This guide will cover the setup and use of Vention’s MachineMotion™ Python Software Development Kit (SDK). After reading this guide, you will be ready to deploy custom motion and control applications using Vention’s MachineMotion controller. Before you begin, we recommended reading the MachineMotion Quick Start Guide to get familiar with the technology.
The MachineMotion python SDK has been designed to allow user applications to execute:
- internally to MachineMotion; or
- on an external computer connected to MachineMotion via the Ethernet or DEFAULT Ethernet port.
The Python SDK includes the following core features:
- Simplified interface to all MachineMotion functionality
- Control of one or multiple MachineMotion from a single program
- Direct access to the internal motion controller via gCode
Figure 1: Structure of a Python program
The Python API V2 requires MachineMotion version V1.12 or newer.
Please use mm-python-api V1.6.7 for prior version of MachineMotion software.
Many systems are built by centralizing application-level software on a host computer. The software interacts with various devices (such as robotic devices, sensors, proprietary products, and data acquisition equipment) and delivers the required application behavior (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: Typical system configuration
Using MachineMotion with Python is ideal for these types of applications, especially where an easy to deploy motion control system is necessary.
To set up the MachineMotion Python library:
-
Download the latest Python SDK
-
Unzip the content on your computer. This location will be your workspace.
-
Install Python 2.7.13
++Note for Windows users++: Make sure to add Python.exe to the PATH environment variable as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Make sure to select "Add python.exe to path" if installing on Windows.
-
Open the command prompt (for Windows) or the terminal (for Mac or Linux users) and run the following installations
pip install -U socketIO-clientpip install -U pathlibpip install -U paho-mqtt -
The MachineMotion Python library is now ready to use. Programs can be created and ran from the workspace folder.
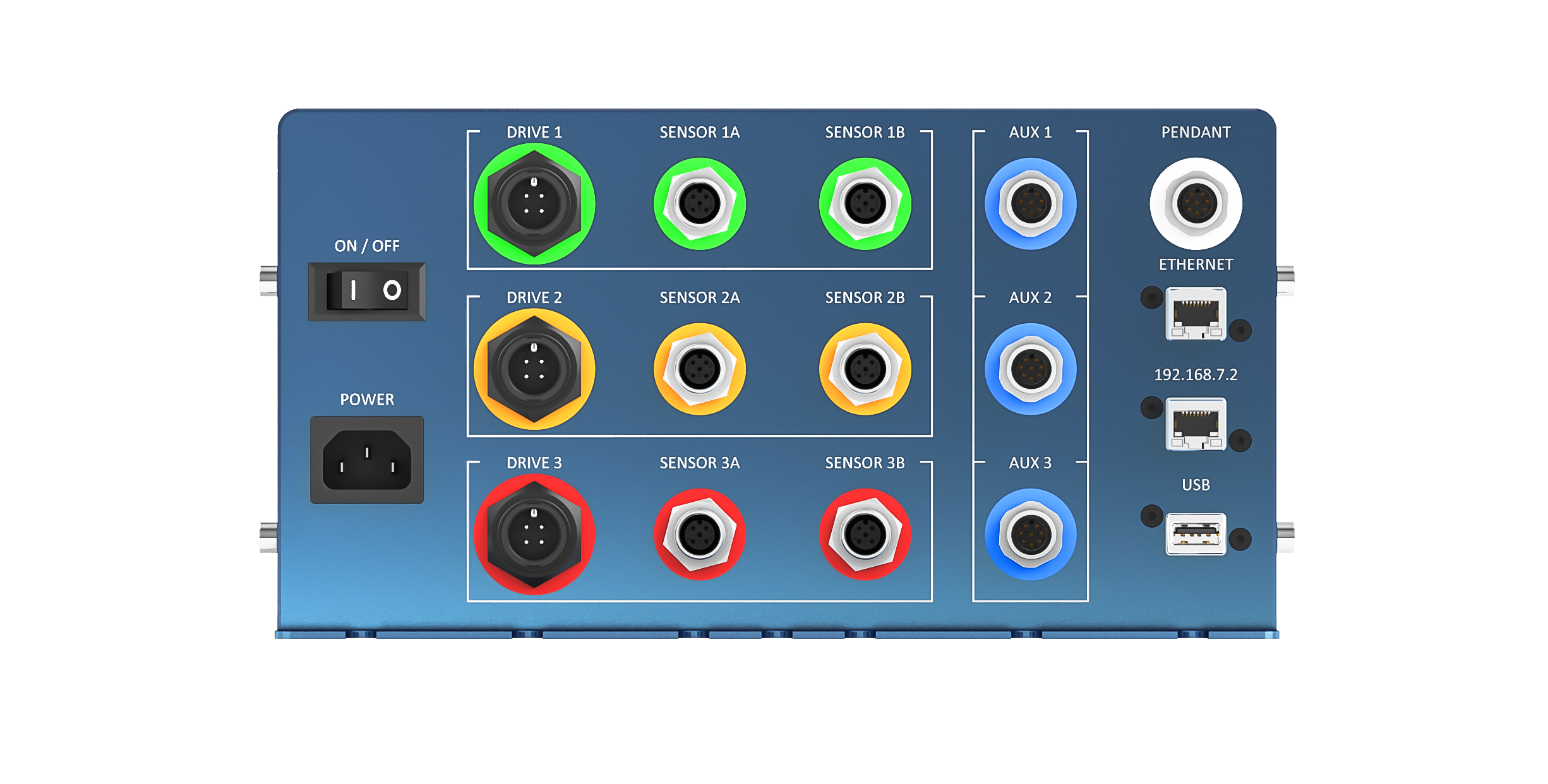
