1 字节(byte)= 8 位(bit) 字节是计算机中表示数据大小的基本单位
在表示 CPU 性能时,可以写成 16 位 CPU、32 位 CPU、64 位 CPU 等,这里的 16、32、64 指的就是 CPU 处理数据的能力大小、并行总线一次可以传输的二进制数位多少等,一般这个数值越大,CPU 的性能越好
1KB=1024B=1024 字节
Visual C++、GCC 以及 LLVM Clang 这三大编译器 Visual C++由微软开发,只能用于 Windows 很多版本的 Linux 都默认使用 GCC 作为C语言编译器,而像 FreeBSD、macOS 等系统默认使用 LLVM Clang 编译器。由于当前 LLVM 项目主要在 Apple 的主推下发展的,所以在 macOS中,Clang 编译器又被称为 Apple LLVM 编译器
程序是由指令和各种数据组成,这些指令和数据是由 0 和 1 两种符号的二进制来表示 在计算机世界中、二进制代码表示的计算机能直接识别和执行的指令和数据的集合(程序)称为“机器语言”
低级语言 机器语言是唯一一种 CPU 能直接理解并执行的编程语言,用其他语言编写的程序计算机是不能直接运行的,必须先转换成机器语言。 汇编语言的助记符以及数据和机器语言的二进制代码都是一一对应的,也需要转化为机器语言。
高级语言 高级语言是以人类日常语言为基础的一种编程语言,使用高级语言编写的程序通常称为源代码 而转换成机器语言的程序就是本地代码。这种转换过程被称为编译 这种执行源代码编译任务的程序称为编译器
C语言中的语句必须以;结尾 字符串就是字符的数组 数组的元素都是按顺序存放在内存一块连续空间。数组定义时需要说明数组的大小,如果数组大了就会有大量空闲存储单元,定义小了又会在运行中发生数组下标越界的错误,这是静态存储分配的局限性。
int str(){
// 普通数组是没有字符串 \0 结束符号的,所以要严格定长
int arr[5] = {1,2,3,4,5};
// 字符串的声明
char math1[5] = {'m','a','t','h','\0'};
char math2[5] = "muth";
char math3[] = "math";
// math2的值,给math3
strcpy(math3, math2);
printf("%s\n", math3);
// 返回字符串长度
printf("%d\n", strlen(math1));
char str[20] = "hello";
char *str1 = "+jack";
// 字符串相加,得保证目标str容量够才行
strcat(str, str1);
puts(str);
}int print1(){
// 屏幕打印字符串消息并换行
puts("Hello World!");
// 十进制有符号
printf("%d\n",-16);
// 十进制无符号
printf("%u\n",-16);
// 八进制无符号
// # 就是带前缀输出
printf("%o\n", 20);
printf("%#o\n", 020);
// 十六进制无符号
printf("%#x\n", 20);
double d = 123.4545565;
// 输出宽度8带4位小数的单精度浮点数
printf("%8.4f\n", d);
return 0;
}void scan(){
char Char_A;
printf("请输入字符然后回车:\n");
scanf("%c",&Char_A);
printf("\n使用scanf()获取输入值以后:\n");
printf("变量Char_A的值为:%c\n",Char_A);
}#include <ctype.h>
void more(){
char a = 'a';
// 单个字母转大写
char a1 = toupper(a);
printf("%c\n", a1);
