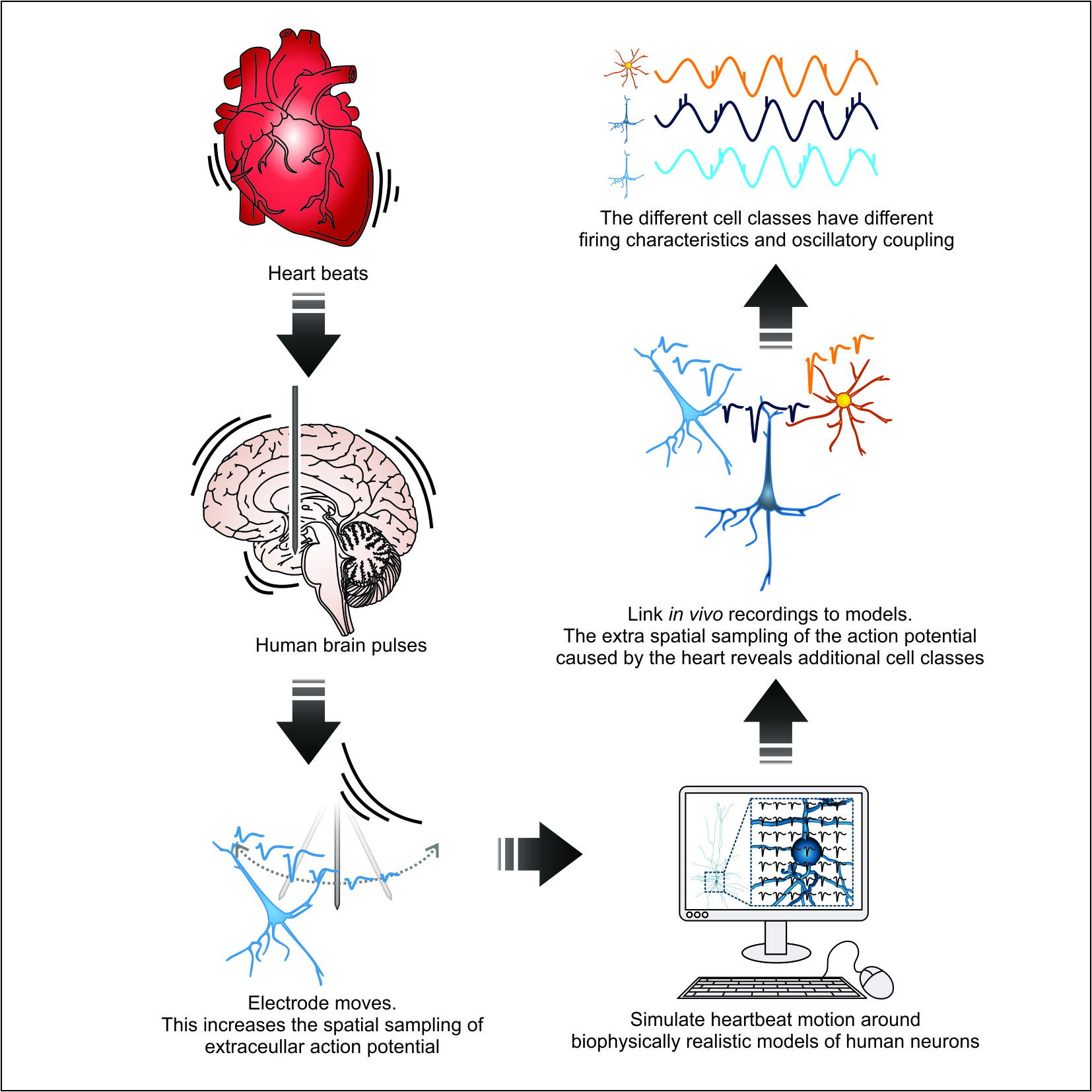
Cellular classes in the human brain revealed in vivo by heartbeat-related modulation of the extracellular action potential waveform
This repository contains a MatLab package for classifying cell types in the human brain using features of the extracellular action potential (EAP) waveform. A user inputs a continusously sampled, broadband neurophysiology signal along with spike times and (optional) heartbeat times. Each cell is first classified as Narrow Spiking (NS, putativie aspiny interneuron) or Broad Spiking (BS, putative spiny excitatory neuron). If heartbeat data is available, the classifier further subdivides BS cells into BS1 and BS2 subtypes which differ in their cardiac-related EAP features and electrical compactness.
