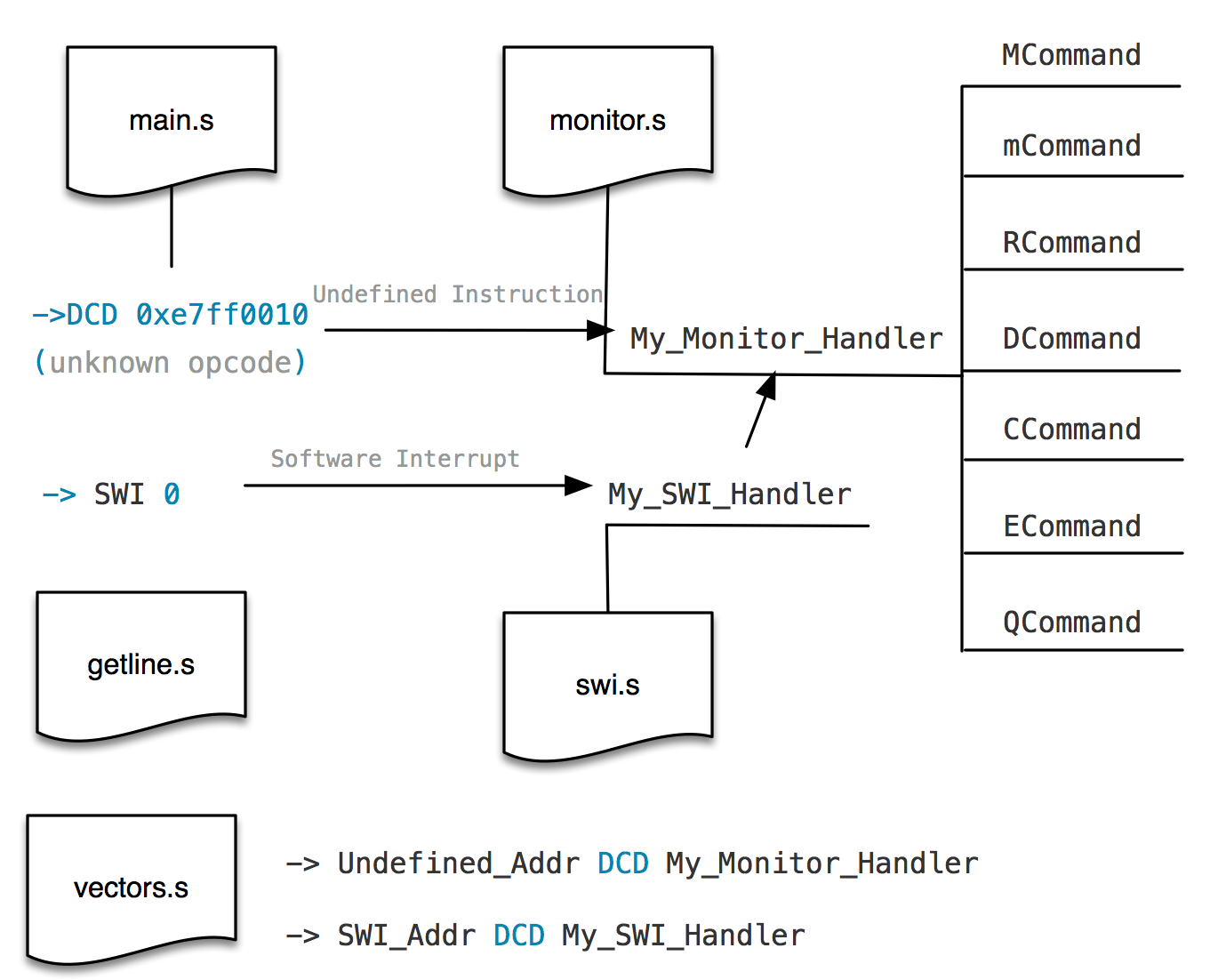
- monitor.s: A skeleton file for your monitor program.
- main.s: The test harness for your monitor. This file doesn't need to be modified. The main application (file main.s), running in User mode, is interrupted in two different manners. The first one is the execution of an undefined instruction. The second one is a software interrupt (SWI). Both interrupts should lead to a jump to your monitor program in order to debug the interrupted application. This should be done in a similar way as in the "SWI handler" exercise studied previously.
