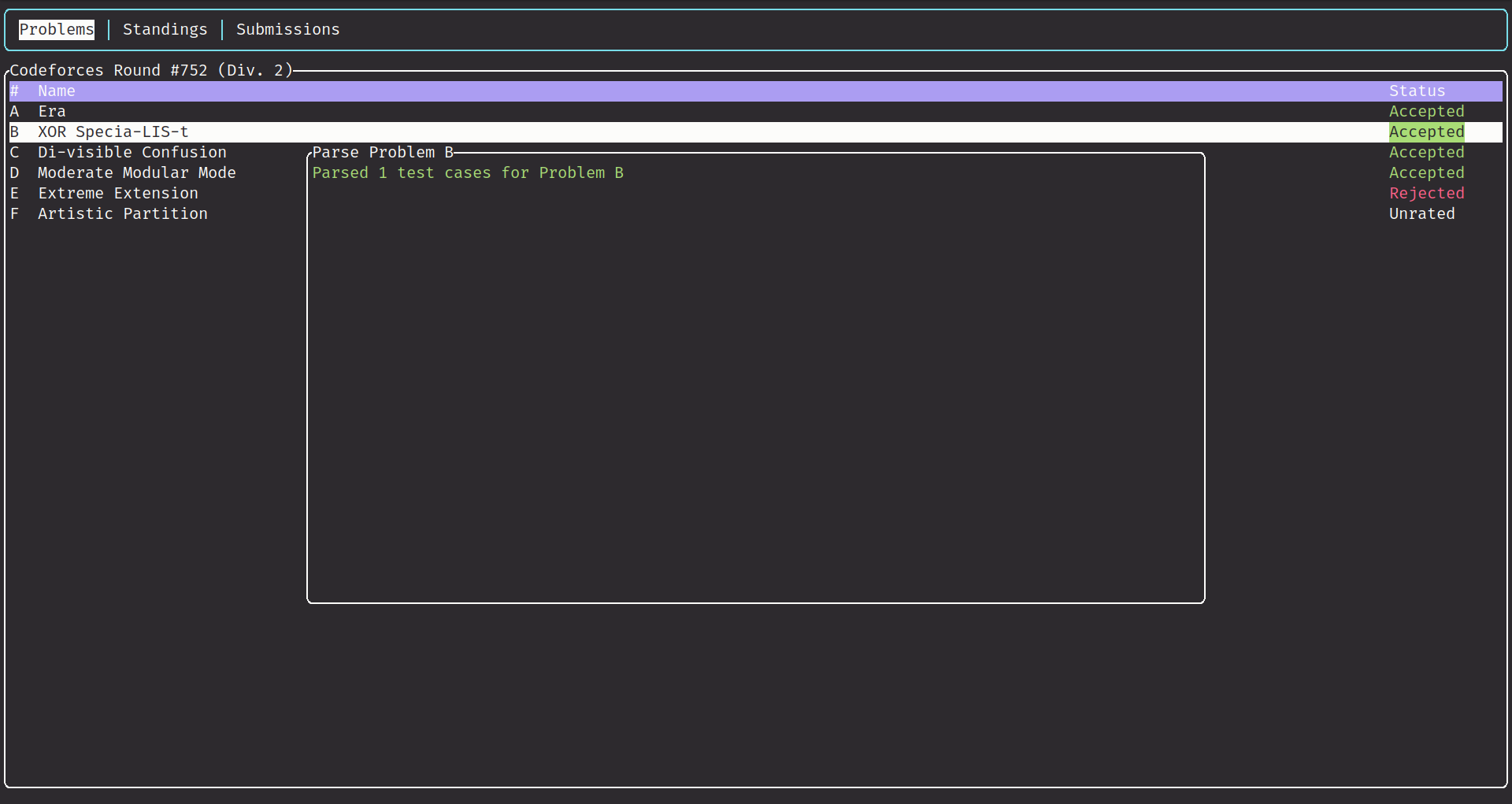
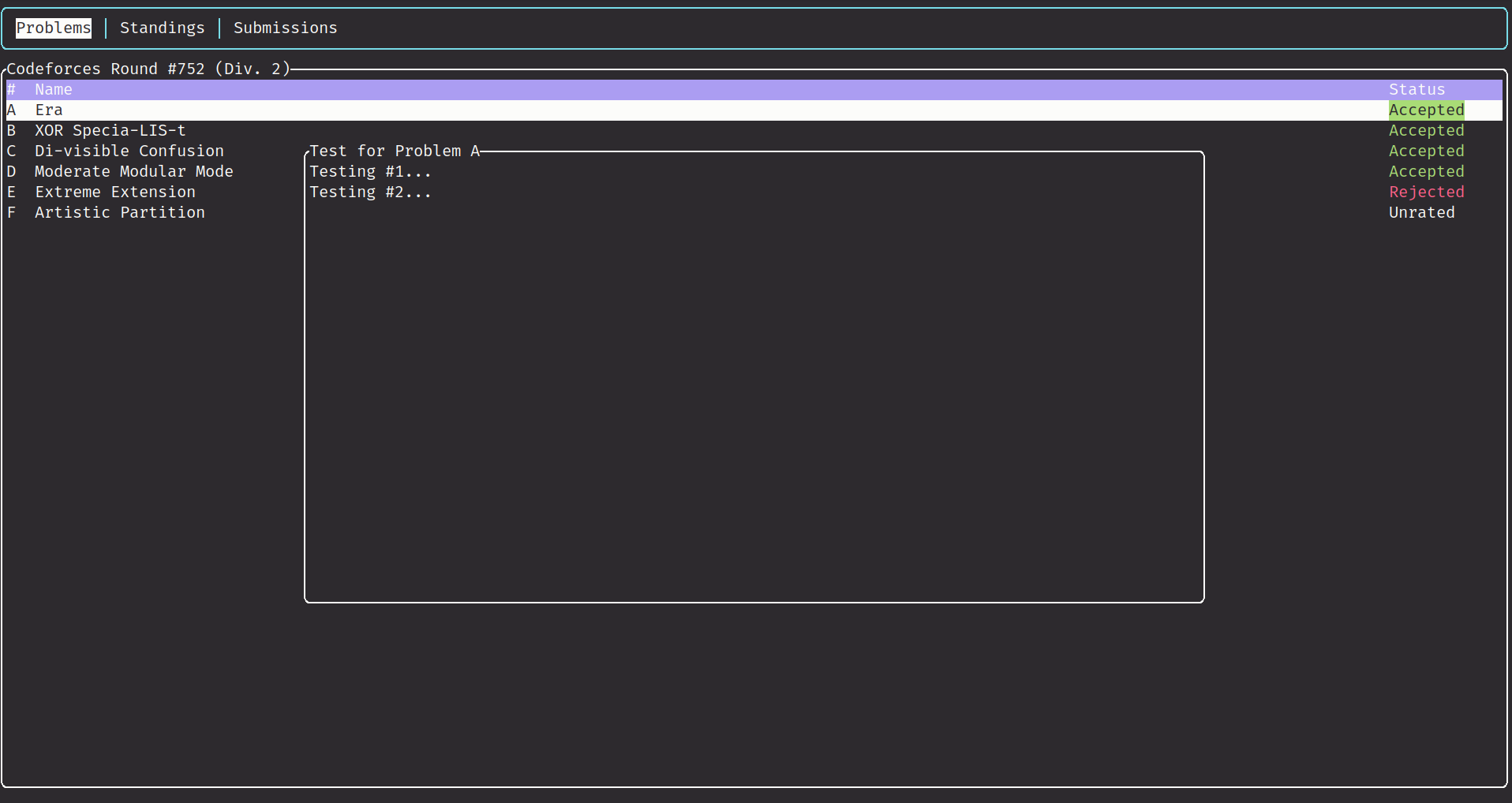
