Infectious disease case detection that is developed in one setting (source) faces a performance drop in a new setting (target), often resulting from differences in patient populations and clinical practices. Able to take into consideration both the similarities and the dissimilarities between source and target settings, deep transfer learning (DTL) is a promising approach for improving the re-usability of source knowledge in a target setting. This study explored whether, when, and how DTL may be useful for infectious disease case detection in emergency department visits. We simulated multiple transfer learning scenarios that varied with respect to the target training size and the extent of dissimilarity between the source and target settings (measured by the Kullback–Leibler divergence, KL). We compared the performance of Domain Adversarial Neural Networks (DANN), which use data from a training source, and a model-based deep transfer learning (MDTL) method, which uses models obtained from the source. Additional baseline models include a source model, a target model, and a model that was developed using a combination of source and target training data.
Through this GitHub repository, we publicly share the main research codes and simulated datasets so that other researchers can leverage them for further analysis. Our codes are derived from an open-source Transfer-Learning-Library, which was developed and released by Machine Learning Group, School of Software, Tsinghua University, under the MIT license.
In the following section, we use this README.md file to briefly explain how our code works. Further information can be found in the to-be-published manuscript and related references.
Language
- Python (version--3.8)
Package:
- PyTorch (version--1.7.1)
- torchvision (version--0.8.2)
- qpsolvers (version--1.8.0)
- pandas
- sklearn
The configuration can be set by conda as below:
conda create --name TL python=3.8 anaconda
conda activate TL
conda install pytorch==1.7.1 torchvision==0.8.2 -c pytorch
pip install qpsolvers==1.8.0
pip install pandas
pip install sklearn
(Note: If you are using torchvision and pytorch that are not compatible with certain versions of Python, or if your version of torchvision is not compatible with your version of PyTorch, you may face some tricky bugs when running our code.)
For example, if you are using a different version of pytorch or torchversion than we are, you may need to make some changes in the import statement section:
change the
from torchvision.models.utils import load_state_dict_from_url
into
from torch.hub import load_state_dict_from_url
to avoid unexpected bugs, we recommend that you run our code in the same configuration as we did.
git clone https://github.com/AI-Public-Health/Deep-Transfer-Learning-Package-Release-Sep2022.git
cd Deep-Transfer-Learning-Package-Release-Sep2022/code/code
Run all of the models in the repository. For illustration, in here, the source data is specified as
findings_final_0814_seed1591536269_size10000.csv and findings_final_0814-portion1ita06round14_seed2016863826_size10000.csv(stored in /synthetic_data_v2/source_train),
target data is
findings_final_0814_seed678668699_size3000.csv and findings_final_0814_seed1033059257_size2000.csv(stored in /synthetic_data_v2/target_train),
initial random seed is 1, number of epoch is 1. You can change these hyperparameters to suit your needs.
If you run main_run.py directly, without setting any parameters, the program will use all defaults (run on all datasets in /synthetic_data_v2, trying several predefined random seeds), which may take some time to complete the whole process.
python main_run.py \
--source \
findings_final_0814_seed1591536269_size10000 \
findings_final_0814-portion1ita06round14_seed2016863826_size10000 \
--target \
findings_final_0814_seed678668699_size3000 \
findings_final_0814_seed1033059257_size2000 \
--seed=1 --epoch=1- Data processing
- Baseline Model
- Data-based Deep Transfer Learning (DDTL)
- Model-based Deep Transfer Learning (MDTL)
- Main Results and Conclusion
- Citation
In the transfer learning scenarios, the source and target data can be recorded/presented differently. Since deep neural network requires the same variable dimension in the source and target setting, the data pre-processing is important.
-
Kullback-Leibler(KL) Divergence
In this project, when the source and target data have the same variable dimension, we use Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence to measure the distribution difference between the source and target settings. Because the main experiments are conducted on synthetic datasets, we just release these datasets in our /data/synthetic_data_v2/ directory.
In our code, we useparse_model.pyto generate probability tables of different datasets, usedistributions.pyto calculate the KL value between probability tables derived from different data sources. (Note: make sure the existence of probability tables before the calculation of KL value between them. Runparse_model.pybefore runningdistributions.py.) -
Zero Padding
Data in the source setting may have and often does have different dimensions than data extracted from the target setting. Therefore, before building models, the source and target data should be mapped into the same space. Our program solve this problem by padding extra zeros so that data from different settings have the same dimensionality.
Even though all the data in the released synthetic datasets have the same dimensionality in both the source and target settings, we still include this zero padding method indata_preprocess.pyfor situations where you might have data with different dimensions.
After this recalibration of the data, we use all of the source data for model training and split our target data into different portions, for training, validation, or testing in the following models.
- Data Splitting
During experiments, the dataset needs to be split into different portions for different purposes--training, testing, validation. Indata_processing.py, the associated methods are defined to split the dataset.
In our experiments, due to the synthetic data being distributed in a balanced fashion, the dataset is split in by rows. However, if your dataset is skewed, you might need to change the methods of data splitting into stratified splitting ones, which are also included in data_procesing.py.