MachineMotion has two communication ports, one labeled 192.168.7.2 and one labeled ETHERNET. Both use IP connectivity and have their own unique IP addresses, (see Figure 3).
Figure 3: MachineMotion front panel.
The IP address associated with the Default Ethernet port is static (192.168.7.2 for Windows; 192.168.7.2 for Mac and Linux). It cannot be configured or modified.
In order to better suit your network requirements, the IP address associated with the ETHERNET port can be either configured as DHCP or as static. Refer to the How-to Guide: MachineMotion Network Setup for more details.
When creating a Python program to control the MachineMotion controller, the first step is always to create a MachineMotion instance. This will establish communication with the actual controller and expose different functions that can be used to send commands.
After creating the MachineMotion instance, you must configure the network and axis. The functions to perform these steps are covered in this section.
Creates a MachineMotion instance and establishes the TCP/IP communication. This function is a constructor.
Handle in which incoming messages from the controller can be processed. The data are passed to the callback as a string argument.
IP address of the MachineMotion controller.
Instance created by the constructor.
from _MachineMotion import *
# Define a callback to process controller gCode responses
def templateCallback(data):
print ( "Controller gCode responses " + data )
machine_motion_example = MachineMotion(templateCallback, DEFAULT_IP_ADDRESS.usb_windows)
print ( "Controller connected" )Controller gCode responses MachineMotion Session Start
Controller gCode responses echo:N0 M110 N0*125
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N1 M111 S247*97
Controller gCode responses echo:DEBUG:ECHO,INFO,ERRORS,COMMUNICATION
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller connected
Configures the IP address of the controller Ethernet interface.
IP configures the network management profile as either static or DHCP. Valid arguments are: NETWORK_MODE.static NETWORK_MODE.dhcp
Desired static IP address to assign to the MachineMotion controller. Format is "nnn.nnn.nnn.nnnn", where n are numbers.
Network netmask. Format is "nnn.nnn.nnn.nnnn", where n are numbers.