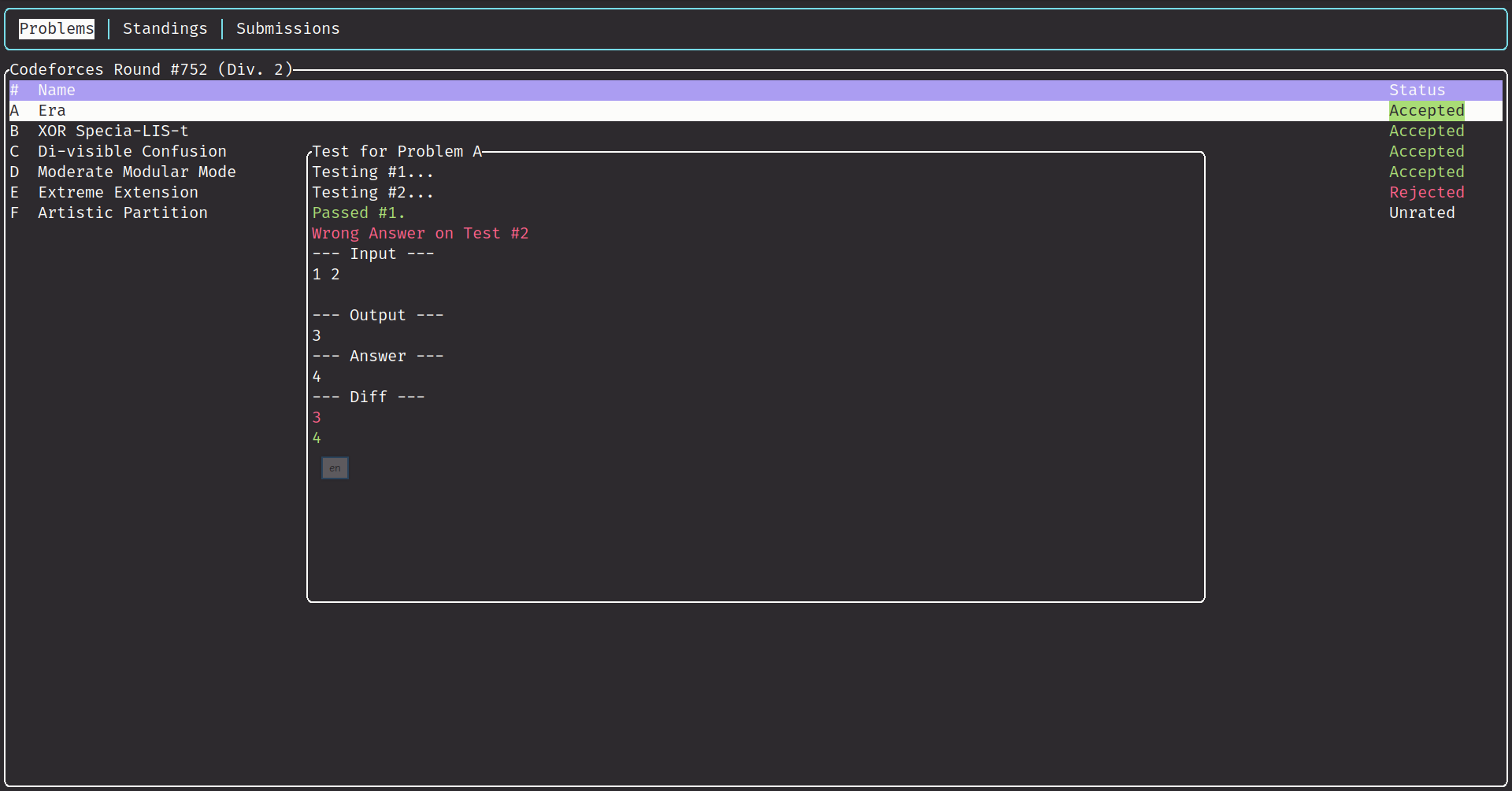
This project is inspired by cf-tool, which has deprecated since change in CodeForces API.
Code Forces tool is a terminal user interface tool for CodeForces.
