To provide a centralized API Server for the Phoenix Parts Angular Application. Phoenix Parts is a centralized Parts Management Server specifically designed for managing the lifecycle of a FIRST robot.
The main objectives for the Phoenix Parts Backend are:
- Team Login System
A full registration system and user profile allows an administrator to oversee the progress of each teammate. Team members are also able to communicate in real time with each other. Also, this system integrates directly into Slack, the team's primary form of communication.
- Parts Management System
This is the core functionality of the application, where the details for a robot part are stored. Details include: Part Status, Raw Materials, and Machine availability.
- Resource Utilization
This is a side function of the application, where resource availabilities (materials, machines, etc...) can be viewed and allocated to maximize resource Utilization and decrease resource downtime.
The Node.js server is built with Composabilitity and Modularity in mind. The overarching goal is to design a server as a composition of logically separated modules. The rest of this readme will be focused around explaining the rationale for the separation of concerns chosen.
As one of the main priorities is designing with Modularity in mind, a standardized module structure was deemed necessary.
Inspiration was taken from Angular's Style of Dependency Injection, whereby a module's specific implementation should be abstracted away from any of it's consumers. More details about can be found at Angular.io's Docs. Research led to three different ways do modularize a javascript codebase without typescript support. The three options ar summarized by Krzysztof Sztompka in this Stack Overflow article.
Due to cleanliness, a modularization system (built on middlewares) was chosen to work as follows.
// Module.js
module.exports = function(app) {
// The app parameter is a representation of the Express.js app, and thus any server settings
// can be accessed in this Module Middleware.
// This return function with these parameters represents an Express.js middleware.
// Used with app.use() in the consumer of this Module Middleware
return function(req, res, next) {
// Perform Middleware functions here. Call next() to move onto subsequent middlewares/routes.
next();
}
};Once the module is created, it is then incorporated into the top-level application in the following manner.
var moduleName = require('<./path/to/module>')(app);
app.use(moduleName);That's it! With one line of code, the module is incorporated into the main application. This method of modularity proved to be the cleanest implementation, and thus is the standard for use in this application.
The core functionality of an API backend is to listen to routes and serve corresponding API responses. Two primary areas of concern are important to the routing layer:
- Control of route endpoint names
- Implementation of correct route behavior
While most Express.js tutorials combine these two listed goals into one file, a cleaner implementation was suggested at Code Mentor, which splits these into two further modularized concepts.
The Routing module is designed as follows:
// user.route.js
module.exports = function(app) {
app.route('/login')
.post(usersController.authenticateUser);
app.route('/register')
.post(usersController.registerUser);
app.route('/me')
.post(auth, usersController.me);
};As you can see, the top level of this module provides a very clean implementation of the routing logic, with specific functional implementation given over to the controller. This provides for a very clean and intuitive routing implementation. It is then the responsibility of the controller to handle database calls and forming the API response. One route module is created per resource entity, as dictated by business logic (ie: Users, Parts, Machines, etc...). One thing to note: this routing logic does not adhere strictly to the above mentioned Module Middleware format (ie: returning function(req, res, next), because routes are the last thing called in the request process. Future implementations may revert to the aforementioned standard so as to allow for logging processes after the API response has been sent.
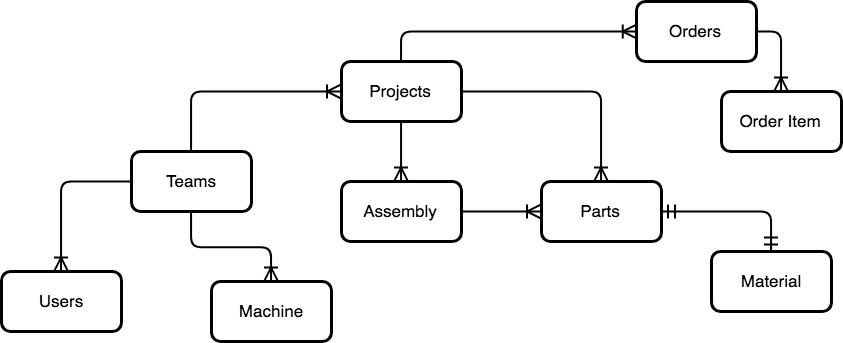
Integral to the functioning of this application is a persistant database. When deciding on a way to persist data, there are many choices to be made. The highest-level choice is between Relational databases(RDBs) and Non-relational databases. While this is a large topic in it's own right, two primary ways to start the choice process is by modeling the data interaction via an Entity-Relationship model(ER). This helps to arrive at a solid understanding of the data being stored, and is a great place to start. Below is a model of the proposed ER diagram for this application (This project is still in development, so not all functionality is instituted).
While an ER model is formally used for relational databases, due to connections in the ER diagram translating directly to primary/foreign keys in the RDBs, it is also very convenient even if a non-relational database is chosen. This is because, there are two ways for a Non-relational database to be implemented. In fact, a proper implementation of a non-relational database can have both types of implementations: Embedded vs. Reference. A full coverage of the advantages/tradeoffs of each can be found in this Microsoft Talk.
In my project, I made the decision to use the Non-relational database known as MongoDb. My choice of using MongoDb is for the added flexibility that MongoDb provides a developer in data-modeling. There is a big misconception that MongoDb is Schema-less. While it is true that, at the database layer, MongoDb does not enforce a particular schema, it is a best-practice for a developer to enforce a schema at the application-layer. This ensures consistency across documents in a collection.
To achieve this, a widely popular Object Document Modeling npm package known as Mongoose is used.
Again, the standardized Module implementation is used, as detailed in the Module Architecture Section. Within this module, are all the database connection-related logic, which is all handled by Mongoose. Mongoose is implemented as a singleton, meaning that the package does not place a restriction on placing all MongoDB-related logic (ie: Schema and Model definitions) in the same middleware. Therefore it was chosen to declare the Mongoose Schemas and Models within their respective controllers (ie: user.controller.js contains a require('./path/to/mongoose-model').
- Currently, User Authentication works using JWTs. If there is a need to extend functionality beyond MongoDB support, Passport.js may be used for User Auth.
- Socket.io Session Handling to support real-time chatroom functionality.
- AWS S3 storage for all media/pdf/picture uploads.
https://12factor.net/config https://stackoverflow.com/questions/18880142/access-app-variable-inside-of-expressjs-connectjs-middleware https://expressjs.com/en/guide/writing-middleware.html https://stackoverflow.com/questions/34468395/express-call-a-middleware-from-another-middleware
https://www.npmjs.com/package/performant-array-to-tree https://stackoverflow.com/questions/22367711/construct-hierarchy-tree-from-flat-list-with-parent-field https://stackoverflow.com/questions/6232753/convert-delimited-string-into-hierarchical-json-with-jquery https://gist.github.com/lineus/99c9e574fdefc2c84b932b6e949c7c8e
https://docs.mongodb.com/ecosystem/use-cases/storing-comments/ http://blog.ijasoneverett.com/2013/11/getting-started-with-mongoose-and-node-js-a-sample-comments-system/ https://www.mongodb.com/blog/post/thinking-documents-part-1?jmp=docs&_ga=2.218000982.134088568.1521985698-1047311511.1521985698
https://docs.mongodb.com/ecosystem/use-cases/storing-comments/ https://stackoverflow.com/questions/46019926/updating-slug-with-mongoose-presave
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/3923015/remove-leading-comma-from-a-string
This is how I set up my JWT auth system: https://medium.freecodecamp.org/securing-node-js-restful-apis-with-json-web-tokens-9f811a92bb52