WhichKey is a lua plugin for Neovim 0.5 that displays a popup with possible keybindings of the command you started typing. Heavily inspired by the original emacs-which-key and vim-which-key.
- opens a poup with suggestions to complete a key binding
- works with any setting for timeoutlen, including instantly (
timeoutlen=0) - works correctly with builtin keybindings
- works correctly with buffer-local mappings
- extensible plugin architecture
- builtin plugins:
- marks: shows your marks when you hit one of the jump keys.
- registers: shows the contents of your registers
- presets: builtin keybinding help for
motions,text-objects,operators,windows,nav,zandg
- Neovim >= 0.5.0
Install the plugin with your preferred package manager:
" Vim Script
Plug 'folke/which-key.nvim'
lua << EOF
require("which-key").setup {
-- your configuration comes here
-- or leave it empty to use the default settings
-- refer to the configuration section below
}
EOF-- Lua
use {
"folke/which-key.nvim",
config = function()
require("which-key").setup {
-- your configuration comes here
-- or leave it empty to use the default settings
-- refer to the configuration section below
}
end
}❗️ IMPORTANT: the timeout when WhichKey opens is controlled by the vim setting timeoutlen. Please refer to the documentation to properly set it up. Setting it to
0, will effectively always show WhichKey immediately, but a setting of500(500ms) is probably more appropriate.❗️ don't create any keymappings yourself to trigger WhichKey. Unlike with vim-which-key, we do this fully automatically. Please remove any left-over triggers you might have from using vim-which-key.
🚑 You can run
:checkhealth which_keyto see if there's any conflicting keymaps that will prevent triggering WhichKey
WhichKey comes with the following defaults:
{
plugins = {
marks = true, -- shows a list of your marks on ' and `
registers = true, -- shows your registers on " in NORMAL or <C-r> in INSERT mode
-- the presets plugin, adds help for a bunch of default keybindings in Neovim
-- No actual key bindings are created
presets = {
operators = true, -- adds help for operators like d, y, ... and registers them for motion / text object completion
motions = true, -- adds help for motions
text_objects = true, -- help for text objects triggered after entering an operator
windows = true, -- default bindings on <c-w>
nav = true, -- misc bindings to work with windows
z = true, -- bindings for folds, spelling and others prefixed with z
g = true, -- bindings for prefixed with g
},
},
-- add operators that will trigger motion and text object completion
-- to enable all native operators, set the preset / operators plugin above
operators = { gc = "Comments" },
icons = {
breadcrumb = "»", -- symbol used in the command line area that shows your active key combo
separator = "➜", -- symbol used between a key and it's label
group = "+", -- symbol prepended to a group
},
window = {
border = "none", -- none, single, double, shadow
position = "bottom", -- bottom, top
margin = { 1, 0, 1, 0 }, -- extra window margin [top, right, bottom, left]
padding = { 2, 2, 2, 2 }, -- extra window padding [top, right, bottom, left]
},
layout = {
height = { min = 4, max = 25 }, -- min and max height of the columns
width = { min = 20, max = 50 }, -- min and max width of the columns
spacing = 3, -- spacing between columns
},
ignore_missing = false, -- enable this to hide mappings for which you didn't specify a label
hidden = { "<silent>", "<cmd>", "<Cmd>", "<CR>", "call", "lua", "^:", "^ "}, -- hide mapping boilerplate
show_help = true, -- show help message on the command line when the popup is visible
triggers = "auto", -- automatically setup triggers
-- triggers = {"<leader>"} -- or specifiy a list manually
}With the default settings, WhichKey will work out of the box for most builtin keybindings, but the real power comes from documenting and organizing your own keybindings.
To document and/or setup your own mappings, you need to call the register method
local wk = require("which-key")
wk.register(mappings, opts)Default options for opts
{
mode = "n", -- NORMAL mode
-- prefix: use "<leader>f" for example for mapping everything related to finding files
-- the prefix is prepended to every mapping part of `mappings`
prefix = "",
buffer = nil, -- Global mappings. Specify a buffer number for buffer local mappings
silent = true, -- use `silent` when creating keymaps
noremap = true, -- use `noremap` when creating keymaps
nowait = false, -- use `nowait` when creating keymaps
}❕ When you specify a command in your mapping that starts with
<Plug>, then we automatically setnoremap=false, since you always wanty recursive keybindings in this case
Group names use the special name key in the tables. There's multiple ways to define the mappings. wk.register can be called multiple times from anywhere in your config files.
local wk = require("which-key")
-- As an example, we will the following mappings:
-- 1. <leader>fn new file
-- 2. <leader>fr show recent files
-- 2. <leader>ff find files
wk.register({
f = {
name = "file", -- optional group name
f = { "<cmd>Telescope find_files<cr>", "Find File" }, -- create a binding with label
r = { "<cmd>Telescope oldfiles<cr>", "Open Recent File", noremap=false, buffer = 123 }, -- additional options for creating the keymap
n = { "New File" }, -- just a label. don't create any mapping
e = "Edit File", -- same as above
["1"] = "which_key_ignore", -- special label to hide it in the popup
b = { function() print("bar") end, "Foobar" } -- you can also pass functions!
