Extension to the OpenSimplex Python library by lmas. This library provides higher-level functions that can generate seamlessly-looping animated images and closed curves, and seamlessy-tileable images. It relies on 4D OpenSimplex noise.
- Github: https://github.com/Dennis-van-Gils/opensimplex-loops
- PyPI: https://pypi.org/project/opensimplex-loops
Inspiration taken from Coding Challenge #137: 4D OpenSimplex Noise Loop by The Coding Train.
Seamlessly-looping animated 2D images.
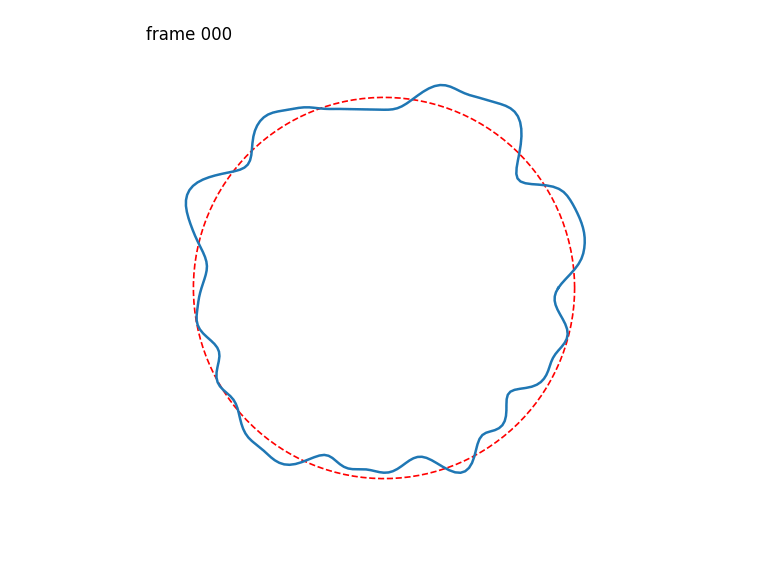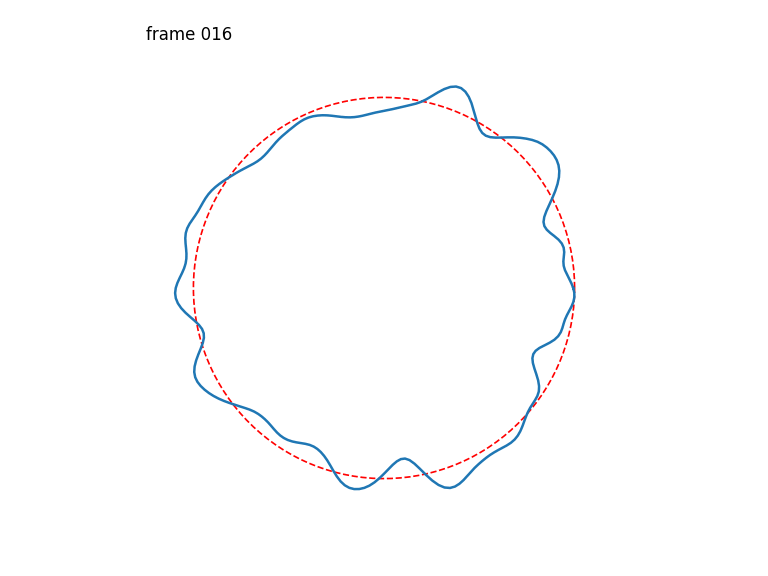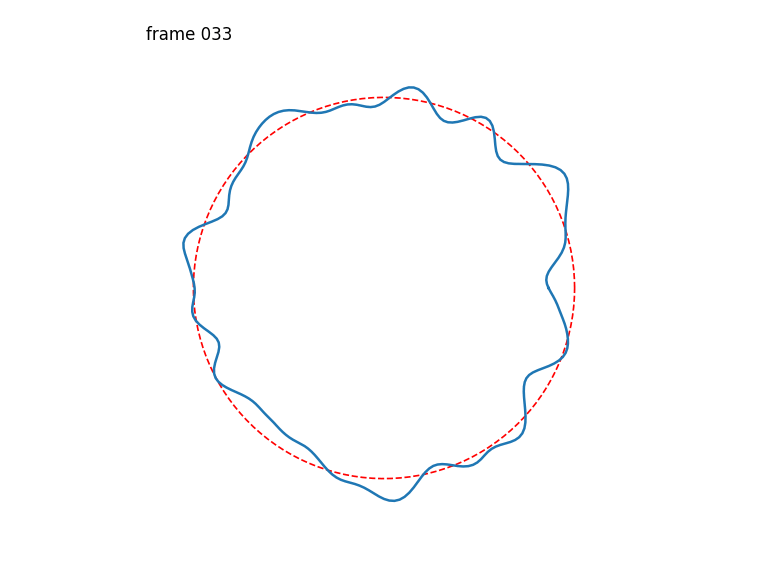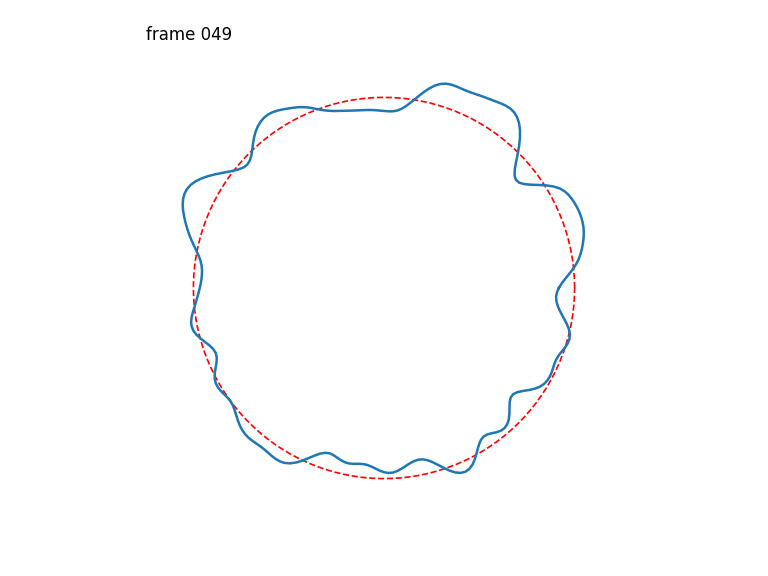
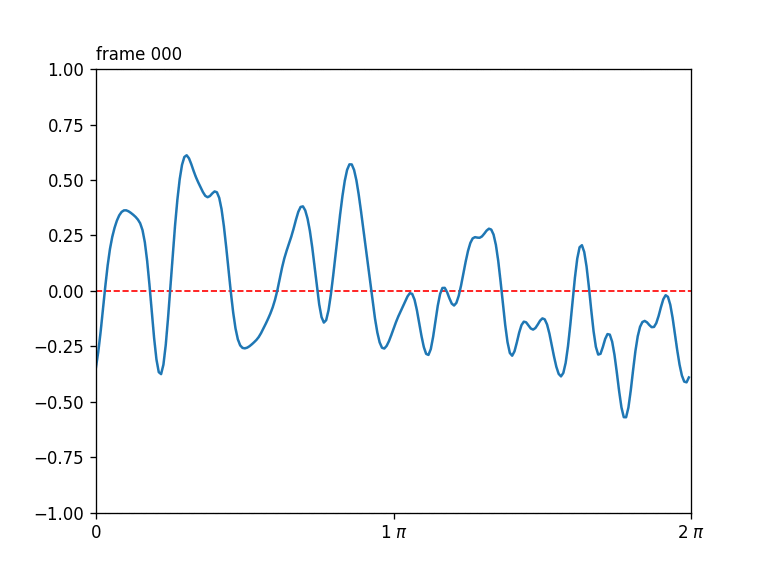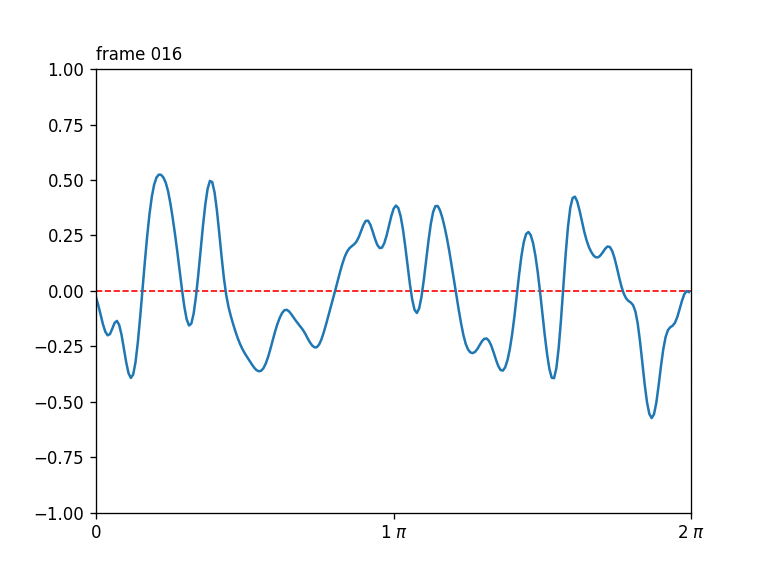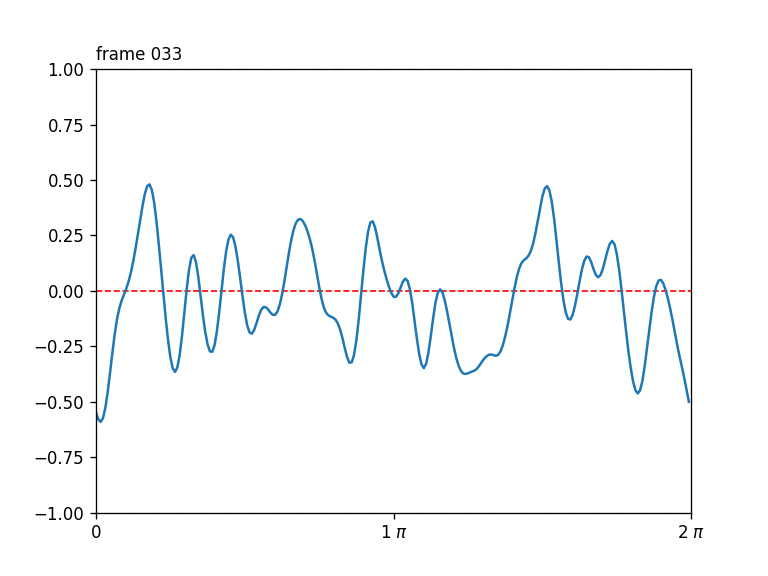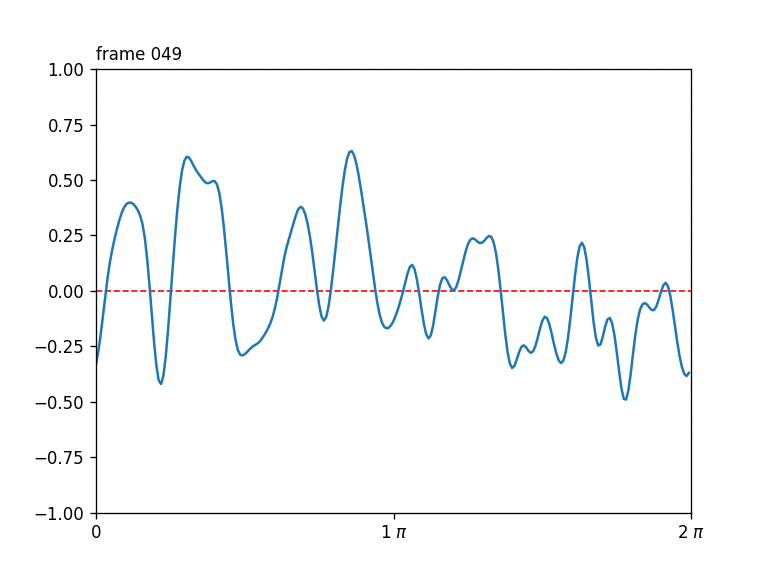
Seamlessly-looping animated 1D curves, each curve in turn also closing up seamlessly back-to-front.
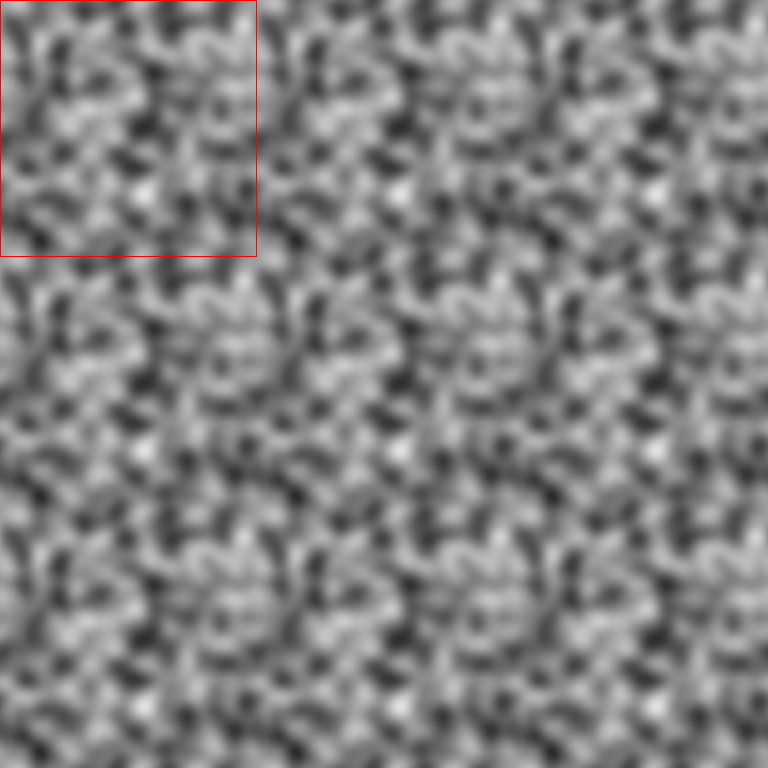
Seamlessly-tileable 2D image.
pip install opensimplex-loopsThis will install the following dependencies:
opensimplexnumpynumbanumba-progress
Notes:
- The OpenSimplex library by lmas does not enforce the use of the numba package, but is left optional instead. Here, I have set it as a requirement due to the heavy computation required by these highler-level functions. I have them optimized for numba which enables multi-core parallel processing within Python, resulting in major speed improvements compared to as running without. I have gotten computational speedups by a factor of ~200.