IP address of the network gateway. Format is "nnn.nnn.nnn.nnnn", where n are numbers.
none
from _MachineMotion import *
# Define a callback to process controller gCode responses (if desired)
def templateCallback(data):
print ( "Controller gCode responses " + data )
machine_motion_example = MachineMotion(templateCallback, DEFAULT_IP_ADDRESS.usb_windows)
machine_motion_example = machine_motion_example.configMachineMotionIp(NETWORK_MODE.static, "192.168.0.2", "255.255.255.0", "192.168.0.1")
print ( "--> Controller connected & ethernet interface configured (static)" )Controller gCode responses MachineMotion Session Start
Controller gCode responses echo:N0 M110 N0*125
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N1 M111 S247*97
Controller gCode responses echo:DEBUG:ECHO,INFO,ERRORS,COMMUNICATION
Controller gCode responses ok
--> Controller connected & ethernet interface configured (static)
from _MachineMotion import *
# Define a callback to process controller gCode responses (if desired)
def templateCallback(data):
print ( "Controller gCode responses " + data )
machine_motion_example = MachineMotion(templateCallback, DEFAULT_IP_ADDRESS.usb_windows)
machine_motion_example = machine_motion_example.configMachineMotionIp(NETWORK_MODE.dhcp, "", "", "")
print ( "--> Controller connected & ethernet interface configured (dhcp)" )Controller gCode responses MachineMotion Session Start
Controller gCode responses echo:N0 M110 N0*125
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N1 M111 S247*97
Controller gCode responses echo:DEBUG:ECHO,INFO,ERRORS,COMMUNICATION
Controller gCode responses ok
--> Controller connected & ethernet interface configured (dhcp)
Configure the axis' mechanical gain and micro-step settings to ensure accurate motion.
Axis to configure
Micro-step setting
Mechanical gain of the axis in mm per turn.
None.
from _MachineMotion import *
# Define a callback to process controller gCode responses (if desired)
def templateCallback(data):
print ( "Controller gCode responses " + data )
machine_motion_example = MachineMotion(templateCallback, DEFAULT_IP_ADDRESS.usb_windows)
# Configure the axis number one, 8 uSteps and 150 mm / turn for a timing belt
machine_motion_example = machine_motion_example.configAxis(1, MICRO_STEPS.ustep_8, MECH_GAIN.timing_belt_150mm_turn)
print ( "--> Controller axis 1 configured" )Controller gCode responses MachineMotion Session Start
Controller gCode responses echo:N0 M110 N0*125
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N1 M111 S247*97
Controller gCode responses echo:DEBUG:ECHO,INFO,ERRORS,COMMUNICATION
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N2 M92 X10*99
Controller gCode responses ok
--> Controller axis 1 configured
Save a key-value pair on the controller.
Key to identify the data.
Dictionary containing the data to save.
None.
from _MachineMotion import *
# Define a callback to process controller gCode responses (if desired)
def templateCallback(data):
print ( "Controller gCode responses " + data )
machine_motion_example = MachineMotion(templateCallback, DEFAULT_IP_ADDRESS.usb_windows)
# Saving a string on the controller
machine_motion_example = machine_motion_example.saveData("data_1", "save_this_string_on_the_controller")
print ( "--> Data sent on controller" )Retrieve a key-value pair that was saved on the controller.
key is a string that identifies the data to retrieve.
Function to invoke once the data is available. The data will be passed to the callback as an argument—specifically, as a serialized JSON string.
from _MachineMotion import *
# Define a callback to process controller gCode responses (if desired)
def templateCallback(data):
print ( "Controller gCode responses " + data )
# Define a callback to print the data retrieved using the getData function
def printGetDataResult(data):
print ( "--> Retrieved data = " + data )
machine_motion_example = MachineMotion(templateCallback, DEFAULT_IP_ADDRESS.usb_windows)
# Saving a string on the controller
machine_motion_example.saveData("data_1", "save_this_string_on_the_controller")
machine_motion_example.getData("data_1", printGetDataResult)Controller gCode responses MachineMotion Session Start
Controller gCode responses echo:N0 M110 N0*125
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N1 M111 S247*97
Controller gCode responses echo:DEBUG:ECHO,INFO,ERRORS,COMMUNICATION
Controller gCode responses ok
--> Retrieved data = {"data": "save_this_string_on_the_controller", "fileName": "data_1"}
Blocking function that waits for the MachineMotion controller to ackowledge the command before continuing code execution. This is a code flow control function.