- getline.a: A binary of the line parsing routine is included since writing your own routine can be tricky. However, to get maximum marks for the project, you are expected to write your own replacement for this routine.
- vectors.s: Already seen in the "SWI handler" exercise, this is an example on how to initialise the ARM Vector Table to a default state. Modify it to link your monitor to the appropriate events.
| Command (params1, 2 , 3) | Action |
|---|---|
| M {<address>} {<value>} | Display the contents of the memory word starting at address <address> and ending at <address+3 bytes>. If <address> is not specified, use the previous word address + 4. If <value> is specified, overwrite the memory contents with the specified value. If <address> is not word-aligned, data manipulations will be necessary to display the proper word value. |
| m {<address>} {<value>} | Display the contents of the memory byte. If <address> is not specified, use the previous byte address + 1. If <value> is specified, overwrite the memory contents with the specified value. |
| R\r {<number>} {<value>} | Display the contents of the specified register. If <number> is not specified, display the contents of all registers. If <value> is specified, overwrite the register contents with the specified value. Handle both decimal and hexadecimal register numbers: "R 12" and "R C" should point to the same register. Think about special needs for every value of <value>. |
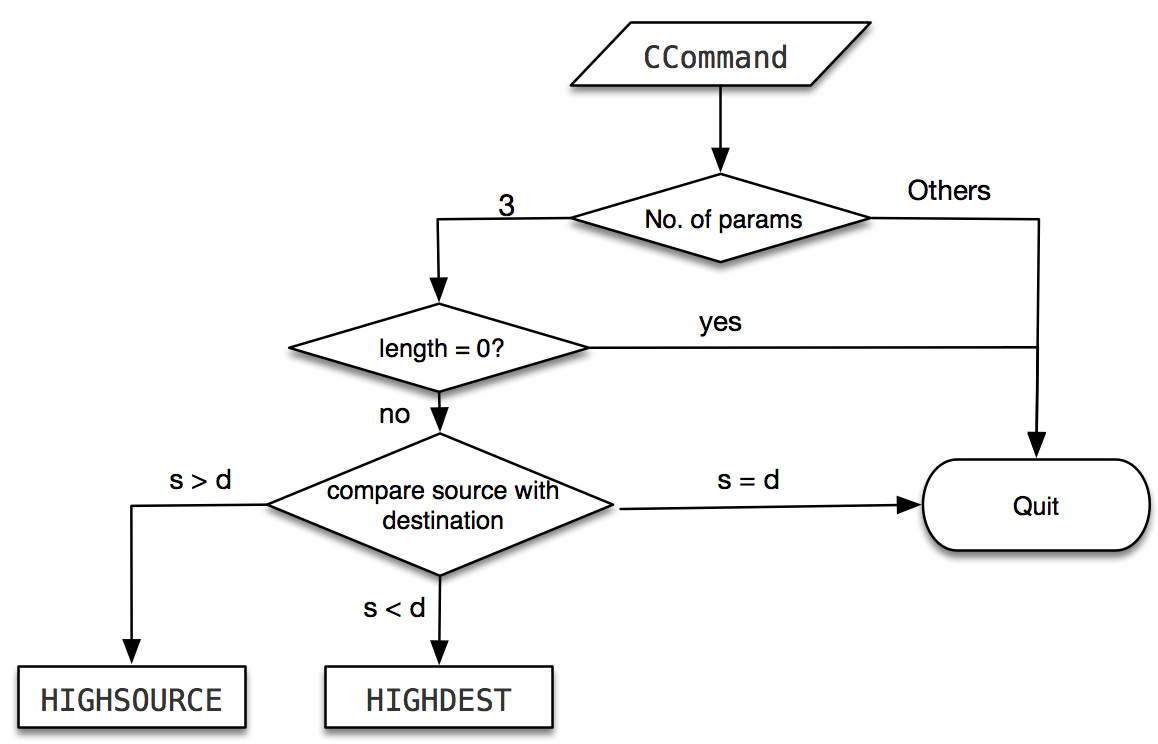
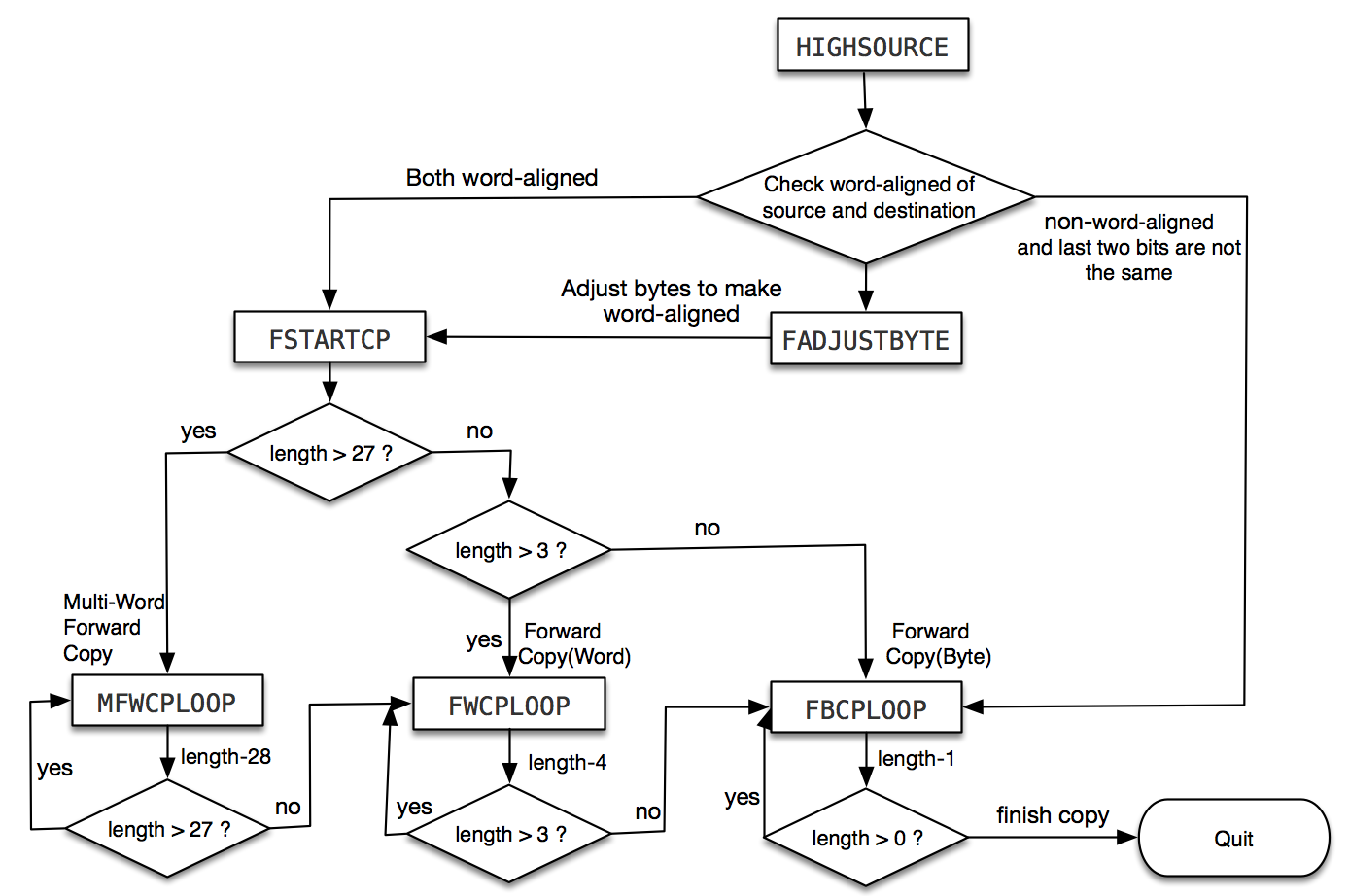