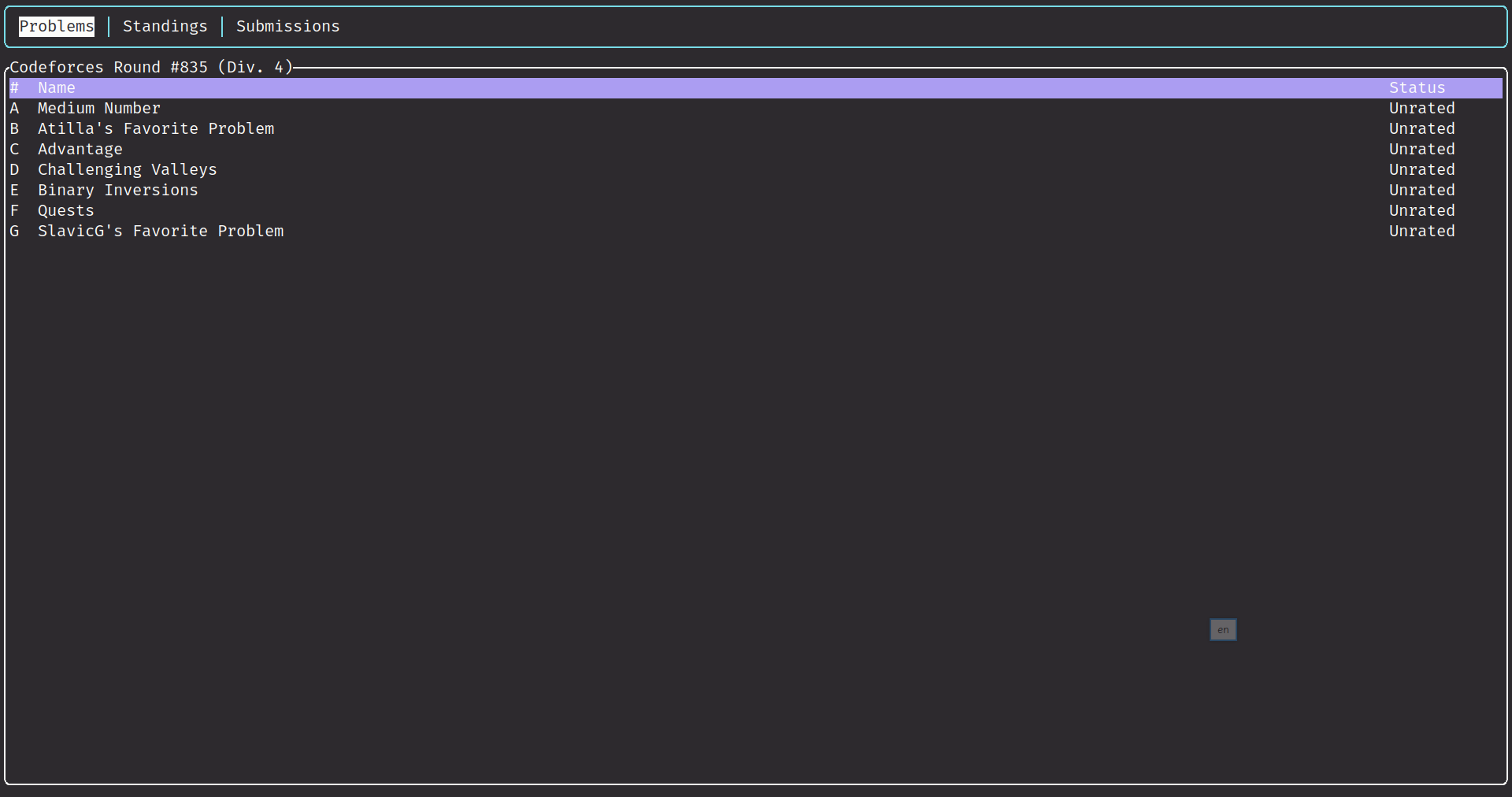
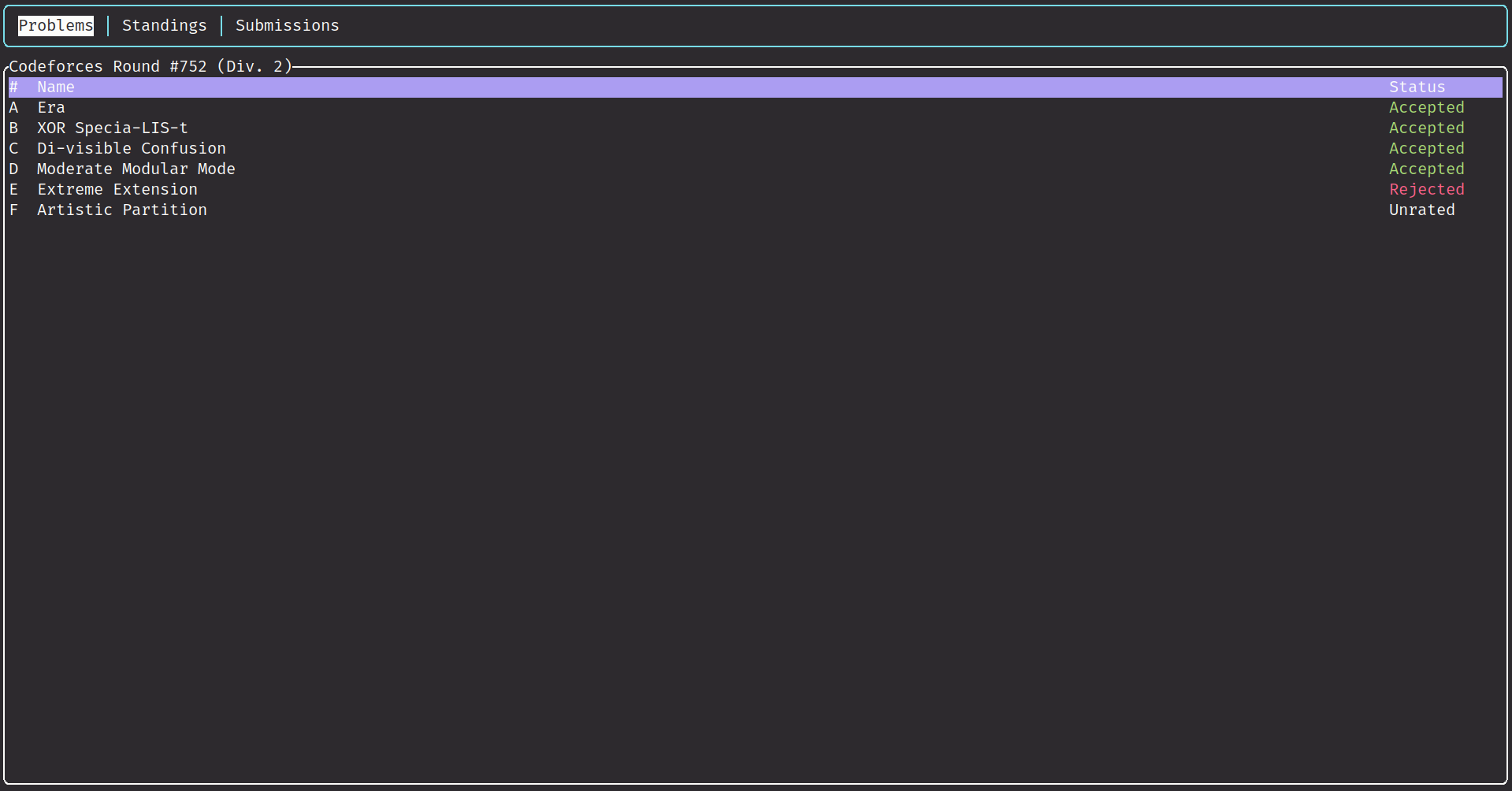
- Support Contests, Gym, Groups and acmsguru.
- Support all programming languages in Codeforces.