// 单个字母转小写
char a2 = tolower(a1);
printf("%c\n", a2);
// 判断是否是字母
printf("%d\n", isalpha(a));
// 判断是否是数字
printf("%d\n", isdigit(a));
// 判断是否是小写字母
printf("%d\n", islower(a));
}void math(){
// 生成随机数
// int a = rand();
// 平方根
int a = sqrt(9);
// 绝对值
int b = fabs(-100);
// 取整操作
int c = ceil(1.6);
int d = floor(1.6);
int e = round(4.6);
printf("%d %d %d \n",c, d, e);
// 指数运算
int f = pow(2,5);
printf("%d %d %d \n", a, b, f);
// 比较
int max = fmax(e, d);
int min = fmin(e, d);
printf("%d %d \n", max, min);
}
在函数外定义的变量,拥有文件作用域,静态存储期 在函数内声明的静态变量,同上 拥有文件作用域的变量,其寿命是从定义变量到整个程序执行结束。
enum week { Mon = 1, Tues, Wed, Thurs, Fri, Sat, Sun };
week w = Tues;
printf("%d\n", w);用户自定义的特殊的复合型的“数据类型”,类似js中的对象
// 结构体
struct Student {
int age;
float wage;
const char *name;
};
Student tom;
tom.age = 11;
tom.wage = 12.2;
tom.name = "tom";
puts(tom.name);
Student jack;
jack.age = 11;
jack.wage = 12.2;
jack.name = "jack";
puts(jack.name);
// 结构体数组
Student list[] = {
{11, 11.1, "11"},
{22, 22, "22"},
};
puts(list[0].name);
// 别名
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node *next;
} Node;- 共用体的所有成员占用同一段内存,修改一个成员会影响其余所有成员
- struct 占用的内存大于等于所有成员占用的内存的总和(成员之间可能会存在缝隙)
- 共用体占用内存等于最长的成员占用的内存。共用体使用了内存覆盖技术,同一时刻只能保存一个成员的值,如果对新的成员赋值,就会把原来成员的值覆盖掉
- 共用体在一般的编程中应用较少,在单片机中应用较多
union data {
int length;
short size;
char tag;
};指针就是变量在内存中的地址,指针变量的类型与它指向变量类型一致
// 基本使用
int a = 1;
int *p = &a;
int b =22;
printf("%p\n", p);
printf("%d\n", *p);
*p = 12;
printf("%d\n", *p);
p = &b;
printf("%d\n", *p);
// 只读指针
int * const p3
// 指针-数组,不用取地符,本身就是地址
int arr[5]={1,2,3,4,5};
int *p = arr; //指针p指向a[0]
for(int a =0; a< 5; a++){
printf("%d\n", *p);
p++;
}
// 指针-字符串,不用取地符,本身就是地址
char str[] = "huahua";