},
}, { prefix = "<leader>" })Click to see more examples
-- all of the mappings below are equivalent
-- method 2
wk.register({
["<leader>"] = {
f = {
name = "+file",
f = { "<cmd>Telescope find_files<cr>", "Find File" },
r = { "<cmd>Telescope oldfiles<cr>", "Open Recent File" },
n = { "<cmd>enew<cr>", "New File" },
},
},
})
-- method 3
wk.register({
["<leader>f"] = {
name = "+file",
f = { "<cmd>Telescope find_files<cr>", "Find File" },
r = { "<cmd>Telescope oldfiles<cr>", "Open Recent File" },
n = { "<cmd>enew<cr>", "New File" },
},
})
-- method 4
wk.register({
["<leader>f"] = { name = "+file" },
["<leader>ff"] = { "<cmd>Telescope find_files<cr>", "Find File" },
["<leader>fr"] = { "<cmd>Telescope oldfiles<cr>", "Open Recent File" },
["<leader>fn"] = { "<cmd>enew<cr>", "New File" },
})WhichKey provides help to work with operators, motions and text objects.
[count]operator[count][text-object]
- operators can be configured with the
operatorsoption- set
plugins.presets.operatorstotrueto automatically configure vim builtin operators - set this to
false, to only include the list you configured in theoperatorsoption. - see here for the full list part of the preset
- set
- text objects are automatically retrieved from operator pending keymaps (
omap)- set
plugins.presets.text_objectstotrueto configure builtin text objects - see here
- set
- motions are part of the preset
plugins.presets.motionssetting- see here
How to disable some operators? (like v)
{
plugins = {
-- ...
presets = {
operators = false
-- ..
},
},
-- add operators that will trigger motion and text object completion
-- to enable all native operators, set the preset / operators plugin above
operators = {
d = "Delete",
c = "Change",
y = "Yank (copy)",
["g~"] = "Toggle case",
["gu"] = "Lowercase",
["gU"] = "Uppercase",
[">"] = "Indent right",
["<lt>"] = "Indent left",
["zf"] = "Create fold",
["!"] = "Filter though external program",
-- ["v"] = "Visual Character Mode",
gc = "Comments"
},
}When the WhichKey popup is open, you can use the following keybindings (they are also displayed at the bottom of the screen):
- hit one of the keys to open a group or execute a key binding
<esc>to cancel and close the popup<bs>go up one level<c-d>scroll down<c-u>scroll up
Apart from the automatic opening, you can also manually open WhichKey for a certain prefix:
❗️ don't create any keymappings yourself to trigger WhichKey. Unlike with vim-which-key, we do this fully automatically. Please remove any left-over triggers you might have from using vim-which-key.
:WhichKey " show all mappings
:WhichKey <leader> " show all <leader> mappings
:WhichKey <leader> v " show all <leader> mappings for VISUAL mode
:WhichKey '' v " show ALL mappings for VISUAL modeThree builtin plugins are included with WhichKey.
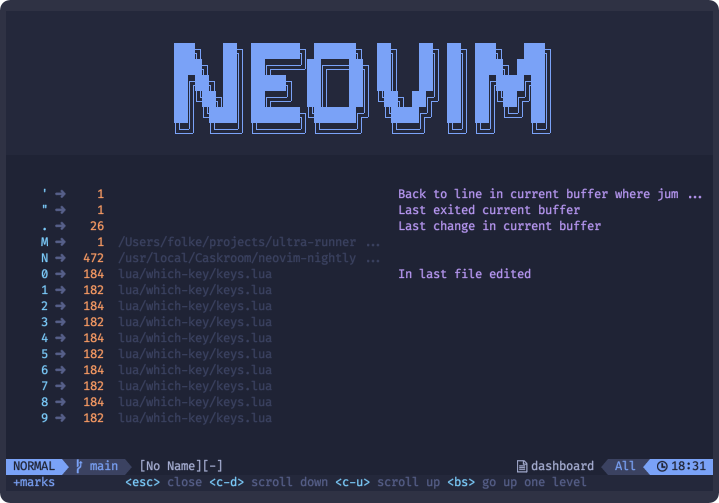
Shows a list of your buffer local and global marks when you hit ` or '
Shows a list of your buffer local and global registers when you hit " in NORMAL mode, or <c-r> in INSERT mode.
Builtin keybinding help for motions, text-objects, operators, windows, nav, z and g
The table below shows all the highlight groups defined for LSP Trouble with their default link.
| Highlight Group | Defaults to | Description |
|---|---|---|
| WhichKey | Function | the key |
| WhichKeyGroup | Keyword | a group |
| WhichKeySeparator | DiffAdded | the separator between the key and its label |
| WhichKeyDesc | Identifier | the label of the key |
| WhichKeyFloat | NormalFloat | Normal in the popup window |
| WhichKeyValue | Comment | used by plugins that provide values |