- 1.0.2 (2019/06/14) Added support for directly opening the project node
- 1.0.3 (2019/12/11) Added support for node wait function
- 1.0.4 (2019/12/31) Optimize the online feedback of multi-thread synchronization to notify the next node to start
- 1.0.5 (2020/01/20) Added demo scenarios such as node release monitoring entry, multi-process / wait / restart new chain, etc. (see Sample example)
- 1.1.0 (2020/05/13) Support kotlin and DSL features
- 1.1.1 (2020/07/31) Optimize the DSL block API
- 1.1.2 (2020/10/08) Optimize the traversal speed of the dependency tree, and fix the problem that the Log-TASK_DETAIL dependency task has no information.
- 1.1.3 (2020/11/10) Support multiple block nodes, AnchorManager is no longer open as a singleton, supports custom thread pool, taskListener supports DSL selective coverage method
- 1.1.4 (2021/04/28) Optimize log and optimize multi-threaded scenarios
- 1.1.5 (2022/06/09) Optimize multi-threaded scenarios
- 1.1.6 (2022/06/14) Support dynamic cutting of subsequent task chains
- 1.1.7 (2022/07/19) Fix java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException for apps running on and targeting Android versions lower than Oreo (API level < 26)
- 1.1.8 (2022/11/22) Fix java.lang.IllegalArgumentException
Anchors is a graph-based structure that supports the asynchronous startup task to initialize the Android startup framework. Its anchor provides a "hook" dependency function that provides flexibility in solving complex synchronization problems during initialization. Refer to alpha and improve some of its details, which is more suitable for Android-initiated scenarios. It also supports optimizing the dependency initialization process and selecting a better path for initialization.
For the thinking about alpha, please see 关于Android异步启动框架alpha的思考
Advantages over alpha
- Support to configure anchors to wait for the task chain. It is often used before application # onCreate to ensure that some initialization tasks are completed before entering the activity lifecycle callback.
- Supports active request blocking waiting tasks, which are commonly used for certain initialization tasks on the task chain that require user logic confirmation.
- Supports synchronous and asynchronous task chains
- Anchors are designed for efficient and convenient completion of complex initialization tasks when the app is launched, not for initializing certain dependencies in business logic.
- Setting the anchor in the api will block and wait until the anchor is completed before continuing to walk the code block after AnchorsManager # start. The reason why the application can handle this is because there are no frequent UI operations. The tasks after the anchor will be autonomously scheduled by the framework, the synchronous tasks will be sent to the main thread for processing via handler # post, and the asynchronous tasks will be driven by the thread pool in the framework.
- The wait function is used in scenarios where anchor is not set. If anchor is set, the waiting task should be placed behind the anchor to avoid uiThead blocking.
- In combination with the asynchronous hybrid chain and anchor function, it can flexibly handle many complex initialization scenarios, but it is necessary to fully understand the thread background when using the function.
-
Add the JitPack repository to the project root path, and no longer use JCenter
allprojects { repositories { ... maven { url 'https://jitpack.io' } } } -
Add dependencies under the app module
implementation 'com.github.DSAppTeam:Anchors:v1.1.8' -
Add dependency graph and start
The framework supports java and kotlin languages. For the two languages,
JDatasis built in the Demo to implement the java scene logic, and theDatasclass is used to implement the kotlin logic. The start-up dependency set is received in the form of a "graph", and the link to the construction node of the graph is realized.==> Take java as an example, the code can refer to the JDatas class To construct a task, the first parameter specifies the name and unique id, and the second parameter specifies whether the task runs asynchronously Task task = new Task("name",false) { @Override protected void run(@NotNull String s) { //todo } }; Build a Project. Project is a Task subclass, used to describe multiple Task scenarios. Because of the use of <TaskName> to build, pass a factory for unified processing The following constructs the logic of task1 <- task2 <- task3 <- task4, A -> B means A depends on B TestTaskFactory testTaskFactory = new TestTaskFactory(); Project.Builder builder = new Project.Builder("name", testTaskFactory); builder9.add("task1Name"); builder9.add("task2Name").dependOn("task1Name"); builder9.add("task3Name").dependOn("task2Name"); builder9.add("task4Name").dependOn("task4Name"); Project