(e.g.: change prepare_datasets_returnSourceVal to prepare_datasets_stratify_returnSourceVal)
Based on the dataset used to train the model, we defined three baseline models (baseline model is required for MDTL from the next part). The corresponding codes for each baseline model are shown as below:
learnSourceModel.py--using the source training dataset to train a model;learnTargetModel.py--using the target training dataset to train a model;learnCombineModel.py-- using both the source and target training datasets to train a model.
In our code, we have pre-defined some hyperparameters, like epochs=10, batch_size=32, lr=0.01, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=0.001, print_freq=100, seed=None, trade_off=1.0, iters_per_epoch=313, via argparse. You can directly change those hyperparameters by using argparse through the command line.
-
BL_source: use the source training dataset to train a model , obtain a trained model under the source setting. All of output, including
AccuracyandAUCinformation, is stored in “results” folder;python learnSourceModel.py --source=findings_final_0814_seed1591536269_size10000 --seed=14942
-
BL_target: use the target training dataset to train a model, obtain a trained model under the target setting. All of output, including
AccuracyandAUCinformation, is stored in “results” folder;python learnTargetModel.py --target=findings_final_0814_seed-53154026_size50 --seed=14942
-
BL_combined: use both the source and target training datasets to train a model, obtain a trained model under the combined setting. All of output, including
AccuracyandAUCinformation, is stored in “results” folder;python learnCombineModel.py --source=findings_final_0814_seed1591536269_size10000 --target=findings_final_0814_seed-53154026_size50 --seed=14942
In the DDTL section, we apply the Domain Adversarial Neural Networks (DANN).
DANN works in three scenarios: the target training data have class labels (DANN_supervised); the target training data do not have any class labels (DANN_unsupervised); a portion of the target training data have class labels (DANN_semi-supervised). We have two separated code files for the first two scenarios. For the third scenario, users need to adjust the code or the structure of input data accordingly.
For Domain Adversarial Neural Networks(DANN), the Loss function is defined as below:
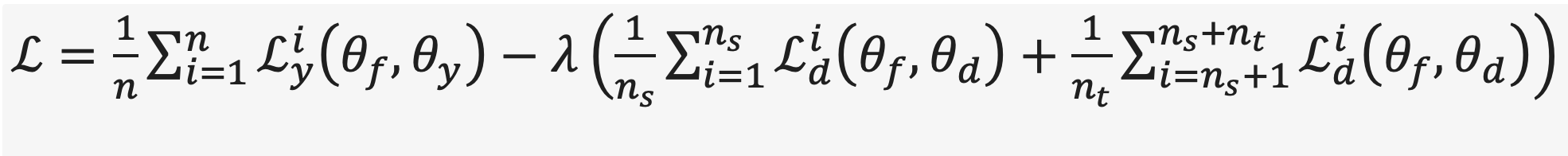
In our code, we use dann_synthetic_noTargetLabel_noTargetVal_outputAUC.py(for unsupervised DANN),dann_synthetic_withTargetLabel_outputAUC.py (supervised DANN) to train and evaluate DDTL models. Viewing our work as a whole picture, models are fed by source and target data files (.cvs) in synthetic_data_v2 directory. After training, trained models will be stored. The program returns and saves a .txt file recording information of the source, target data, accuracy, AUC of models during training.
For the network structure, it is defined in feedforward.py. If you want to modify the network structure used in the DANN model, you can modify the corresponding part of that .py file.
Related code:
dann_synthetic_noTargetLabel_noTargetVal_outputAUC.py
In the unsupervised DANN, the Label Classifier is only trained by source training data (target training data is not to be used for the training of the Label Classifier). Both target and source data are used to train the Feature Generator and the Domain Classifier.
Run the following code to return the corresponding Accuracy and AUROC for later performance in the comparison section ---all of the input data (.csv files of source and target data) are declared in the if __name__ == '__main__' module.
#run program with specified learning rate (0.02), specified trade-off(3),specified source dataset(findings_final_0814_seed1591536269_size10000.csv), specified target dataset(indings_final_0814_seed-53154026_size50.csv),, specified seed(1), specified epoch(1)
python dann_synthetic_noTargetLabel_noTargetVal_outputAUC.py --lr=0.02 --trade-off=3 --source=findings_final_0814_seed1591536269_size10000 --target=findings_final_0814_seed-53154026_size50 --seed=1 --epoch=1
#run program using default hyperparameters---calculate accuracy and AUC values from all of the models derived from different combinations of target and source dataset
python dann_synthetic_noTargetLabel_noTargetVal_outputAUC.py
Related code:
dann_synthetic_withTargetLabel_outputAUC.py
In the supervised DANN, both source and target training data is used in training the Label Classifier. Both target and source data are used in training the Feature Generator and Domain Classifier.
Run the following code to return the corresponding Accuracy and AUROC for later performance in the comparison section ---all of the input data (.csv files of source and target data) are declared in the if __name__ == '__main__' module.