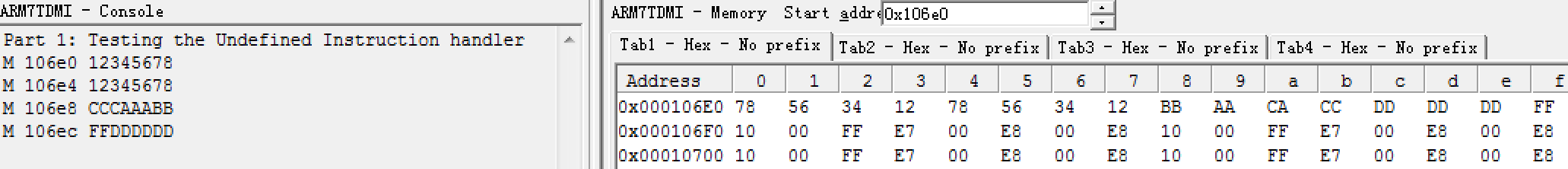
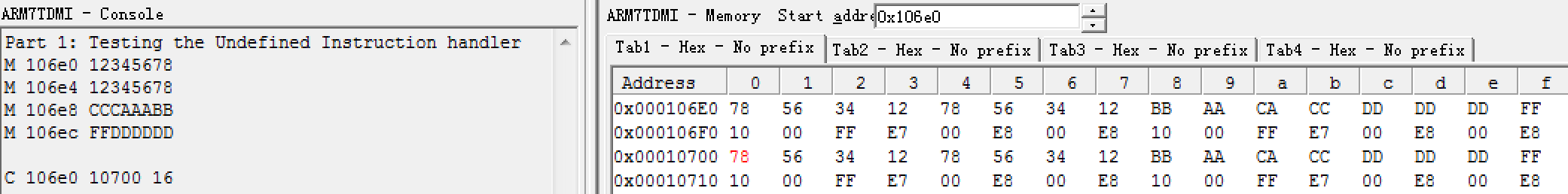
| C <source> <dest> <length> (bytes) | Copy a memory block of <length> bytes starting at address <source> to a destination address starting at <dest>. Your program should cope with <dest> being an arbitrary location i.e. below <source>, above <source+length> or in-between the two. Addresses can be non-word-aligned. Points will be given for efficiency (e.g. use words and multi-words copies when possible). |
| E {0 | 1} | Change the data representation to either little-endian ("E 0", default) or big-endian ("E 1"). No parameter indicates toggle the representation. |
| D {10 | 16 | 2} | Change the display of memory/register to decimal, hexadecimal or binary. |
| Q | Leave the monitor and return to the main application. |