project = builder.build(); Combination, in fact, the above project#dependOn is a combination method project.dependOn(task); ... You can build a dependency graph through various combinations, and then call start to pass the graph head node to start AnchorsManager.getInstance() .start(task); When debugging is needed AnchorsManager.getInstance() .debuggable(true) .start(task); When the anchor needs to be set, <anchorYouNeed> represents some tasks, and these tasks need to be guaranteed to be initialized before the end of Application#onCreate AnchorsManager.getInstance() .addAnchors(anchorYouNeed) .start(task); For some scenarios, you may need to monitor the running status of a task, you can use the block blocking function. After blocking and waiting, you can release/destroy the waiting according to the business logic. WaitTaskYouNeed is the task you need to wait for AnchorsManager anchorsManager = AnchorsManager.getInstance(); LockableAnchor lockableAnchor = anchorsManager.requestBlockWhenFinish(waitTaskYouNeed); lockableAnchor.setLockListener(...){ //lockableAnchor.unlock() Release the waiting and continue the task chain //lockableAnchor.smash() Destroy waiting and terminate the task chain } anchorsManager.start(task); ==> koltin also supports all the above processes, and also provides a dsl build form to build a dependency graph, the code can refer to the Datas class Describe a dependency graph by calling the graphics method, use <TaskName> to build, and pass a factory for unified processing AnchorsManager.getInstance() .debuggable { true } .taskFactory { TestTaskFactory() } //The factory that generates task according to id .anchors { arrayOf(TASK_93, TASK_10) } //task id corresponding to anchor .block("TASK_10000") { // The task id of the block scene and the lambda that handles the monitoring //According to business it.smash() or it.unlock() } .graphics { // Build dependency graph UITHREAD_TASK_A.sons( TASK_10.sons( TASK_11.sons( TASK_12.sons( TASK_13))), TASK_20.sons( TASK_21.sons( TASK_22.sons(TASK_23))), UITHREAD_TASK_B.alsoParents(TASK_22), UITHREAD_TASK_C ) arrayOf(UITHREAD_TASK_A) } .startUp() Where anchorYouNeed is the anchor you need to add, waitTaskYouNeed is the task you need to wait for, and dependencyGraphHead is the head of the dependency graph.
For code logic, please refer to the sample case under the app module.
The following describes the main scenarios involved in the demo.
-
Multi-process initialization
SampleApplication.class is implemented for multiple processes to meet most initialization scenarios.
SampleApplication#onCreatewill be called again when the business involving the new process is started, so the initialization scenarios for different processes can be customized based on the process name. The code can refer to theSampleApplication#initDependenciesCompatMultiProcessmethod. Reer toMainActivity#testPrivateProcessorMainActivity#testPublicProcessfor triggering a new process. -
An intermediate node in an initialization chain needs to wait for a response
Some very demanding initialization chains may need to wait for certain conditions. (Note: The response here should be the response of the UI thread. If it is an asynchronous response, it can be actively initialized in advance as a node). Scenarios such as some apps require the user to select the "Interest Scenario" when initializing, and then initialize all logic of subsequent pages. The code can refer to
MainActivity#testUserChoose. -
After an initialization chain is completed, another new chain may be started
This kind of function is also supported, but in fact the framework advocates unified management of all initialization chains in the application.Because the framework emphasizes that arbitrary initialization tasks should be business heavyweight initialization code or third-party SDK init . The code can refer to
MainActivity#testRestartNewDependenciesLink. -
The subsequent task chain needs to be modified according to the running result of a certain task
When defining a task, you can override
Task#modifySonsto obtain the follow-up tasks of the current task, and you can return a new follow-up task id list after cutting according to your needs. (Note: It can only be deleted in the original task chain and cannot be added). The code can refer toMainActivity#testCutoutTask.
debuggale mode can print logs of different dimensions as debugging information output, and do Trace tracking for each dependent task. You can output trace.html for performance analysis by python systrace.py .
Anchors defines different TAG for filtering logs, you need to open Debug mode.