This code accompanies the paper:
"Cellular classes in the human brain revealed in vivo by heartbeat-related modulation of the extracellular action potential waveform" Clayton P. Mosher, Yina Wei, Jan Kamiński, Anirban Nandi, Adam N. Mamelak, Costas A. Anastassiou, Ueli Rutishauser Cell Reports (in press) (2020)
Abstract of the paper:
Determining cell types is critical for understanding neural circuits but remains elusive in the living human brain. Current approaches discriminate units into putative cell classes using features of the extracellular action potential (EAP) – in absence of ground truth data, this remains a problematic procedure. We found that EAPs in deep structures of the brain exhibit robust and systematic variability during the cardiac cycle. These cardiac-related features refine neural classification. We use these features to link bio-realistic models generated from in vitro human whole-cell recordings of morphologically classified neurons to in vivo recordings. We differentiate aspiny inhibitory and spiny excitatory human hippocampal neurons and, in a second stage, demonstrate that cardiac-motion features reveal two types of spiny neurons with distinct intrinsic electrophysiological properties and phase-locking characteristics to endogenous oscillations. This multi-modal approach markedly improves cell classification in humans, offers interpretable cell classes, and is applicable to other brain areas and species.
In addition to the tools provided here you will need helper functions of running circular statistics if you're interested in heartbeat-related classification. You can find these here: Philipp Berens (2020). Circular Statistics Toolbox (Directional Statistics) (https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/10676-circular-statistics-toolbox-directional-statistics), MATLAB Central File Exchange. Retrieved April 18, 2020.
Data should be prepared as three variables (see ExampleData)
- broadbandSignal: (n x 1) vector of broadband neurophysiology data sampled at 32 kHz
- spikeTimes: {k x 1} cell array. Each entry in the array is an (n x 1) vector of spike times for a different single unit. Times are in samples and correspond to the time when the spike occurs in the broadband signal.
- beatTimes: (n x 1) that contains the time of each R-wave in the EKG (this variable is optional, if it is not included the code will still classify NS vs. BS cell types but will be unable to differentiate BS1 vs. BS2)
Refer to "classify_EAPs_Main" to run the code. The major steps are as follows:
- Load the data (line 31); Example data can be downloaded here: https://www.dropbox.com/s/wmou14168j7xkh1/exampleData.mat?dl=0
- Filter the broadband signal to match the filters used in our in vivo recordings (an important step, if you use different filters you will obtain different EAP metrics) (line 35)
- Extract the spikes from the broadband signal and calculate the mean EAP features (lines 39-52)
- Classify the unit as NS or BS (line 53)
- If EKG heartbeat times are available, calculate motion-related changes in the EAP (lines 77-100)
- If EKG heartbeat times are availalbe and the unit is BS, classify this unit as BS1 or BS2.
The output of the code will be a figure that contains the cell type (NS, BS1, or BS2), average EAP features, and cardiac-motion EAP features. For example, the neuron below is classified as BS2, has a mean EAP amplitude of 87 microvolts, a half-width of 0.264 ms, a trough-to-peak width of 0.733 ms, and a repolarization time of 0.376 ms (see left panel). The four panels at right show how each of the features varies as a function of the cardiac cycle. For each feature we fit a circular linear regression model and calculate the modulation index (MI). We also report the coefficient of determination (R2) for the circular linear regression and the p-value for the slope coefficient in the regression. Data is in black traces, circular-linear fit is in red.
- Clayton Mosher
- Yina Wei
- Costas Anastassiou (Principal Investigator)
- Ueli Rutishauser (Principal Investigator)
Feel free to ask questions and/or join the development discussion. You can post bug reports and feature requests. You are welcome to use/modify the code/data in this repository as you wish -- if you do, please cite our paper:
- Mosher et al. (2020) "Cellular classes in the human brain revealed in vivo by heartbeat-related modulation of the extracellular action potential waveform" Cell Reports (in press).
Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health (R01MH110831to U.R.) and the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (U01NS103792, U01NS098961 to U.R.).
"CellClassifier" Copyright (c) 2020, Rutishauser Lab. All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
-
Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
-
Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
-
Neither the name of the copyright holder nor the names of its contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.