- Submit codes (Copy codes to clipboard and open it in default web browser).
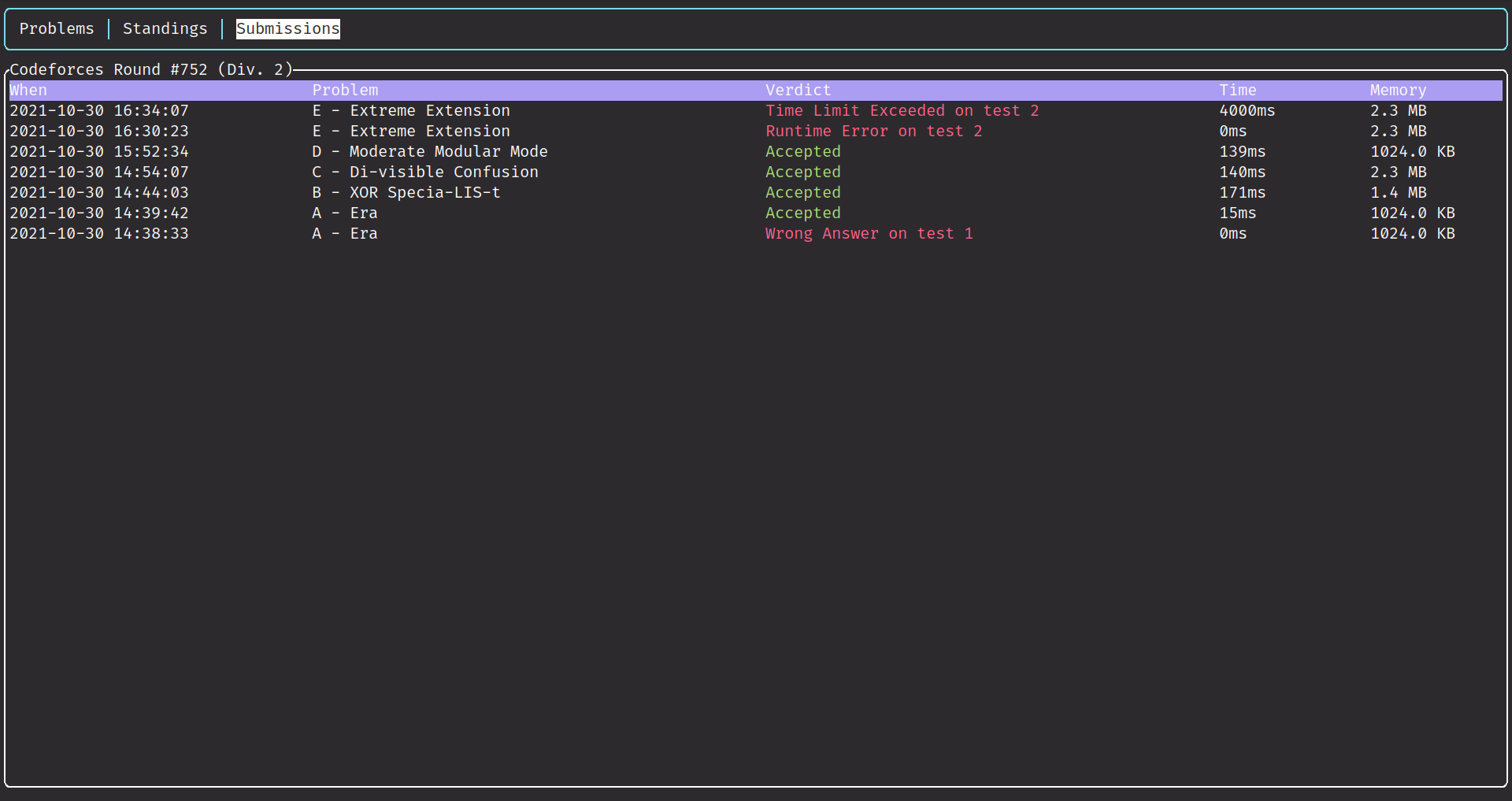
- Watch submissions' status dynamically.