None.
from _MachineMotion import *
# Define a callback to process controller gCode responses (if desired)
def templateCallback(data):
print ( "Controller gCode responses " + data )
machine_motion_example = MachineMotion(templateCallback, DEFAULT_IP_ADDRESS.usb_windows)
# Homing axis 1
machine_motion_example.emitHome(1)
# Wait for the message to be acknowledged by the motion controller
while machine_motion_example.isReady() != "true": pass
print ( "--> This line executes after the motion controller has acknowledged receipt of the command." )Controller gCode responses MachineMotion Session Start
Controller gCode responses echo:N0 M110 N0*125
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N1 M111 S247*97
Controller gCode responses echo:DEBUG:ECHO,INFO,ERRORS,COMMUNICATION
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N2 G28 X*105
Controller gCode responses X:0.00 Y:0.00 Z:0.00 E:0.00 Count X: 0 Y:0 Z:0
Controller gCode responses ok
--> This line executes after the motion controller has acknowledged the reception of the command.
Blocking function that prevents program execution until the last motion has been completed. Until the machine has not finished its final movement, the code will not be executed.
None.
from _MachineMotion import *
# Define a callback to process controller gCode responses (if desired)
def templateCallback(data):
print ( "Controller gCode responses " + data )
machine_motion_example = MachineMotion(templateCallback, DEFAULT_IP_ADDRESS.usb_windows)
# Homing axis 1
machine_motion_example.emitHome(1)
# Wait for the message to be acknowledged by the motion controller
while machine_motion_example.isReady() != "true": pass
machine_motion_example.waitForMotionCompletion()
print ( "--> This line executes after the motion controller has acknowledged the reception of the command." )Controller gCode responses MachineMotion Session Start
Controller gCode responses echo:N0 M110 N0*125
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N1 M111 S247*97
Controller gCode responses echo:DEBUG:ECHO,INFO,ERRORS,COMMUNICATION
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N2 G28 X*105
Controller gCode responses X:0.00 Y:0.00 Z:0.00 E:0.00 Count X: 0 Y:0 Z:0
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N3 V0*59
A motion status was requested
move is in progress
Controller gCode responses Motion Status = COMPLETED
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N4 V0*60
A motion status was requested
Move was completed
Controller gCode responses Motion Status = COMPLETED
--> This line executes after the motion controller has acknowledged receipt of the command.
Controller gCode responses ok
Immediately stops motion on all axes.
none
from _MachineMotion import *
# Define a callback to process controller gCode responses (if desired)
def templateCallback(data):
print ( "Controller gCode responses " + data )
machine_motion_example = MachineMotion(templateCallback, DEFAULT_IP_ADDRESS.usb_windows)
# Send a stop command to the machine (this works even if the machine has not started moving yet)
machine_motion_example.emitStop()
print ( "--> Machine Stopped" )Controller gCode responses MachineMotion Session Start
Controller gCode responses echo:N0 M110 N0*125
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N1 M111 S247*97
Controller gCode responses echo:DEBUG:ECHO,INFO,ERRORS,COMMUNICATION
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N2 M410*36
Controller gCode responses ok
--> Machine Stopped
Moves all carriages to their home location sequentially, axis 1 to axis 3.
none
from _MachineMotion import *
# Define a callback to process controller gCode responses (if desired)
def templateCallback(data):
print ( "Controller gCode responses " + data )
machine_motion_example = MachineMotion(templateCallback, DEFAULT_IP_ADDRESS.usb_windows)
# Homing all the axes of the controller sequentially
machine_motion_example.emitHomeAll()
machine_motion_example.waitForMotionCompletion()
print ( "--> All axes are now at home position." )Moves the carriage of the corresponding axis to its home location.