Todo:
Handle undefined instructions and Implement Q commandImplement D command (decimal, hexadecimal and binary print functions)Implement E command ( little-endian & big-endian)Implement software interrupt (SWI)Implement M commandImplement m commandImplement R/r commandImplement C commandWrite parsing routine to replace getline.aOptimize the code
#Resource
-
All subroutines should adhere to the APCS ARM Cross-Platform Development
-
Some answers of labs(swi) answers
#Changelog
##08/03/2016
###COMMIT INFORMATION "add QDE command"
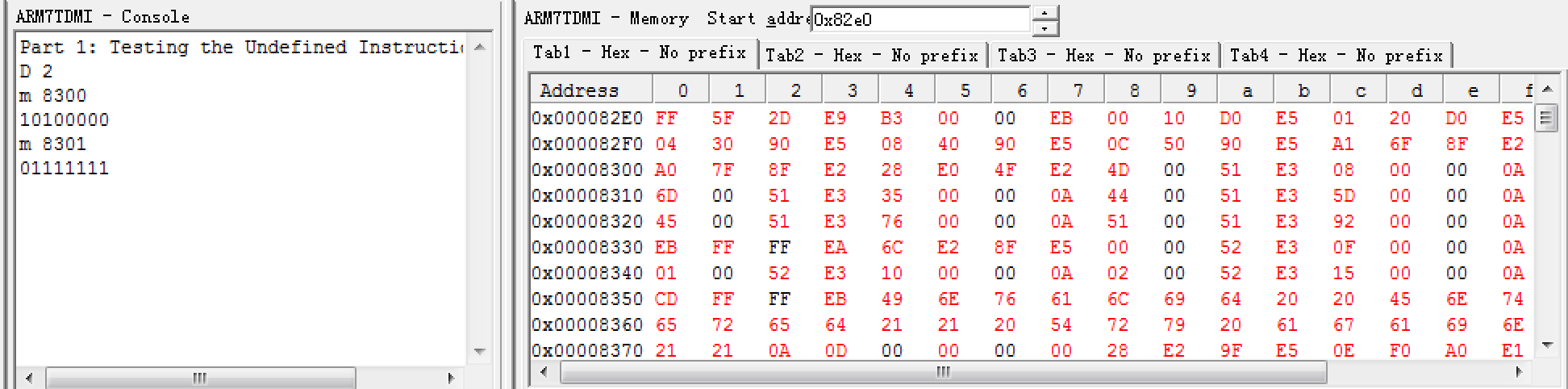
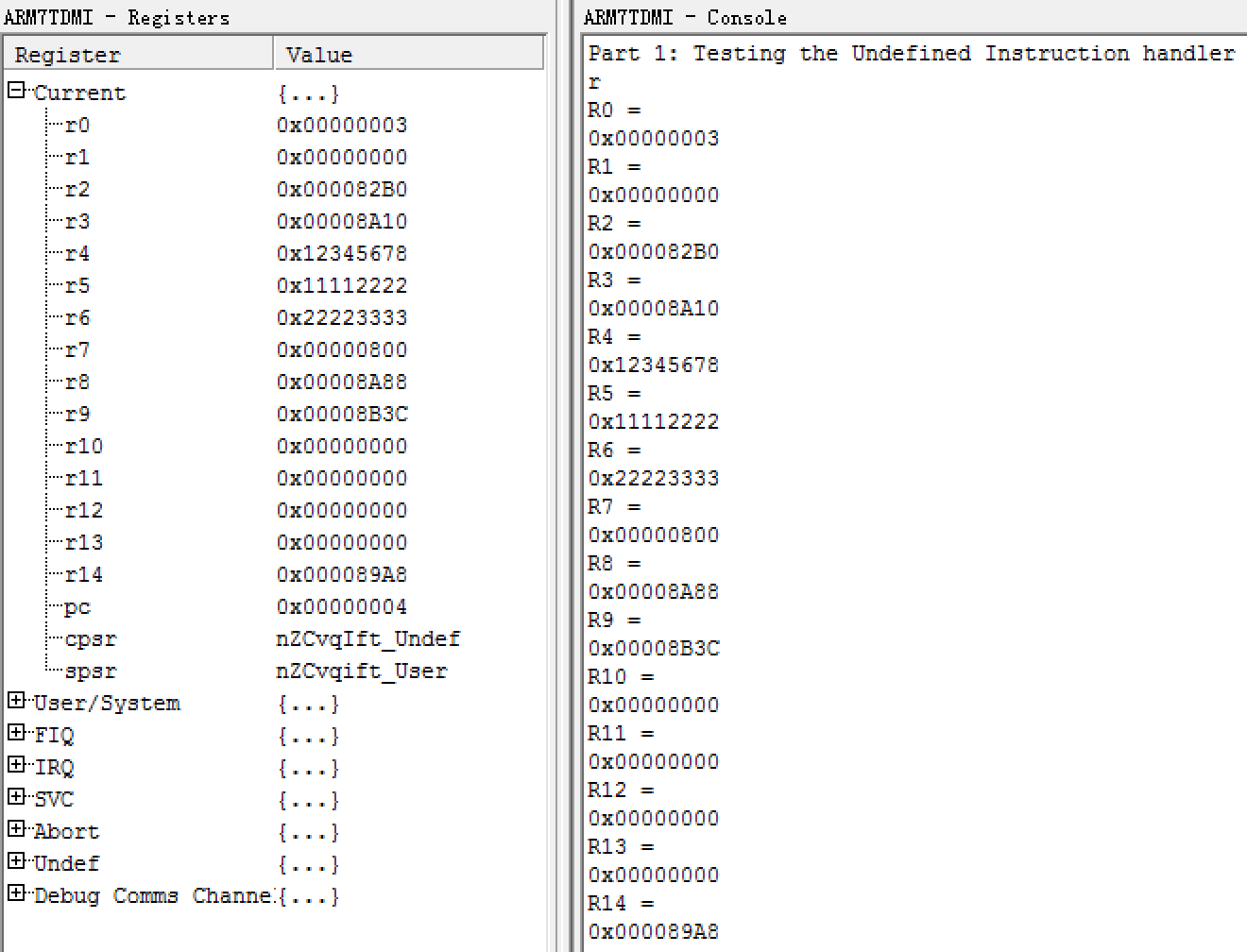
- Change vectors.s to an exception and handle undefined instructions successfully.
- Add Q command. Restore r13, r14 return to user mode code.
