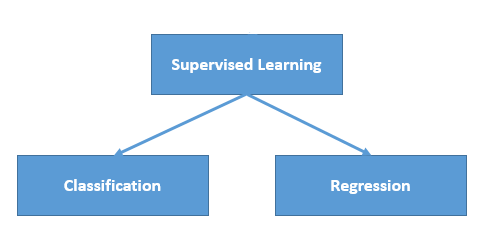
The majority of practical machine learning uses supervised learning.
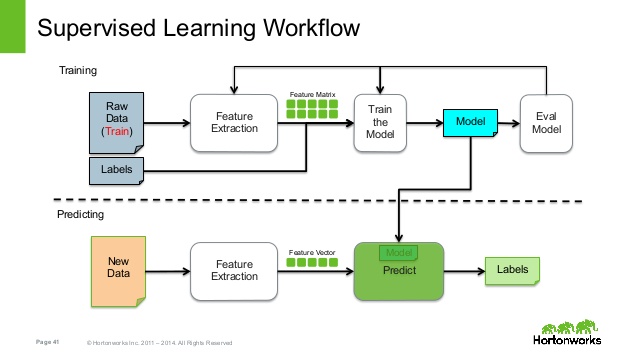
Supervised learning is where you have input variables (x) and an output variable (Y) and you use an algorithm to learn the mapping function from the input to the output.
Y = f(X)
The goal is to approximate the mapping function so well that when you have new input data (x) that you can predict the output variables (Y) for that data.
It is called supervised learning because the process of an algorithm learning from the training dataset can be thought of as a teacher supervising the learning process. We know the correct answers, the algorithm iteratively makes predictions on the training data and is corrected by the teacher. Learning stops when the algorithm achieves an acceptable level of performance.
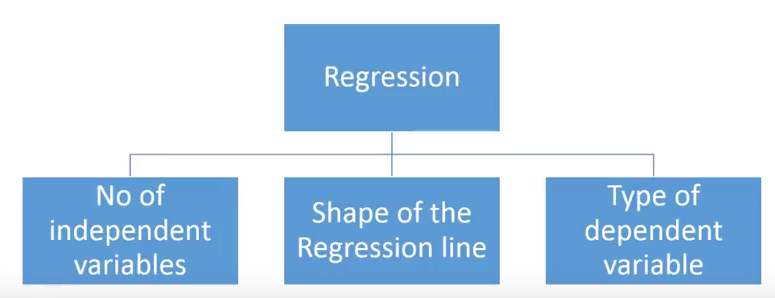
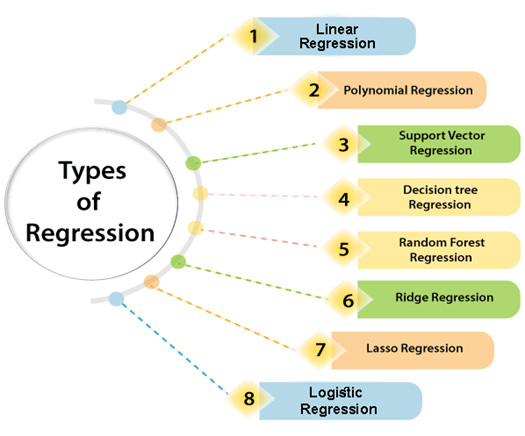
Regression analysis consists of a set of machine learning methods that allow us to predict a continuous outcome variable (y) based on the value of one or multiple predictor variables (x).
Briefly, the goal of regression model is to build a mathematical equation that defines y as a function of the x variables.
Classification is a process of categorizing a given set of data into classes, It can be performed on both structured or unstructured data. The process starts with predicting the class of given data points. The classes are often referred to as target, label or categories.
The classification predictive modeling is the task of approximating the mapping function from input variables to discrete output variables. The main goal is to identify which class/category the new data will fall into.
- Lazy Learners – Lazy learners simply store the training data and wait until a testing data appears. The classification is done using the most related data in the stored training data. They have more predicting time compared to eager learners.
Eg – k-nearest neighbor, case-based reasoning.
- Eager Learners – Eager learners construct a classification model based on the given training data before getting data for predictions. It must be able to commit to a single hypothesis that will work for the entire space. Due to this, they take a lot of time in training and less time for a prediction.
Eg – Decision Tree, Naive Bayes, Artificial Neural Networks.



_(1).jpg)

