At first glance, Python and Ruby appear to be very similar languages. Both are high-level, dynamic languages used for rapid development. Both are beautiful languages that, when written well, are intuitive and can read much like English.
What do I mean by dynamic? Well, with a dynamically typed language you can do this:
>>> variable = 1
>>> type(variable)
<type 'int'>
>>> variable = "Foo"
>>> type(variable)
<type 'str'>
>>> variable = ["bar",10]
>>> type(variable)
<type 'list'>Essentially, you can change the datatype (from an integer to a string to a list, in the above example) at any point in a program. In a statically typed language, this would result in an error when compiled.
Both support multiple programming paradigms as well - e.g, procedural, functional, object oriented, and so forth.
However, there are a number of differences ..
This article begins with the language structure, then moves toward detailing what you can do with the two languages. Although the differences are important, it's much more important to focus on your end goal - that is, what you want to accomplish with said language. More on this later.
Open your terminal and enter the Python shell then type import this:
>>> import this
The Zen of Python, by Tim Peters
Beautiful is better than ugly.
Explicit is better than implicit.
Simple is better than complex.
Complex is better than complicated.
Flat is better than nested.
Sparse is better than dense.
Readability counts.
Special cases aren't special enough to break the rules.
Although practicality beats purity.
Errors should never pass silently.
Unless explicitly silenced.
In the face of ambiguity, refuse the temptation to guess.
There should be one-- and preferably only one --obvious way to do it.
Although that way may not be obvious at first unless you're Dutch.
Now is better than never.
Although never is often better than *right* now.
If the implementation is hard to explain, it's a bad idea.
If the implementation is easy to explain, it may be a good idea.
Namespaces are one honking great idea -- let's do more of those!
This is what is known as the Zen of Python, which are the guiding principles of Python. These 19 guidelines can be trimmed down to five points:
- Beautiful is better than ugly.
- Explicit is better than implicit.
- Simple is better than complex.
- Complex is better than complicated.
- Readability counts.
Essentially, Pythonists value code readability and productivity over all else.
Check out this Slideshare to see examples of all the guidelines in use. Highly recommended!
Finally, if shortened to one major point-
There should be one – and preferably only one – obvious way to do it
-we get to one of the main differences between Python and Ruby ..
While Python values one main way of solving a problem, Ruby - influenced by Perl - provides the developer with more freedom and power:
Ruby inherited the Perl philosophy of having more than one way to do the same thing. I inherited that philosophy from Larry Wall, who is my hero actually. I want to make Ruby users free. I want to give them the freedom to choose. People are different. People choose different criteria. But if there is a better way among many alternatives, I want to encourage that way by making it comfortable. So that’s what I’ve tried to do. Maybe Python code is a bit more readable. Everyone can write the same style of Python code, so it can be easier to read, maybe. But the difference from one person to the next is so big, providing only one way is little help even if you’re using Python, I think. I’d rather provide many ways if it’s possible, but encourage or guide users to choose a better way if it’s possible.
—Yukihiro Matsumoto (Matz)
Source: http://www.artima.com/intv/rubyP.html
With more freedom and less syntactical rules, many Rubyists believe that Ruby is a much more elegant language - and it is. Also, while Python focuses on simplicity, Ruby focuses on making the programmer happy, while this tends to be true and people can make truly beautiful programs, you can also often see messy code (especially from beginners) that can be difficult for other developers to read( or even themselves in a not so distant future). For example, you can put multiple statements on one line. This can look good and be readable, depending on how it's coded - or it can be a mess.
###The principle of least astonishment
One princpiple very present in the design of Ruby is the principle of least astonishment, it's basically about the language working the way you think it should, thinks like using a function with a strange name will leave you astonished, and will make you look in the documentation. In order to behave like this Ruby tends to do things like having the same functions with different names,however some people would argue this is confusing for beginners. Also, Python , although not having this principle in mind when making the language, also behaves quite like this by make pretty much everything work in a standard way, however one could say this only benefits advanced Python users.