#run program with specified learning rate (0.02), specified trade-off(3),specified source dataset(findings_final_0814_seed1591536269_size10000.csv), specified target dataset(indings_final_0814_seed-53154026_size50.csv), specified seed(1), specified epoch(1)
python dann_synthetic_withTargetLabel_outputAUC.py --lr=0.02 --trade-off=3 --source=findings_final_0814_seed1591536269_size10000 --target=findings_final_0814_seed-53154026_size50 --seed=1 --epoch=1
#run program using default hyperparameters---calculate accuracy and AUC values from all of the models derived from different
python dann_synthetic_withTargetLabel_outputAUC.py`(Note: in our code, we have already defined the default hyperparameters -- like epochs=10, batch_size=32, lr=0.01, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=0.001, trade_off=1.0, etc.. Those hyperparameters can be changed via argparse on the command line).
Model-based transfer learning keeps the source model’s network structure and a few parameters unchanged and tunes the remaining parameters using some of the target training data. We use the following structure for a source model: an input layer, two hidden layers, and an output layer. Among these layers, there are three sets of parameters. Thus, there are three model-based transfer learning strategies: tuning all three sets of parameters (MDTL_Tune_All), tuning two sets of parameters that involve the two hidden layers and the output layer (MDTL_Tune2), and tuning one set of parameters that involves the second hidden layer and the output layer (MDTL_Tune1). Because we will compare data-based transfer learning with model-based transfer learning, we choose the same structure as we used in the DANN feature modeling part. That is, two fully connected layers with 128 nodes in each layer was chosen as the hidden layers for the neural network architecture.
Since the MDTL module relies on the learned source model, make sure all the learned source model exist before fine-tuning them.
- MDTL_Tune1 ---
model-based-TL-TuneLast1Layer.py - MDTL_Tune2 ---
model-based-TL-TuneLast2Layers.py - MDTL_Tune_All ---
model-based-TL-TuneAllLayers.py
For each model, source and target data (.csv file) are fed into models, for training and evaluating. After that, programs will return trained models and save a .txt file recording information of source, target data, accuracy, and AUC during training.
In MDTL, we fine-tuned the parameters based on the original source model.
Based on the structure of Neural Network and the definition of PyTorch, we froze parameters in specific layers in specific missions.
For example, in the task of MDTL_Tune2, we tuned the parameters in the last two layers; therefore, we froze the parameters in the first layer during the following training under the target setting.
# freeze parameters in the first layer.
for param in classifier.fc1.parameters():
param.requires_grad = FalseFor the specific tasks, we froze specific parameters, and ran the code below to obtain our models:
For MDTL_Tune1, the parameters of the first two layers are frozen and the source model is trained under the target setting.
##run program with specified learning rate (0.02), on the model derived from source dataset-findings_final_0814_seed1591536269_size10000.csv, target dataset-indings_final_0814_seed-53154026_size50.csv.
python model-based-TL-TuneLast1Layer.py --lr=0.02 --source=findings_final_0814_seed1591536269_size10000 --target=findings_final_0814_seed-53154026_size50
# run it in the command line, to obtain MDTL_Tune1 model---fine-tuning all of the models derived from different combination of source and target dataset
python model-based-TL-TuneLast1Layer.pyFor MDTL_Tune2, the parameters of the first layer are frozen and the source model is trained under the target setting.
##run program with specified learning rate (0.02), on the model derived from source dataset-findings_final_0814_seed1591536269_size10000.csv, target dataset-indings_final_0814_seed-53154026_size50.csv.
python model-based-TL-TuneLast2Layers.py --lr=0.02 --source=findings_final_0814_seed1591536269_size10000 --target=findings_final_0814_seed-53154026_size50
# run it in the command line, to obtain MDTL_Tune2 model---fine-tuning all of the models derived from different combination of source and target dataset
python model-based-TL-TuneLast2Layers.pyFor MDTL_Tune_ALL, all of the parameters are fine-tuned under the target setting.
##run program with specified learning rate (0.02),on the model derived from source dataset-findings_final_0814_seed1591536269_size10000.csv, target dataset-indings_final_0814_seed-53154026_size50.csv.
python model-based-TL-TuneAllLayers.py --lr=0.02 --source=findings_final_0814_seed1591536269_size10000 --target=findings_final_0814_seed-53154026_size50
# run it in the command line, to obtain MDTL_Tune_All model---fine-tuning all of the models derived from different combination of source and target dataset
python model-based-TL-TuneAllLayers.py
Our experiments show that Simply combining source and target data for modeling does not work well, as expected. Both DANN and MDTL performed better than baseline models when the source and target distribution are not largely different (KL is close to 1) and the target setting has few training samples (fewer than 1000). The performance level of MDTL was similar to that of DANN models (mean of AUROCs: 0.83 vs. 0.84, P value of Wilcoxon signed-rank test = 0.15). Transfer learning may be able to facilitate healthcare data or model sharing to enhance infectious disease case detection. Deep transfer learning may be useful when the source and target are similar, and the target training data are sparse. Sharing a well-developed model can achieve performance that is similar to sharing data.
We have summarized our research findings in a manuscript, which will be submitted to a peer-reviewed journal soon.