Axis to move to home location
none
from _MachineMotion import *
# Define a callback to process controller gCode responses (if desired)
def templateCallback(data):
print ( "Controller gCode responses " + data )
machine_motion_example = MachineMotion(templateCallback, DEFAULT_IP_ADDRESS.usb_windows)
# Homing axis 1
machine_motion_example.emitHome(1)
machine_motion_example.waitForMotionCompletion()
print ( "--> Axis 1 is now at home position." )Controller gCode responses MachineMotion Session Start
Controller gCode responses echo:N0 M110 N0*125
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N1 M111 S247*97
Controller gCode responses echo:DEBUG:ECHO,INFO,ERRORS,COMMUNICATION
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N2 G28 X*105
Controller gCode responses X:0.00 Y:0.00 Z:0.00 E:0.00 Count X: 0 Y:0 Z:0
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N3 V0*59
A motion status was requested
Movement is in progress
Controller gCode responses Motion Status = COMPLETED
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N4 V0*60
A motion status was requested
Move was completed
Controller gCode responses Motion Status = COMPLETED
--> Axis 1 is now at home position.
Controller gCode responses ok
Configures the travel speed. Travel speed applies to combined axis moves and single axis moves.
Motion speed in mm per minute
none
from _MachineMotion import *
# Define a callback to process controller gCode responses (if desired)
def templateCallback(data):
print ( "Controller gCode responses " + data )
machine_motion_example = MachineMotion(templateCallback, DEFAULT_IP_ADDRESS.usb_windows)
# Configuring the travel speed to 10,000 mm / min
machine_motion_example.emitSpeed(10000)
print ( "--> Machine moves are not set to 10 000 mm / min" )Configures travel acceleration. Travel acceleration applies to combined axis moves and single axis moves.
Motion speed in mm per minute
none
from _MachineMotion import *
# Define a callback to process controller gCode responses (if desired)
def templateCallback(data):
print ( "Controller gCode responses " + data )
machine_motion_example = MachineMotion(templateCallback, DEFAULT_IP_ADDRESS.usb_windows)
# Configuring the travel speed to 1000 mm / second^2
machine_motion_example.emitAcceleration(1000)
print ( "--> Machine moves are not set to accelerate @ 1000 mm / second^2" )Controller gCode responses MachineMotion Session Start
Controller gCode responses echo:N0 M110 N0*125
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N1 M111 S247*97
Controller gCode responses echo:DEBUG:ECHO,INFO,ERRORS,COMMUNICATION
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N2 M204 T1000*82
Controller gCode responses Setting Travel Acceleration: 1000.00
Controller gCode responses ok
--> Machine moves are not set to accelerate @ 1000 mm / second^2
Configures the travel acceleration. Travel acceleration applies to combined axis moves and single axis moves.
Axis to move to home location
Position of the carriage
none
from _MachineMotion import *
# Define a callback to process controller gCode responses (if desired)
def templateCallback(data):
print "Controller gCode responses " + data
machine_motion_example = MachineMotion(templateCallback, DEFAULT_IP_ADDRESS.usb_windows)
# Configuring the travel speed to 10 000 mm / min
machine_motion_example.emitSpeed(10000)
# Configuring the travel speed to 1000 mm / second^2
machine_motion_example.emitAcceleration(1000)
# Homing axis 1
machine_motion_example.emitHome(1)
machine_motion_example.waitForMotionCompletion()
# Move axis 1 to position "100 mm"
machine_motion_example.emitAbsoluteMove(1, 100)
machine_motion_example.waitForMotionCompletion()
print ( "--> Example completed." )Controller gCode responses MachineMotion Session Start
Controller gCode responses echo:N0 M110 N0*125
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N1 M111 S247*97
Controller gCode responses echo:DEBUG:ECHO,INFO,ERRORS,COMMUNICATION
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N2 G0 F10000*124
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N3 M204 T1000*83
Controller gCode responses Setting Travel Acceleration: 1000.00
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N4 G28 X*111
Controller gCode responses echo:busy:processing
Controller gCode responses X:0.00 Y:0.00 Z:0.00 E:0.00 Count X: 0 Y:0 Z:0
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N5 G90*21
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N6 G0 X100*102
Controller gCode responses ok
--> Example completed.
Moves the gantry to a position relative to its current location.