Let's compare some code. The following snippets of code are for solving the Fibonacci sequence:
Ruby:
def fib(n)
return n if n < 2
fib(n-1) + fib(n-2)
end
alias :fibonacci :fibPython:
def fib(n):
if n < 2:
return n
else:
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2)Although you can write this code in many ways, both of these methods are true to the language, Ruby code demonstrates the practice of having multiple names for the same function (fib and fibonacci are the same). In other words, the Ruby example is very Ruby-ish while the Python example is very Pythonic. Can you read the Ruby code? It may be more elegant but it's a bit harder to read. Meanwhile, it's easy to follow the Python code, right? You of course can write code anyway you want. It's advisable to write Ruby code, when beginning, in a more Pythonic way - which simply means making it more readable:
def fib(n)
if n < 2
n
else
fib(n-1) + fib(n-2)
end
endKeep in mind that in many cases with Python there are still a number of ways to do one thing. Take copying a list for example. There's a least four different ways:
>>> my_list = [1,2,3]
>>> my_new_list = my_list[:]
>>> my_new_list
[1, 2, 3]
>>> my_new_list = list(my_list)
>>> my_new_list
[1, 2, 3]
>>> from copy import copy
>>> my_new_list = copy(my_list)
>>> my_new_list
[1, 2, 3]
>>> my_new_list = [x for x in my_list]
>>> my_new_list
[1, 2, 3]The difference is that there is one right way of doing this given the situation. The latter two probably are not the best to do since you have to use an extra library and list comprehensions can often be hard to read, respectively. The second example is the most readable, so that should probably be used in most situations.
As you can imagine, there are many more differences that just the syntax and philosophies of the two languages. Let's quickly look at some examples.
Without a doubt, Python is much easier to learn because of how the language is structured - and how explicit it is. One can literally become proficient in two to three months. Ruby takes much longer to learn due to its flexibility. Beneath the elegant surface, there's a lot of magic happening. It takes a while to grasp exactly what is happening. It can take upwards of six months to become proficient in Ruby.
You can see just how explicit Python is based on this example:
from twitter import Twitter
twit = Twitter()require 'twitter'
twit = Twitter.newIn the first example (Python), we are importing the Twitter() class from the twitter library, while in the latter example (Ruby), we are simply importing the twitter library, giving us access to the entire library, not just the Twitter() class. So you can see that in Python, you import only what you need, nothing else.
Again, you can use the same paradigms in both languages (procedural, functional, object oriented ...). When it comes to object oriented programming, Ruby used to have the upper hand, as it was built specifically for object orientation. That said, Python has moved more towards being a true object orientated language over the last few years. However, Ruby has one advantage, Ruby can add methods to existing classes, Python by default can't do this (although it's possible with the use of a external library)
Performance is a toss up as well. In some cases Python performs better, while in other cases, Ruby outperforms Python. It all depends on the task at hand.
Ruby has a bigger web presence with Rails than Python does with Django, so if you're looking to move into web development, Ruby may be the way to go. Python is a great general-purpose language and has more momentum going for it for areas outside outside of the web, such as sys admin/DevOps, statistics, and scientific computation.
That said, take a look at the two code snippets below -
print "Hello, World!"and
puts 'Hello, world!'End users do not care about the syntactical differences; they just want to see "Hello, World!" outputted on their screen. Think about this site that you're reading this post on now. Do you really care of it's Ruby/Rails-based or Python/Django-based? I imagine you just want to be able to read this post. So, if you want to go into web development, worry less about the back-end language. Learn one, then get really good at. Then go learn JavaScript.
The Python community is active, vibrant, and truly helpful. Although, you can say the same about the Ruby community, the community itself is very much tied into Rails. If Rails is your thing, then you are in luck.