-
Anchors, The most basic TAG -
TASK_DETAIL, Filter details of dependent tasks2019-03-18 14:19:45.687 22493-22493/com.effective.android.sample D/TASK_DETAIL: TASK_DETAIL ======================= task (UITHREAD_TASK_A ) ======================= | 依赖任务 : | 是否是锚点任务 : false | 线程信息 : main | 开始时刻 : 1552889985401 ms | 等待运行耗时 : 85 ms | 运行任务耗时 : 200 ms | 结束时刻 : 1552889985686 ============================================== -
ANCHOR_DETAIL, Filter output anchor task information2019-03-18 14:42:33.354 24719-24719/com.effective.android.sample W/ANCHOR_DETAIL: anchor "TASK_100" no found ! 2019-03-18 14:42:33.354 24719-24719/com.effective.android.sample W/ANCHOR_DETAIL: anchor "TASK_E" no found ! 2019-03-18 14:42:33.355 24719-24719/com.effective.android.sample D/ANCHOR_DETAIL: has some anchors!( "TASK_93" ) 2019-03-18 14:42:34.188 24719-24746/com.effective.android.sample D/ANCHOR_DETAIL: TASK_DETAIL ======================= task (TASK_93 ) ======================= | 依赖任务 : TASK_92 | 是否是锚点任务 : true | 线程信息 : Anchors Thread #7 | 开始时刻 : 1552891353984 ms | 等待运行耗时 : 4 ms | 运行任务耗时 : 200 ms | 结束时刻 : 1552891354188 ============================================== 2019-03-18 14:42:34.194 24719-24719/com.effective.android.sample D/ANCHOR_DETAIL: All anchors were released! -
LOCK_DETAIL, 过滤输出等待信息2019-12-11 14:53:11.784 6183-6437/com.effective.android.sample D/LOCK_DETAIL: Anchors Thread #9- lock( TASK_10 ) 2019-12-11 14:53:13.229 6183-6183/com.effective.android.sample D/LOCK_DETAIL: main- unlock( TASK_10 ) 2019-12-11 14:53:13.229 6183-6183/com.effective.android.sample D/LOCK_DETAIL: Continue the task chain... -
DEPENDENCE_DETAIL, Filter dependency graph information2019-03-18 14:27:53.724 22843-22843/com.effective.android.sample D/DEPENDENCE_DETAIL: UITHREAD_TASK_A --> PROJECT_9_start(1552890473721) --> TASK_90 --> TASK_91 --> PROJECT_9_end(1552890473721) 2019-03-18 14:27:53.724 22843-22843/com.effective.android.sample D/DEPENDENCE_DETAIL: UITHREAD_TASK_A --> PROJECT_9_start(1552890473721) --> TASK_90 --> TASK_92 --> TASK_93 --> PROJECT_9_end(1552890473721) 2019-03-18 14:27:53.724 22843-22843/com.effective.android.sample D/DEPENDENCE_DETAIL: UITHREAD_TASK_A --> PROJECT_8_start(1552890473721) --> TASK_80 --> TASK_81 --> PROJECT_8_end(1552890473721) 2019-03-18 14:27:53.724 22843-22843/com.effective.android.sample D/DEPENDENCE_DETAIL: UITHREAD_TASK_A --> PROJECT_8_start(1552890473721) --> TASK_80 --> TASK_82 --> TASK_83 --> PROJECT_8_end(1552890473721) 2019-03-18 14:27:53.725 22843-22843/com.effective.android.sample D/DEPENDENCE_DETAIL: UITHREAD_TASK_A --> PROJECT_7_start(1552890473720) --> TASK_70 --> TASK_71 --> PROJECT_7_end(1552890473720) 2019-03-18 14:27:53.725 22843-22843/com.effective.android.sample D/DEPENDENCE_DETAIL: UITHREAD_TASK_A --> PROJECT_7_start(1552890473720) --> TASK_70 --> TASK_72 --> TASK_73 --> PROJECT_7_end(1552890473720) 2019-03-18 14:27:53.725 22843-22843/com.effective.android.sample D/DEPENDENCE_DETAIL: UITHREAD_TASK_A --> PROJECT_6_start(1552890473720) --> TASK_60 --> TASK_61 --> PROJECT_6_end(1552890473720) 2019-03-18 14:27:53.725 22843-22843/com.effective.android.sample D/DEPENDENCE_DETAIL: UITHREAD_TASK_A --> PROJECT_6_start(1552890473720) --> TASK_60 --> TASK_62 --> TASK_63 --> PROJECT_6_end(1552890473720) 2019-03-18 14:27:53.725 22843-22843/com.effective.android.sample D/DEPENDENCE_DETAIL: UITHREAD_TASK_A --> PROJECT_5_start(1552890473720) --> TASK_50 --> TASK_51 --> PROJECT_5_end(1552890473720) 2019-03-18 14:27:53.725 22843-22843/com.effective.android.sample D/DEPENDENCE_DETAIL: UITHREAD_TASK_A --> PROJECT_5_start(1552890473720) --> TASK_50 --> TASK_52 --> TASK_53 --> PROJECT_5_end(1552890473720) 2019-03-18 14:27:53.725 22843-22843/com.effective.android.sample D/DEPENDENCE_DETAIL: UITHREAD_TASK_A --> PROJECT_4_start(1552890473720) --> TASK_40 --> TASK_41 --> TASK_42 --> TASK_43 --> PROJECT_4_end(1552890473720) 2019-03-18 14:27:53.726 22843-22843/com.effective.android.sample D/DEPENDENCE_DETAIL: UITHREAD_TASK_A --> PROJECT_3_start(1552890473720) --> TASK_30 --> TASK_31 --> TASK_32 --> TASK_33 --> PROJECT_3_end(1552890473720) 2019-03-18 14:27:53.726 22843-22843/com.effective.android.sample D/DEPENDENCE_DETAIL: UITHREAD_TASK_A --> PROJECT_2_start(1552890473719) --> TASK_20 --> TASK_21 --> TASK_22 --> TASK_23 --> PROJECT_2_end(1552890473719) 2019-03-18 14:27:53.726 22843-22843/com.effective.android.sample D/DEPENDENCE_DETAIL: UITHREAD_TASK_A --> PROJECT_1_start(1552890473719) --> TASK_10 --> TASK_11 --> TASK_12 --> TASK_13 --> PROJECT_1_end(1552890473719) 2019-03-18 14:27:53.726 22843-22843/com.effective.android.sample D/DEPENDENCE_DETAIL: UITHREAD_TASK_A --> UITHREAD_TASK_B 2019-03-18 14:27:53.726 22843-22843/com.effective.android.sample D/DEPENDENCE_DETAIL: UITHREAD_TASK_A --> UITHREAD_TASK_C
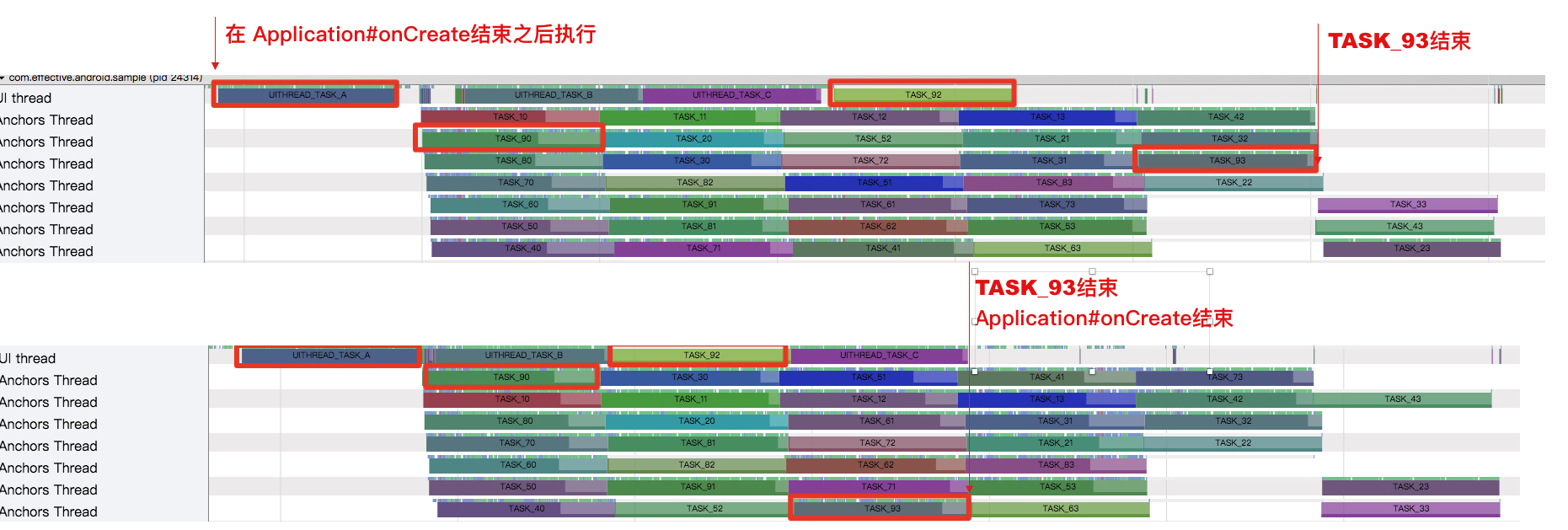
Below is the execution time given by Trace without using anchor points and using anchor points in the scene
The dependency graph has a UITHREAD_TASK_A -> TASK_90 -> TASK_92 -> Task_93 dependency. Assuming that our dependency path is a precondition for subsequent business, we need to wait for the business to complete before proceeding with its own business code. If not then we don't care about their end time. When using the anchor function, we hook TASK_93, and the priority from the beginning to the anchor will be raised. As you can see from the above figure, the time to execute the dependency chain is shortened.
The dependency graph is used to resolve the dependencies between tasks when the task is executed, and the anchor setting is used to resolve the synchronization relationship between the execution dependencies and the code call points.
The project was written only to improve the efficiency of day-to-day development and focus on the business. If you have a better practice or suggestions, please write to [email protected], ask Issues or initiate Pull requests, any problems will be resolved in the first time.