char *p1 = str;
for(int a =0; a< 6; a++){
printf("%c\n", *p1);
p1++;
}
// 指针-结构体要用取地址符号
struct student {
int age;
};
student tom = { 11 };
student *p = &tom;
printf("%d\n", tom.age);
printf("%d\n", p->age);C语言中,所有的数据必须存储在指定大小的内存中,所以在建立链表时,每新增一个结点,就用内存分配函数malloc(size)向系统申请一块内存空间用于存储该结点数据。同样地删除一个结点后,也用函数free(指针名)释放它所占用的内存空间。因而,我们把链表结构称为是一种动态存储分配结构。
// windows
#include <malloc.h>
// mac
#include <mm_malloc.h>
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node *next;
} Node;
Node *node3 = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));;
node3->data = 3;
node3->next = NULL;
Node *node4 = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));;
node4->data = 4;
node4->next = NULL;
Node *node1 = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));;
node1->data = 2;
node1->next = node4;
Node *head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->data = 1;
head->next = node1;
Node *q;
// 遍历查找
for(q=head; q!=NULL; q=q->next){
printf("%d\n", q->data);
}
puts("end");
// 插入node3
for(q=head; q!=NULL; q=q->next){
if(q->data == 2){
Node *next = q->next;
q->next = node3;
node3->next = next;
}
}
for(q=head; q!=NULL; q=q->next){
printf("%d\n", q->data);
} - 在结构体定义时,我们可以指定某个成员变量所占用的二进制位数(Bit),这就是位域
- C语言标准规定,位域的宽度不能超过它所依附的数据类型的长度
struct bs{
int a:8;
int b:2;
int c:6;
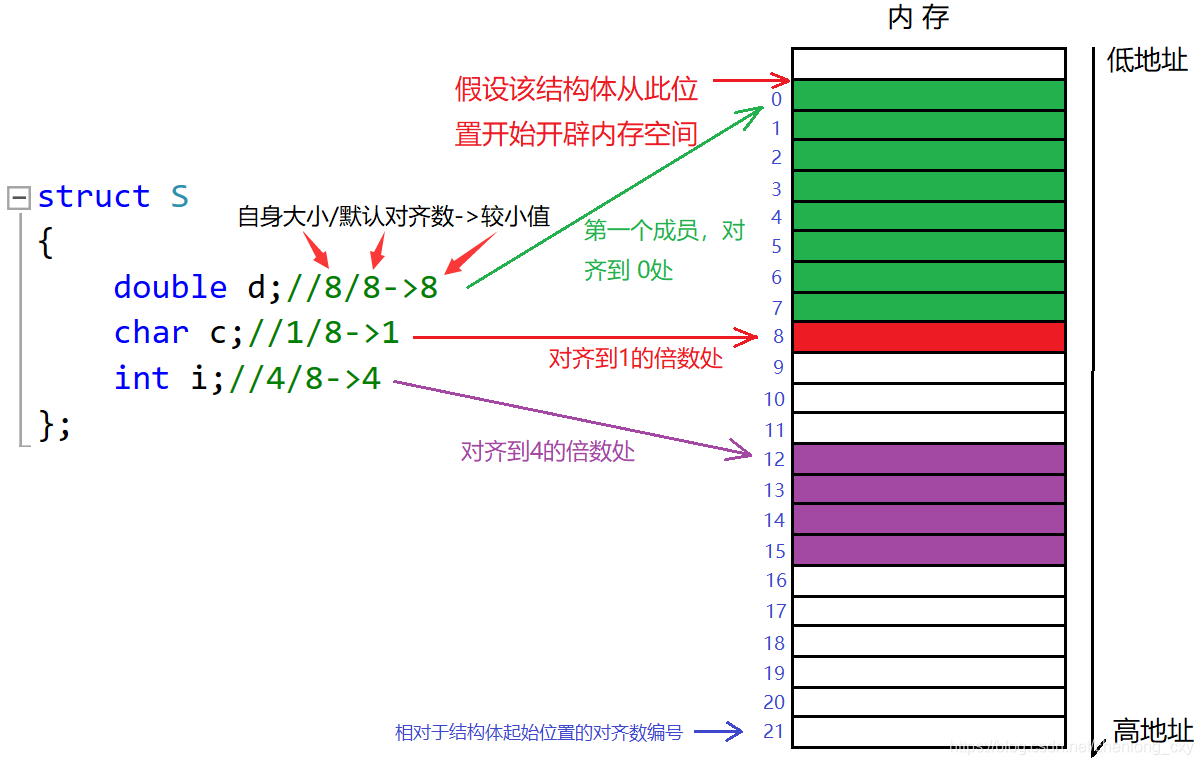
}data;为了使CPU能够对变量进行快速的访问,变量的起始地址应该具有某些特性,即所谓的”对齐” 字节对齐的作用不仅是便于cpu快速访问,同时合理的利用字节对齐可以有效地节省存储空间
对齐跟数据在内存中的位置有关。如果一个变量的内存地址正好位于它长度的整数倍,他就被称做自然对齐
- 第一个成员在与结构体变量偏移量为0的地址处。(即结构体的首地址处,即对齐到0处)
- 其他成员变量要对齐到,这个成员变量(对齐数)的整数倍的地址处。
- 结构体的总大小为最大对齐数(每个成员变量都有一个对齐数)的整数倍。
- 如果嵌套了结构体,嵌套的结构体对齐到自己的最大对齐数的整数倍处,结构体的整体大小就是所有最大对齐数(含嵌套结构体的对齐数)的整数倍
数据的低位存在内存的高地址处,数据的高位存在内存的低地址处