- Note that the very first call of each of these OpenSimplex functions will take a longer time than later calls. This is because numba needs to compile this Python code to bytecode specific to your platform, once.
- The
numba-progresspackage is actually optional. When present, a progress bar will be shown during the noise generation.
Generates a stack of seamlessly-looping animated 2D raster images drawn from 4D OpenSimplex noise.
The first two OpenSimplex dimensions are used to describe a plane that gets projected onto a 2D raster image. The last two dimensions are used to describe a circle in time.
- Args:
- N_frames (int, default = 200)
Number of time frames
- N_pixels_x (int, default = 1000)
Number of pixels on the x-axis
- N_pixels_y (int | None, default = None)
Number of pixels on the y-axis. When set to None N_pixels_y will be set equal to N_pixels_x.
- t_step (float, default = 0.1)
Time step
- x_step (float, default = 0.01)
Spatial step in the x-direction
- y_step (float | None, default = None)
Spatial step in the y-direction. When set to None y_step will be set equal to x_step.
- dtype (type, default = numpy.double)
Return type of the noise array elements. To reduce the memory footprint one can change from the default numpy.double to e.g. numpy.float32.
- seed (int, default = 3)
Seed value for the OpenSimplex noise
- verbose (bool, default = True)
Print 'Generating noise...' to the terminal? If the numba_progress package is present a progress bar will also be shown.
- Returns:
The 2D image stack as 3D array [time, y-pixel, x-pixel] containing the OpenSimplex noise values as floating points. The output is garantueed to be in the range [-1, 1], but the exact extrema cannot be known a-priori and are probably quite smaller than [-1, 1].
Generates a stack of seamlessly-looping animated 1D curves, each curve in turn also closing up seamlessly back-to-front, drawn from 4D OpenSimplex noise.
The first two OpenSimplex dimensions are used to describe a circle that gets projected onto a 1D curve. The last two dimensions are used to describe a circle in time.
- Args:
- N_frames (int, default = 200)
Number of time frames
- N_pixels_x (int, default = 1000)
Number of pixels of the curve
- t_step (float, default = 0.1)
Time step
- x_step (float, default = 0.01)
Spatial step in the x-direction
- dtype (type, default = numpy.double)
Return type of the noise array elements. To reduce the memory footprint one can change from the default numpy.double to e.g. numpy.float32.
- seed (int, default = 3)
Seed value for the OpenSimplex noise
- verbose (bool, default = True)
Print 'Generating noise...' to the terminal? If the numba_progress package is present a progress bar will also be shown.
- Returns:
The 1D curve stack as 2D array [time, x-pixel] containing the OpenSimplex noise values as floating points. The output is garantueed to be in the range [-1, 1], but the exact extrema cannot be known a-priori and are probably quite smaller than [-1, 1].
Generates a seamlessly-tileable 2D raster image drawn from 4D OpenSimplex noise.
The first two OpenSimplex dimensions are used to describe a circle that gets projected onto the x-axis of the 2D raster image. The last two dimensions are used to describe another circle that gets projected onto the y-axis of the 2D raster image.
- Args:
- N_pixels_x (int, default = 1000)
Number of pixels on the x-axis
- N_pixels_y (int | None, default = None)
Number of pixels on the y-axis. When set to None N_pixels_y will be set equal to N_pixels_x.
- x_step (float, default = 0.01)
Spatial step in the x-direction
- y_step (float | None, default = None)
Spatial step in the y-direction. When set to None y_step will be set equal to x_step.
- dtype (type, default = numpy.double)
Return type of the noise array elements. To reduce the memory footprint one can change from the default numpy.double to e.g. numpy.float32.
- seed (int, default = 3)
Seed value for the OpenSimplex noise
- verbose (bool, default = True)
Print 'Generating noise...' to the terminal? If the numba_progress package is present a progress bar will also be shown.
- Returns:
The 2D image as 2D array [y-pixel, x-pixel] containing the OpenSimplex noise values as floating points. The output is garantueed to be in the range [-1, 1], but the exact extrema cannot be known a-priori and are probably quite smaller than [-1, 1].