CUBE.gl is a geospatial data visualization framework for visualizing large-scale geo-related datasets or create digital twin in a few line of code. The CUBE.gl is built upon the brilliant 3D library three.js by mrdoob, powered by Web-GL.
This version is in publish for testing and in active development / update. It is not recommended to use this library in production enviornment. Please report Bugs and issues the Github issue page.
-
Visualize numeric data by cylinder, arc, text etc.
-
Visualize datasets by point cloud and heatmap.
-
Visualize geographic data by buildings, roads, terrain, tile map, administrative geojson and custom polygon.
-
Load model and attach other object, eg. THREE.Light.
-
Create animation by WGS84 coordinate path (eg. vehicle) or simply circular around something (eg. satellite).
-
Attach shader to an object to create visual effects.
Simply add this line in your .HTML file.
<script src="https://unpkg.com/cube.gl@latest/dist/cubegl.js"></script>By importing the project from NPM module system, you need to install node.js. Open a terminal, direct to your project folder, execute following command:
npm i cube.gl
- Create a div block with id in HTML:
<div id="container" style="position: absolute; width: 100%; height: 100%;"></div>- Write following code
// Get target container
const container = document.getElementById('container')
// Init CUBE instance
const C = new CUBE.Space(container, {
background: "333333", // Set Background Color
center: {latitude: 34.710554, longitude: 103.699520}, // Set a geo location center
scale: .002, // Set a map scale
camera:{
position: {x: 5, y: 5, z: 5} // Set camera default position
}
})
// Add a basic box with wgs84 coordinate
const posi = new CUBE.Coordinate("GPS", {latitude: 34.710554, longitude: 103.699520}).ComputeWorldCoordinate()