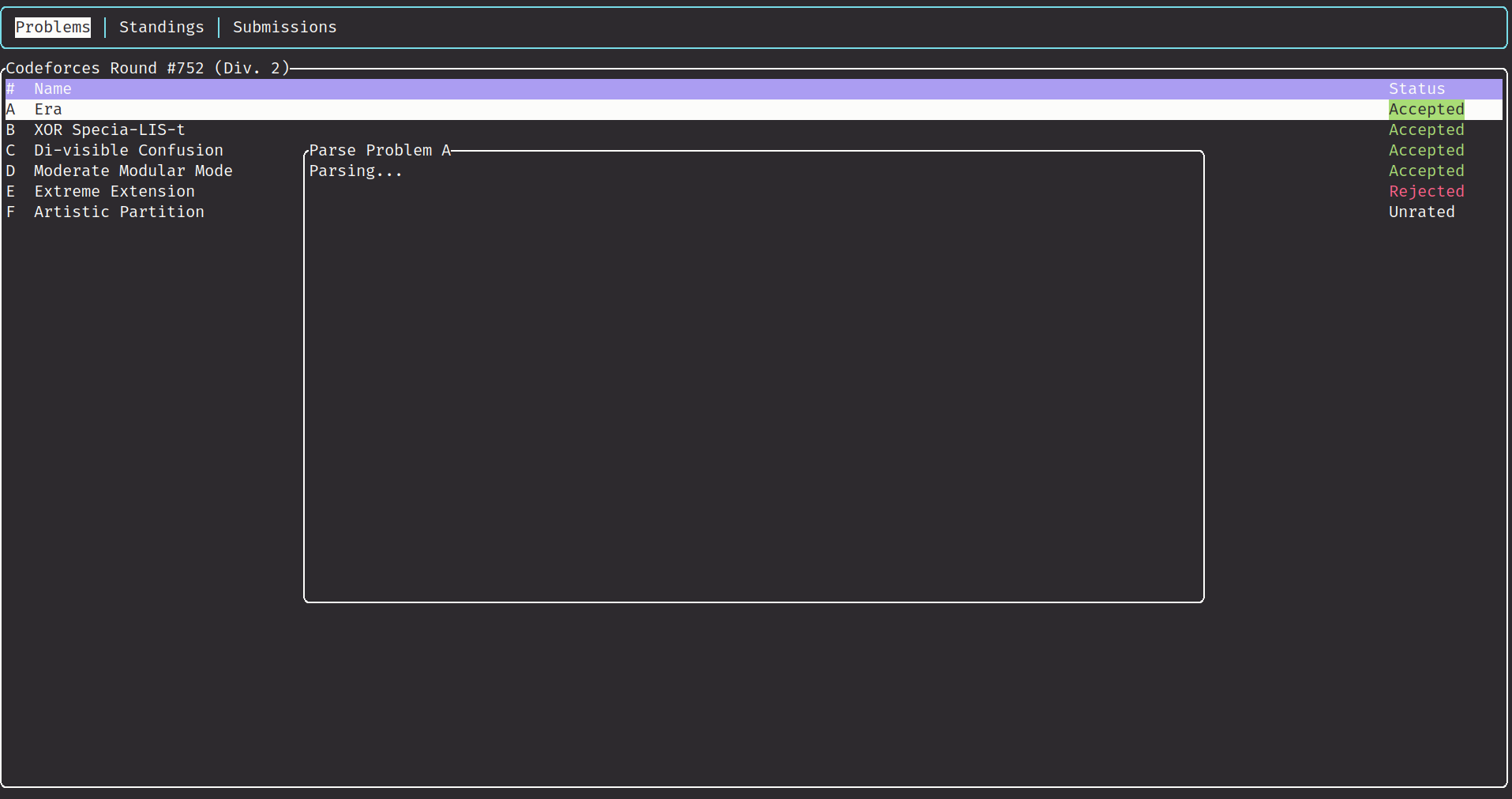
- Fetch problems' samples.