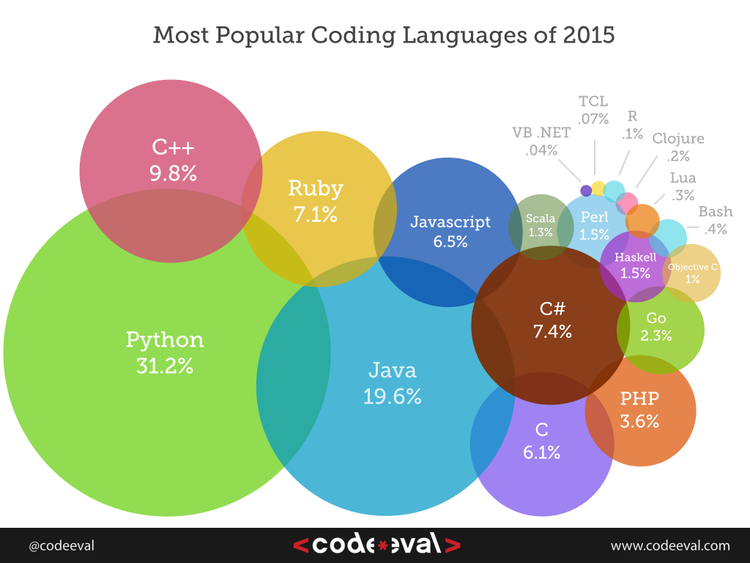
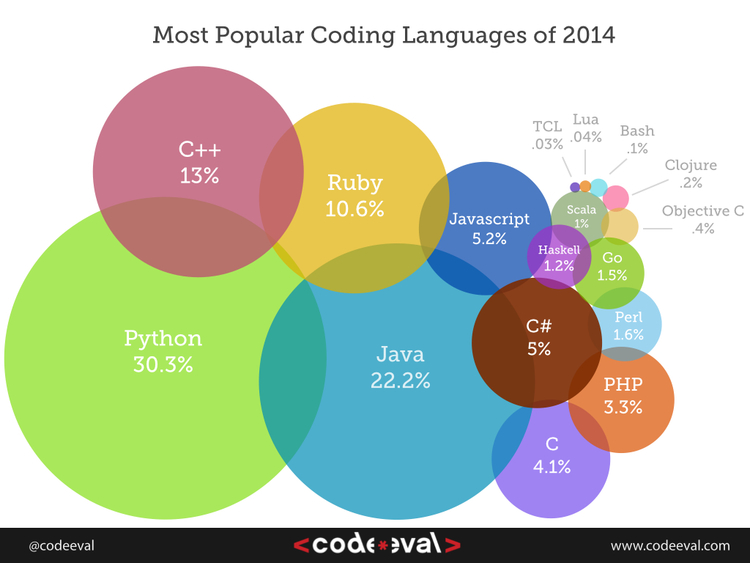
For the fourth year in a row, Python is the most popular language. Also, notice how Ruby decreased in popularity:
Source: http://blog.codeeval.com/codeevalblog/2014#.Uxewd_SwL5g
Excellent article about jobs by programming language.
Indeed:
- Python - Disqus, Dropbox, Yelp, Google, Reddit
- Ruby - Hulu, Twitter, Github, Airbnb
Guessing game ...
import random
import os
number = random.randint(1, 20)
guesses = 0
print 'Hello! What is your name?'
name = raw_input()
print "Hi, {}. I'm thinking of a number from 1 and 20.".format(name)
while guesses < 6:
print 'What is your guess. You have {} more guesses.'.format(6-guesses)
guess = raw_input()
guess = int(guess)
guesses = guesses + 1
if guess < number:
print 'Too low.'
elif guess > number:
print 'Too high.'
elif guess == number:
print 'Good job, {}! You guessed my number in {} guesses!'.format(name,guesses)
break
if guess != number:
print 'Nope. The number I was thinking of was {}.'.format(number)number = rand(1..20)
guesses = 0
puts 'Hello! What is your name?'
name = gets.chomp.to_s
puts "Hi, #{name}. I'm thinking of a number between 1 and 20."
while guesses < 6
puts "What is your guess? You have #{6-guesses} more guesses."
guess = gets.chomp.to_i
guesses += 1
unless guess == number
message = if guess > number
"Too high"
else
"Too low"
end
puts message
else
puts "Good job, #{name}! You guessed my number in #{guesses} guesses."
exit
end
end
puts "Nope. The number I was thinking of was #{number}."What are the syntactical differences? Is the Python code Pythonic? Is the Ruby code Ruby-ish? Do either (or both) need to be refactored?
As you can tell, there's not too many differences in the languages themselves. Yes, Python values readability, one method of doing things, and being explicit - but these are minor differences. It's more about the end goal. What are you trying to accomplish? My advice: Try both languages. See which language you like better, then learn that one. After that, learn the other.
Always, always, ALWAYS remember that no language can do it all. In other words, all languages have their positives and negatives
Cheers!