Throughput: 0.787007 infer/sec
p50 latency: 14846319 usec
p90 latency: 19347880 usec
p95 latency: 19409555 usec
p99 latency: 19451863 usec
Avg gRPC time: 15540920 usec ((un)marshal request/response 27 usec + response wait 15540893 usec)
Server:
Inference count: 85
Execution count: 85
Successful request count: 85
Avg request latency: 15540166 usec (overhead 665 usec + queue 13297430 usec + compute 2242071 usec)
Composing models:
fastertransformer, version:
Inference count: 85
Execution count: 55
Successful request count: 85
Avg request latency: 15218325 usec (overhead 274 usec + queue 13243878 usec + compute input 274 usec + compute infer 1973257 usec + compute output 641 usec)
postprocessing, version:
Inference count: 85
Execution count: 85
Successful request count: 85
Avg request latency: 151795 usec (overhead 35 usec + queue 41996 usec + compute input 24690 usec + compute infer 78925 usec + compute output 6149 usec)
preprocessing, version:
Inference count: 85
Execution count: 85
Successful request count: 85
Avg request latency: 169757 usec (overhead 67 usec + queue 11556 usec + compute input 52 usec + compute infer 157564 usec + compute output 516 usec)
Request concurrency: 16
Client:
Request count: 102
Throughput: 0.944408 infer/sec
p50 latency: 16850786 usec
p90 latency: 16856213 usec
p95 latency: 16857189 usec
p99 latency: 16859793 usec
Avg gRPC time: 16851236 usec ((un)marshal request/response 24 usec + response wait 16851212 usec)
Server:
Inference count: 102
Execution count: 102
Successful request count: 102
Avg request latency: 16850482 usec (overhead 0 usec + queue 14235794 usec + compute 2615172 usec)
Composing models:
fastertransformer, version:
Inference count: 102
Execution count: 51
Successful request count: 102
Avg request latency: 16483049 usec (overhead 364 usec + queue 14149846 usec + compute input 314 usec + compute infer 2331779 usec + compute output 746 usec)
postprocessing, version:
Inference count: 102
Execution count: 102
Successful request count: 102
Avg request latency: 194317 usec (overhead 31 usec + queue 69480 usec + compute input 32813 usec + compute infer 79091 usec + compute output 12902 usec)
preprocessing, version:
Inference count: 102
Execution count: 102
Successful request count: 102
Avg request latency: 174050 usec (overhead 55 usec + queue 16468 usec + compute input 50 usec + compute infer 156992 usec + compute output 484 usec)
Inferences/Second vs. Client p95 Batch Latency
Concurrency: 4, throughput: 0.833305 infer/sec, latency 6896744 usec
Concurrency: 8, throughput: 0.629612 infer/sec, latency 12873772 usec
Concurrency: 12, throughput: 0.787007 infer/sec, latency 19409555 usec
Concurrency: 16, throughput: 0.944408 infer/sec, latency 16857189 usec