const box = C.Add(new CUBE.Shapes("Box", posi.world).Box(1))
box.position.y = 1
// Animate scene every frame
Update()
function Update(){
requestAnimationFrame(Update)
C.Runtime()
}The scale is set to 0.002 because we are going to load a administrative map for an whole country in the next step, set it to 5-10 if you want to visualize in city / street level.
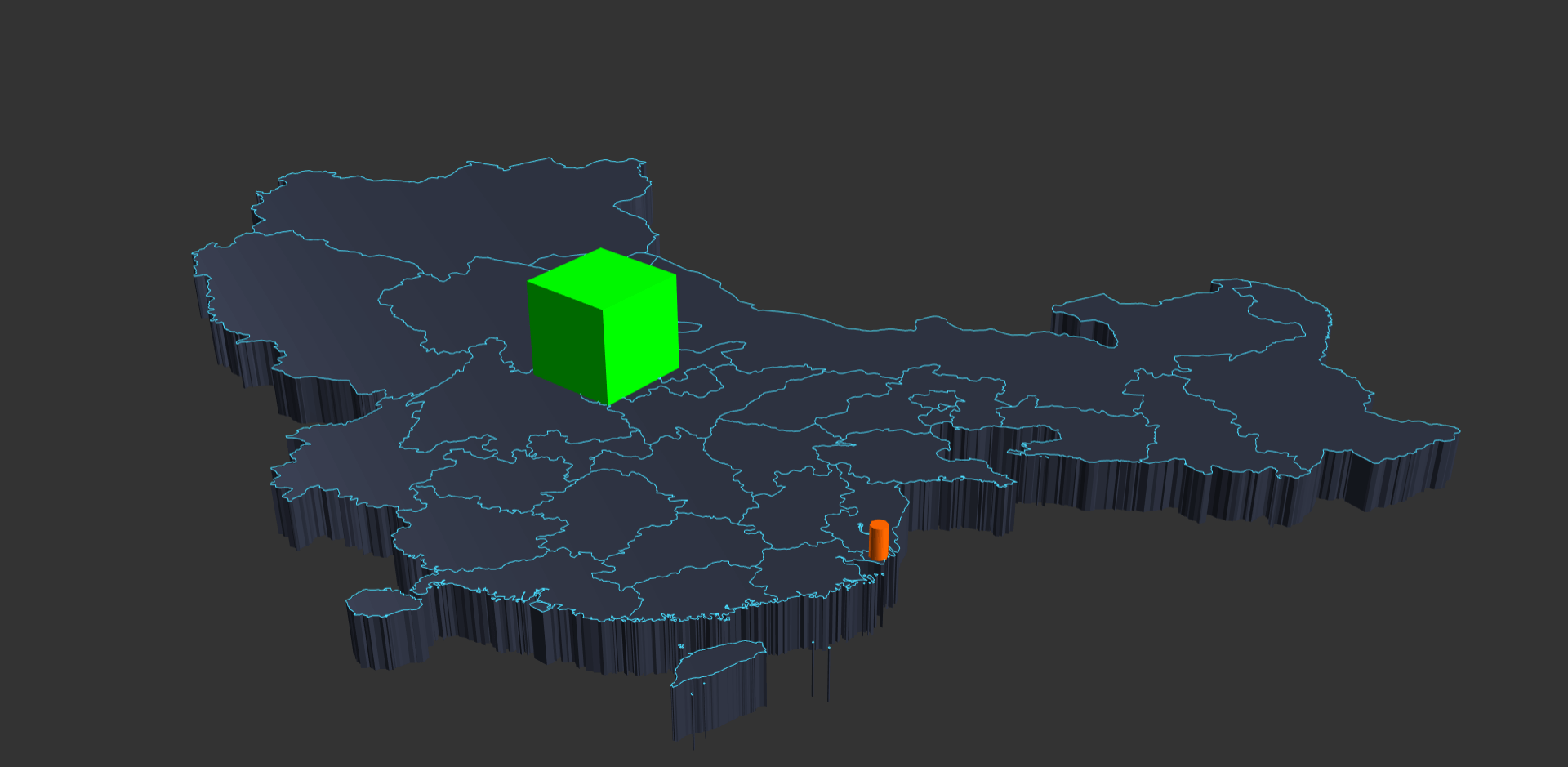
Run your project, you will see a green cube placed in the middle of your screen as the coordinate is equal to the center coordinate.
- Now let's explore more. Add the following line before Update()
// Add Geojson Map Layer
const china = 'https://gistcdn.githack.com/isjeffcom/787220f51465c8365b4ccc7247a919e7/raw/1afd3f92f64d8dd01534b6831d65de395f07b43e/china.geojson'
fetch(china).then(async (res)=>{
C.Add(new CUBE.GeoLayer("china", await res.json()).AdministrativeMap({border: true, height: .5}))
})
// Add an cylinder bar at Shanghai City Center
const shanghai = {latitude: 31.230689, longitude: 121.473723}
const bar = new CUBE.Data("shanghai").Cylinder(shanghai, 150, 40, .5, 0xff6600)
C.Add(bar)*If the .geojson file fail to request, download it from here *
Run your project, you will see an administrative map of China display in the center, with a cylinder bar and... Great. You have finished your first project.
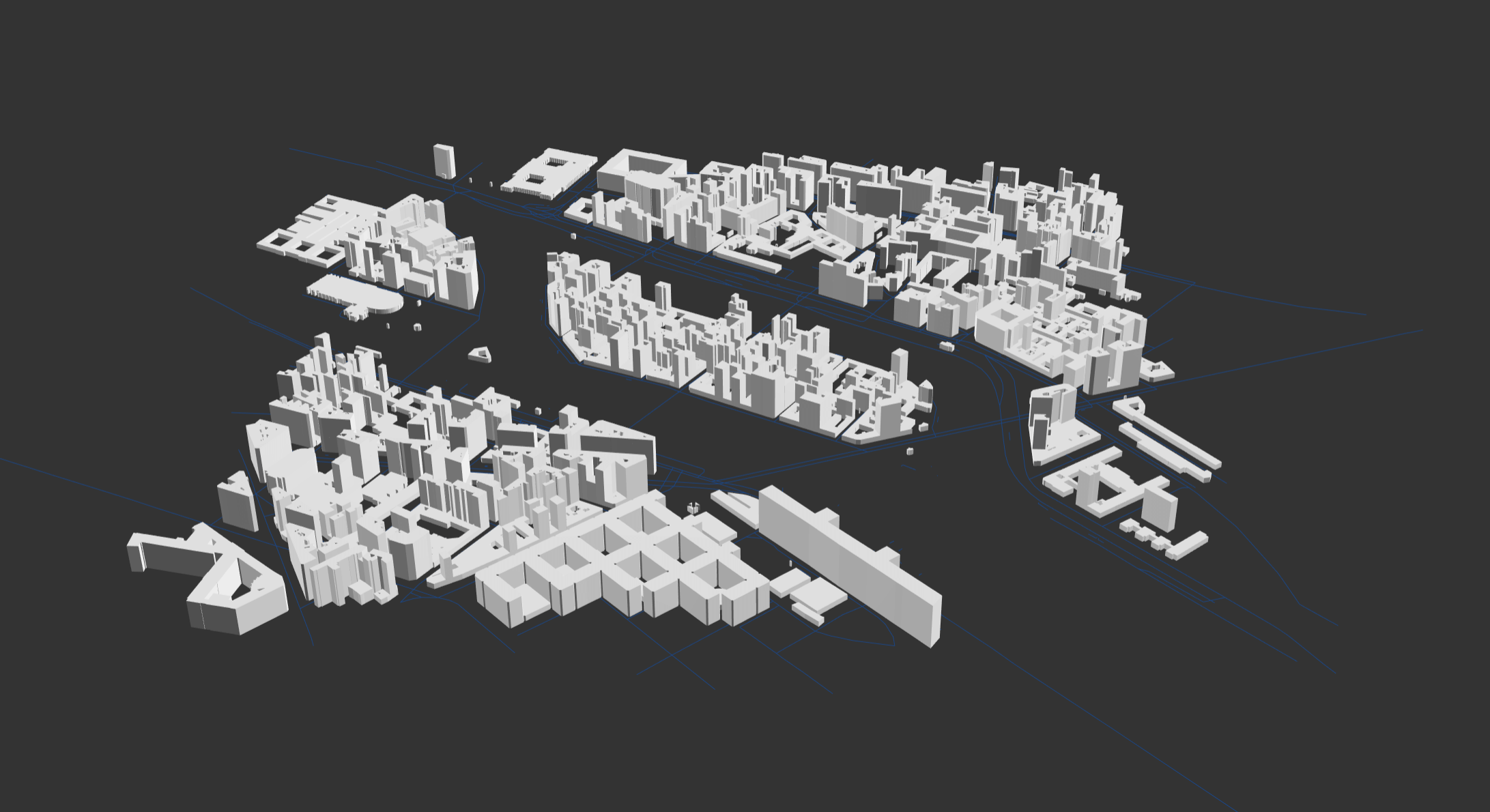
High-level API only contain City constructor for now. The City class enables the abilities to download data, and display any part of city (most of) in 3D around the world by CUBE.gl. You can create a Paris city center (Cathédrale Notre-Dame) in range 500 meters by
Init()
Update()
// Get Container
const container = document.getElementById('cont')
// Ready for CUBE Instance
let C
async function Init(){
// Init CUBE Instance