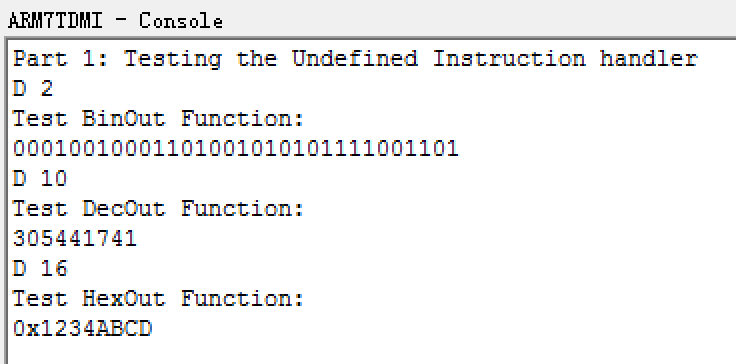
- Write HexOut, BinOut , DecOut and TextOut functions. First store initial value(0x1234abcd) into r2 and then test the program in the DCOMMAND routine. BASEM records the way to print.
- Add little-endian & big-endian support in print functions, write a E command to switch on the basis of ENDIAN.
###COMMIT INFORMATION "Implement software interrupt"
- Add software interrupt (SWI), modify vectors.s and monitor.s. In order to debug the interrupted application, It will enter to Command interface when it extracted the same swi number.
##09/03/2016
###COMMIT INFORMATION "add M command"
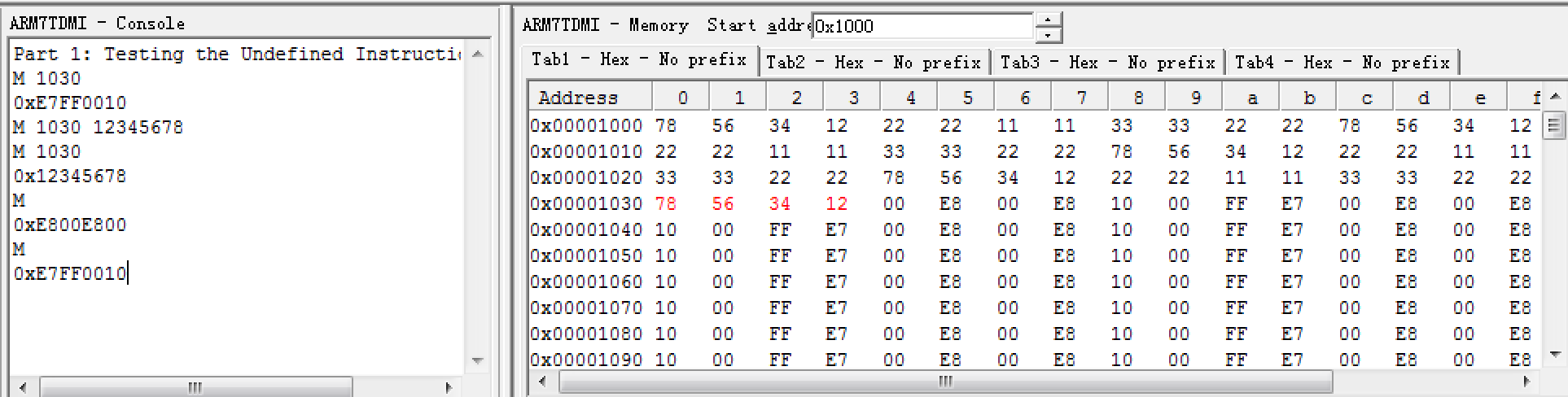
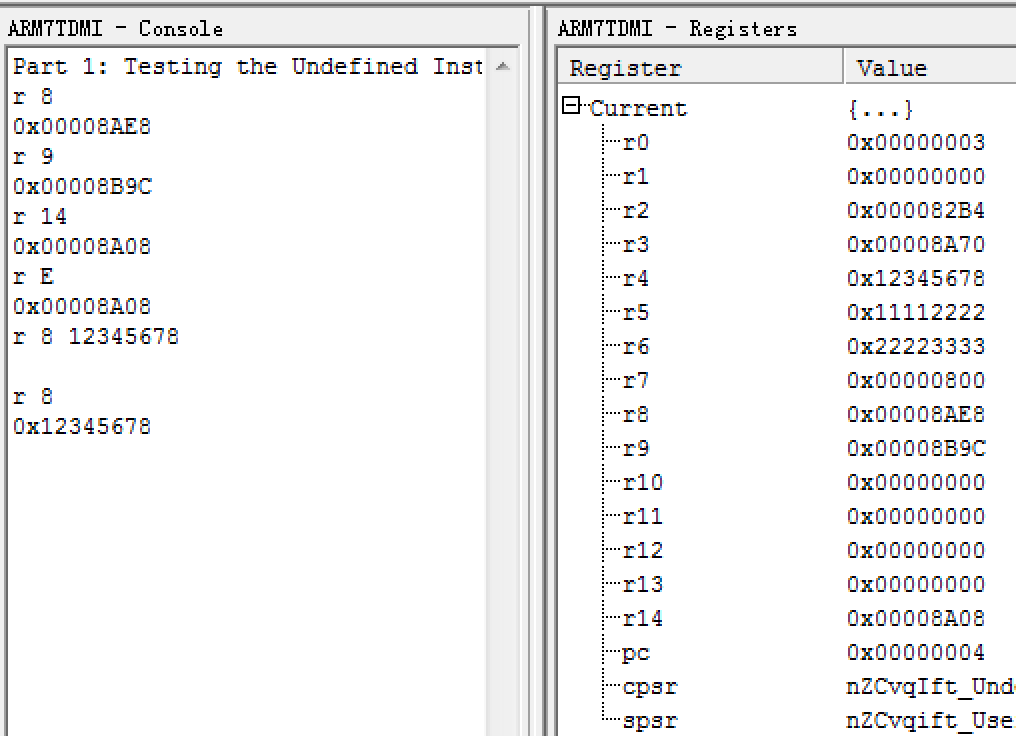
- There are mainly three routines depending on input parameter numbers. If there is only one parameter(<address>) input, It display the contents of the memory word starting at address . If there are two parameter(<address> and <value>) inputs, it will overwrite the memory contents with the specified value.
If there is no parameter input, it will use the previous word address + 4. So, we preserve r6 to restore last time memory address. Note:when the first time call this route, it will print stack top address.