Axis to be moved
Motion direction
Distance to move in mm
none
from _MachineMotion import *
# Define a callback to process controller gCode responses (if desired)
def templateCallback(data):
print ( "Controller gCode responses " + data )
machine_motion_example = MachineMotion(templateCallback, DEFAULT_IP_ADDRESS.usb_windows)
# Configuring the travel speed to 10 000 mm / min
machine_motion_example.emitSpeed(10000)
# Configuring the travel speed to 1000 mm / second^2
machine_motion_example.emitAcceleration(1000)
# Homing axis 1
machine_motion_example.emitHome(1)
# Move axis 1 to position 100 mm
machine_motion_example.emitAbsoluteMove(1, 100)
machine_motion_example.waitForMotionCompletion()
# Move axis 1 by an increment of negative 100 mm
machine_motion_example.emitRelativeMove(1, "negative", 100)
machine_motion_example.waitForMotionCompletion()
print ( "--> Example completed." )Controller gCode responses MachineMotion Session Start
Controller gCode responses echo:N0 M110 N0*125
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N1 M111 S247*97
Controller gCode responses echo:DEBUG:ECHO,INFO,ERRORS,COMMUNICATION
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N2 G0 F10000*124
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N3 M204 T1000*83
Controller gCode responses Setting Travel Acceleration: 1000.00
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N4 G28 X*111
Controller gCode responses X:0.00 Y:0.00 Z:0.00 E:0.00 Count X: 0 Y:0 Z:0
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N5 G90*21
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N6 G0 X100*102
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N7 G91*22
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N8 G0 X-100*69
--> Example completed.
Controller gCode responses ok
Sends a direct G-Code string command. See the G-Code Commands section for more details.
G-Code command to send to controller
none
from _MachineMotion import *
# Define a callback to process controller gCode responses (if desired)
def templateCallback(data):
print ( "Controller gCode responses " + data )
machine_motion_example = MachineMotion(templateCallback, DEFAULT_IP_ADDRESS.usb_windows)
# Configuring travel speed to 10 000 mm / min
machine_motion_example.emitSpeed(10000)
# Configuring travel speed to 1000 mm / second^2
machine_motion_example.emitAcceleration(1000)
# Homing axis 1
machine_motion_example.emitHome(1)
machine_motion_example.waitForMotionCompletion()
# Use the G0 command to move both axis 1 and two by 500mm at a travel speed of 10 000 mm / minute
machine_motion_example.emitgCode("G0 X500 Y500 F10000")
machine_motion_example.waitForMotionCompletion()
print ( "--> Example completed." )Controller gCode responses MachineMotion Session Start
Controller gCode responses echo:N0 M110 N0*125
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N1 M111 S247*97
Controller gCode responses echo:DEBUG:ECHO,INFO,ERRORS,COMMUNICATION
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N2 G0 F10000*124
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N3 M204 T1000*83
Controller gCode responses Setting Travel Acceleration: 1000.00
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N4 G28 X*111
Controller gCode responses echo:busy: processing
Controller gCode responses X:0.00 Y:3000.00 Z:0.00 E:0.00 Count X: 0 Y:24000 Z:0
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N5 V0*61
Controller gCode responses Motion Status = COMPLETED
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N6 V0*62
Controller gCode responses Motion Status = COMPLETED
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N7 G0 X50 Y50 F10000*120
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N8 V0*48
Controller gCode responses Motion Status = IN_PROGRESS
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N9 V0*49
Controller gCode responses Motion Status = IN_PROGRESS
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N10 V0*9
Controller gCode responses Motion Status = IN_PROGRESS
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N11 V0*8
Controller gCode responses Motion Status = IN_PROGRESS
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N12 V0*11
Controller gCode responses Motion Status = IN_PROGRESS
Controller gCode responses ok
Controller gCode responses echo:N13 V0*10
Controller gCode responses Motion Status = COMPLETED
--> Example completed.
Controller gCode responses ok
Functions that exchange data with the MachineMotion controller (no movement involved).