- Compile and test locally.
- Generate codes from the specified template (including timestamp, author, etc.)
- List problems' stats of one contest.
- Use default web browser to open problems' pages, standings' page, etc.
- Colorful TUI.
git clone https://github.com/jerrywcy/cf-tool.git
cd cf-tool
cargo install --path . --bin cf-tuiThen enjoy cf-tool!
-
Run
cf-tuito enter the main browser view. -
Run
cf-tui race <CONTEST_ID>to take part in a give contest. -
Run
cf-tui configto configure cf-tool using a configuration guide. -
Press
qorEscto exit current view. -
Press
TaborhorRightto go to the next tab. -
Press
Shift + TaborlorLeftto go to the previous tab. -
Press
Enteron contests to enter contest view. -
Press
Enteron problems to open the problem in default web browser. -
Press
pon problems to parse sample for the current problem. -
Press
Pon problems tab to parse all samples for the current contest. -
Press
gon problems to generate codes according to template for the current problem. -
Press
oon problems to open them using theopen_scriptconfigured. -
Press
ton problems to test current problems.
cf-tool will save data in config_dir.
Normally, config_dir is ~/.config/cf where ~ is the home directory of current user in your system.
In config_dir there are following files:
config_dir/cf.jsonYour configuration file.config_dir/templatesThe folder to store templates.
Configuration file consists of the following parts:
username: Your username.key: Your API key.secret: Your API secret.
API key and secret can be created here.
templates is an array of templates.
Each template is configured as the following:
{
\"alias\": The alias of this template.
This can be anything you want to recoginize this template but must be configured.
\"lang\": The language this template uses.
This can be anything you want to recoginize this template and doesn't follow any restriction.
For example, this can be configured as either \"cpp\" or \"C++\".
This must be configured.
\"path\": The path to your code for this template. cf-tool will read from this directory when the path specified in templates in configuration file is not an absolute path.
For example, when path = /home/cf/dcode.cpp , cf-tool will read from /home/cf/dcode.cpp .
when path = dcode.cpp, cf-tool will read from config_dir/templates/dcode.cpp;
}You can insert some placeholders into your template code.
When generate a code from the template, cf will replace all placeholders by following rules:
| Placeholder | Content |
|---|---|
<% username %> |
Handle (e.g. xalanq) |
<% year %> |
Year (e.g. 2022) |
<% month %> |
Month (e.g. 12) |
<% day %> |
Day (e.g. 19) |
<% hour %> |
Hour (e.g. 09) |
<% minute %> |
Minute (e.g. 08) |
<% second %> |
Second (e.g. 02) |
For example, the following code:
/*
* user: <% username %>
* time: <% year %>-<% month %>-<% day %> <% hour %>:<% minute %>:<% second %>
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
return 0;
}will be generated as:
/*
* user: jerrywcy
* time: 2022-12-19 18:01:05
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
return 0;
}cf-tool will run 3 scripts in sequence when you run press t on a problem:
before_script(execute once)script(execute the number of samples times)after_script(execute once)
You could set before_script or after_script to empty string, meaning not executing.
You have to run your program in script with standard input/output (no
need to redirect).
You can insert some placeholders in your scripts. When execute a script, cf will replace all placeholders by following rules:
| Placeholder | Content |
|---|---|
| <% path %> | Path to source file (Excluding <% full %>, e.g. /home/jerrywcy/) |
| <% full %> | Full name of source file (e.g. a.cpp) |
| <% file %> | Name of source file (Excluding suffix, e.g. a) |
For example, a script that runs C++ can be written as follow:
{
"before_script": "g++ <% full %> -o <% file %>",
"script": "./<% file %>" (or "./<% file %>.exe" on Windows system)
}home_dir: The directory that stores all codes and samples generated by cf-tool and the directory to read from when testing or submitting.
The directory looks like the following:
home_dir
└── Contests
└── contest_id
└── problem_index
├── problem_index.cpp
├── ans1.txt
├── ans2.txt
├── in1.txt
└── in2.txt