C = new CUBE.Space(container, {
background: "333333",
center: {latitude: 48.851837, longitude: 2.356544},
scale: 10,
camera:{
position: {x: 6, y: 10, z: 6}
}
})
const cm = new CUBE.City(500) // range 500 meters
const building = await cm.buildings()
const roads = await cm.roads()
document.getElementById("loading").style.display = "none"
roads.position.y -= 1
C.Add(building)
C.Add(roads)
}
function Update(){
requestAnimationFrame(Update)
C.Runtime()
}The CUBE.gl is build upon three.js. You can access the built-in three.js by CUBE.Space.three or CUBE.Space.Three(). The current CUBE build is using three.js 0.119. You can also try to implement a different version.
More about three.js you can check here
The CUBE.gl has no limitation to use in any MVVM framework as long as you can access DOM element to rendering.
Here is an example how to use CUBE.gl in Vue.js with Vue-Cli.
<template>
<div id="app">
<div id="cont"></div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import * as CUBE from 'cube.gl'
export default {
name: "app",
data(){
return{
C: null,
Center: {latitude: 41.157937, longitude: -8.629108}, // Porto
}
},
mounted(){
this.Init()
this.Update()
},
methods: {
Init(){
let container = document.getElementById('cont')
// Init CUBE Instance
this.C = new CUBE.Space(container, {
background: "333333",
center: this.Center,
scale: 10
})
//Add a basic box with wgs84 coordinate
let posi = new CUBE.Coordinate("GPS", {latitude: 41.157937, longitude: -8.629108}).ComputeWorldCoordinate()
this.C.Add(new CUBE.Shapes("Box", posi.world).Box(1))
// Add Sphere
this.C.Add(new CUBE.Shapes("Sphere", {x: 2, y: 0, z: 2}).Sphere(1, 0x00ffff))
this.C.Add(new CUBE.Shapes("Cylinder", {x: -2, y: 0, z: -2}).Cylinder(1, 0xff0000))
},
Update(){
requestAnimationFrame(this.Update)
this.C.Runtime()
}
}
}
</script>