IMPORTANT: The following interfaces:
- attachControlDevice(port, device, callback)
- detachControlDevice(port, callback)
- readControlDevice(port, signal, callback)
- writeControlDevice(port, signal, callback)
have been obsoleted and replaced with:
- isIoExpanderAvailable( device )
- digitalRead( device, pin )
- digitalWrite( device, pin )
- readEncoderRealtimePosition( device )
Determines if the io-expander with the given id is available
@param device - The io-expander device identifier
@return - True if the io-expander exists; False otherwise
from _MachineMotion import *
def templateCallback(data):
print ( "Controller gCode responses " + data )
machine_motion_example = MachineMotion(templateCallback, DEFAULT_IP_ADDRESS.usb_windows)
io_expander_id = 1
if ( machine_motion_example.isIoExpanderAvailable( io_expander_id ) ):
machine_motion_example.digitalWrite(io_expander_id, 1, 0 )Read the digital input from the given pin in put on the IO Expander
@param device - The IO expander device identifier (1-3)
@param pin. - The pin index to read from (0-3)
@return. - The level at the IO expander pin
from _MachineMotion import *
def templateCallback(data):
print ( "Controller gCode responses " + data )
machine_motion_example = MachineMotion(templateCallback, DEFAULT_IP_ADDRESS.usb_windows)
io_expander_id = 1
input_pin = 0
pinValue = machine_motion_example.digitalRead( io_expander_id , input_pin )Modify the digital output of the given pin a the specified device.
@param device - The IO expander device identifier (1-3)
@param pin. - The pin index to write to (0-3)
@param value - The pin value to be written
from _MachineMotion import *
def templateCallback(data):
print ( "Controller gCode responses " + data )
machine_motion_example = MachineMotion(templateCallback, DEFAULT_IP_ADDRESS.usb_windows)
io_expander_id = 1
input_pin = 0
machine_motion_example.digitalWrite( io_expander_id , input_pin, 0 )Returns the realtime position of the given encoder.
@param encoder - The identifier of the encoder (0-2)
@return - The relatime encoder position (deled by up to 250ms)
NOTE: The encoder position return may be offset by up to 250ms caused by internal propagation delays
from _MachineMotion import *
def templateCallback(data):
print ( "Controller gCode responses " + data )
machine_motion_example = MachineMotion(templateCallback, DEFAULT_IP_ADDRESS.usb_windows)
encoder_id = 1
encoder_1_position = machine_motion_example.readEncoderRealtimePosition( encoder_id )-
Open the command prompt (for Windows) or terminal (for Mac and Linux).
-
Browse to the directory where you program is saved.
-
Execute your program.
python yourProgram.py
-
The console or terminal will display various status messages while the program runs.
-
To stop the execution of the program, press CRTL + c
G-Code is a text based protocol that controls the motion of multi axis machines. The API presented in the previous section employs it to communicate motion-related commands to the MachineMotion controller
More advanced users might wish to use commands that are available via the G-Code protocol. The emitgCode (gCode) function presented in Table 6 can be used.
The MachineMotion Python Library Package contains a list of G-Code commands available for advanced users. You can also download it here: G-Code Reference Functions.
Below, we've listed some handy G-Code commands that can be utilized via the emitgCode function.
| G-Code Function ID | Description |
|---|---|
| M201 | Set Max Acceleration |
| M203 | Set Max Feedrate |
| M204 | Set Acceleration |
| G0 & G1 | Set Feedrate (Travel Speed) |
Table 1: G-Code Configuration Functions
| G-Code Function ID | Description |
|---|---|
| G90 | Set Absolute Motion |
| G91 | Set Relative Motion |
| G0 | Linear Move |
| G28 | Home |
Table 2: G-Code Control Functions
| G-Code Function ID | Description |
|---|---|
| M114 | Get Current Position |
| M119 | GEt EndStop States |
Table 3: G-Code Communication Functions
Note on Axis Mapping
Note that when using direct G-Code commands, the axis name mapping in Table 4 applies.
| G-Code Axis Name | MachineMotion Axis Name |
|---|---|
| X | 1 |
| Y | 2 |
| z | 3 |
Table 4: G-Code to MachineMotion Axis Mapping.