If <address> is not word-aligned, data manipulations will be necessary to display or write(?) the proper word value(next word-aligned address).
###COMMIT INFORMATION "add m command"
- The same step as previous Mcommand. This has no real relevance with endian. In addition, the print functions were modified to support printing byte. It is notable that It only overwrite one byte instead of 4 bytes when it has <value> input.
##10/03/2016
###COMMIT INFORMATION "add R/r command"
- This stack is an area of memory which stores r0~r12 and r14. In order to get the contents of the specified register, point to the bottom of stack and then add 4 address each time. Note: <address> need to be filtered.
##12/03/2016
###COMMIT INFORMATION "change SWI & add C command"
- Modified the swi function.
- add C command (Byte by Byte memory copy).
#Issues
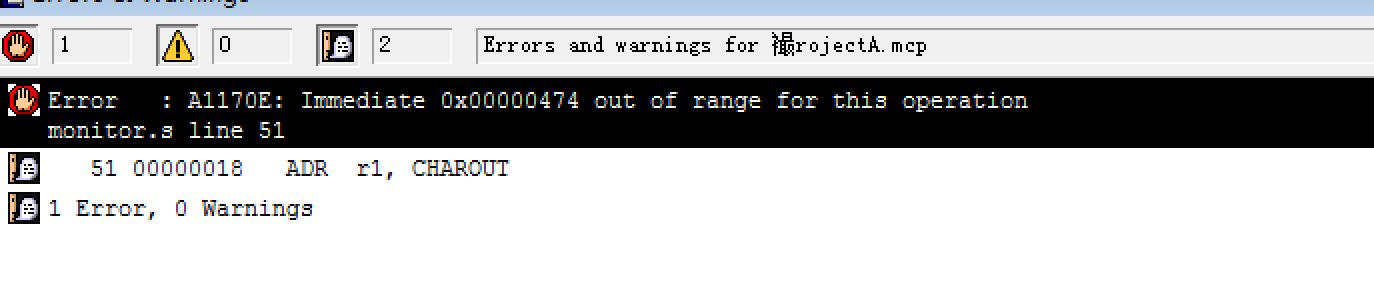
1 . Immediate value out of range. Solve problem Use ADRL instead of ADR
2 . Use BLNE operation, called routine doesn't return? why?
Solve: Add MOV pc, lr at last line.
3 . Error starting external debugger. Process Error Code 87 (0x57) The parameter is incorrect.
Solve: Restart project.